Original source: Block Beats
For the highly hyped collectible NFT in the current market, whether the storage method of its pictures is decentralized and whether there is any risk of tampering after purchase are issues that many buyers are very concerned about. The Metadata field in NFT is generally used to store pictures, so we need a simple and efficient way to help users view the metadata in NFT.
At present, some products do provide certain metadata security assessment functions. For example, Opensea will display whether the metadata of NFT is frozen. However, since the function names contained in the underlying smart contracts of various NFT projects are not exactly the same, and the metadata storage methods of each project are very different, so a single query product cannot be compatible with all NFT products, and even some May provide misleading information to users.
first level title
text
First of all, it needs to be clear that the uniqueness of the NFT we talk about every day is determined by three basic elements. They are the public chain that deploys the NFT, the smart contract that generates the NFT, and the number of the NFT in the smart contract.
This article will take Ethereum, which is currently the most abundant NFT project, and the ERC-721 protocol of NFT as an example, to introduce readers to the method of querying NFT metadata through Etherscan.
First of all, readers can find the NFT collection page they want to verify through the most commonly used Opensea. Here we take a collection in Bored Ape Yacht Club as an example. You can see that the details page in the lower left corner indicates the three most critical information of this NFT: 1. Contract address; 2. The number of NFT in the contract, which is Token ID ;3. The public chain, which is Ethereum;
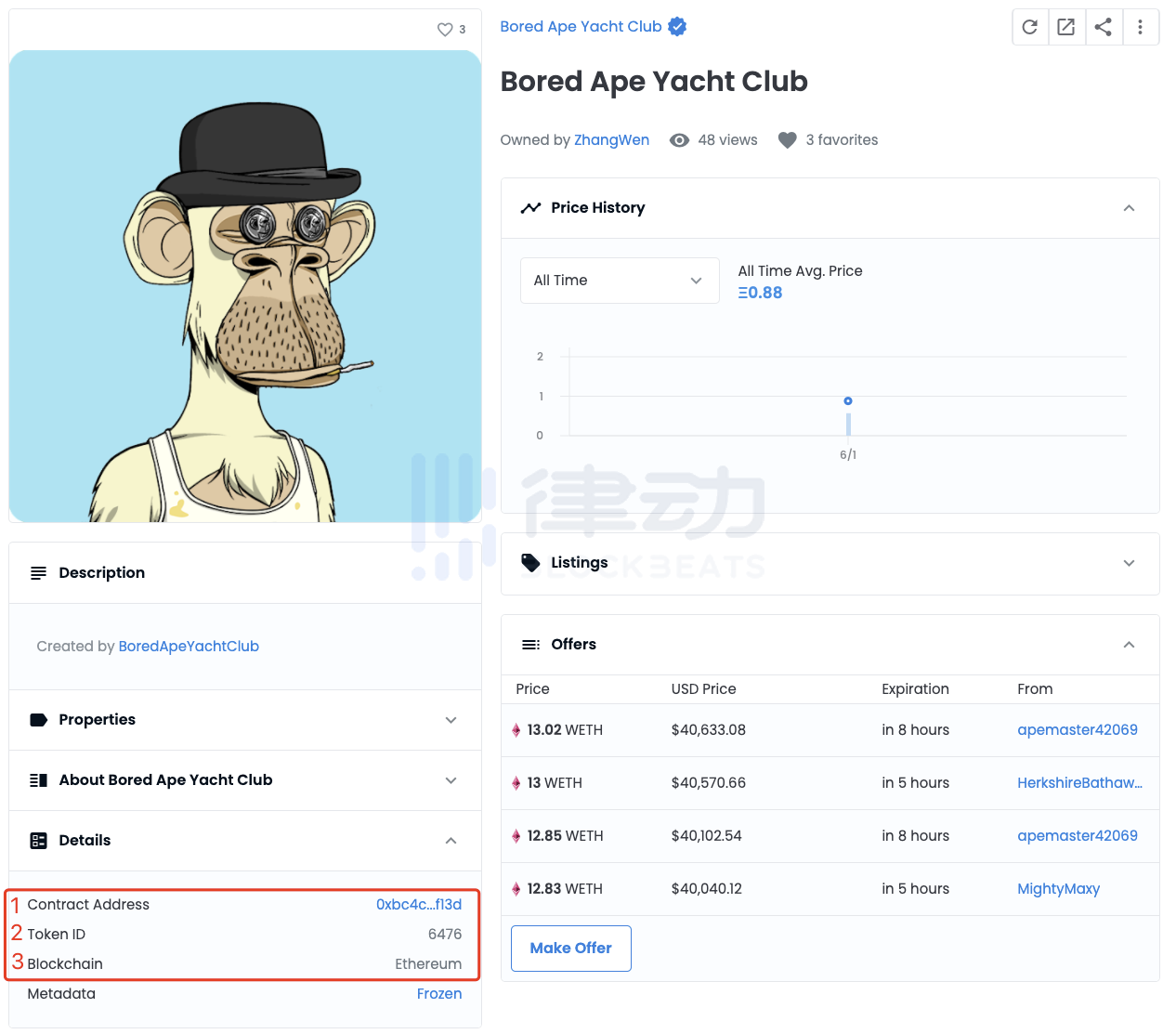
Click the link on the right side of the contract address (Contract Address), and the page will automatically jump to the Etherscan browser page corresponding to the contract address.
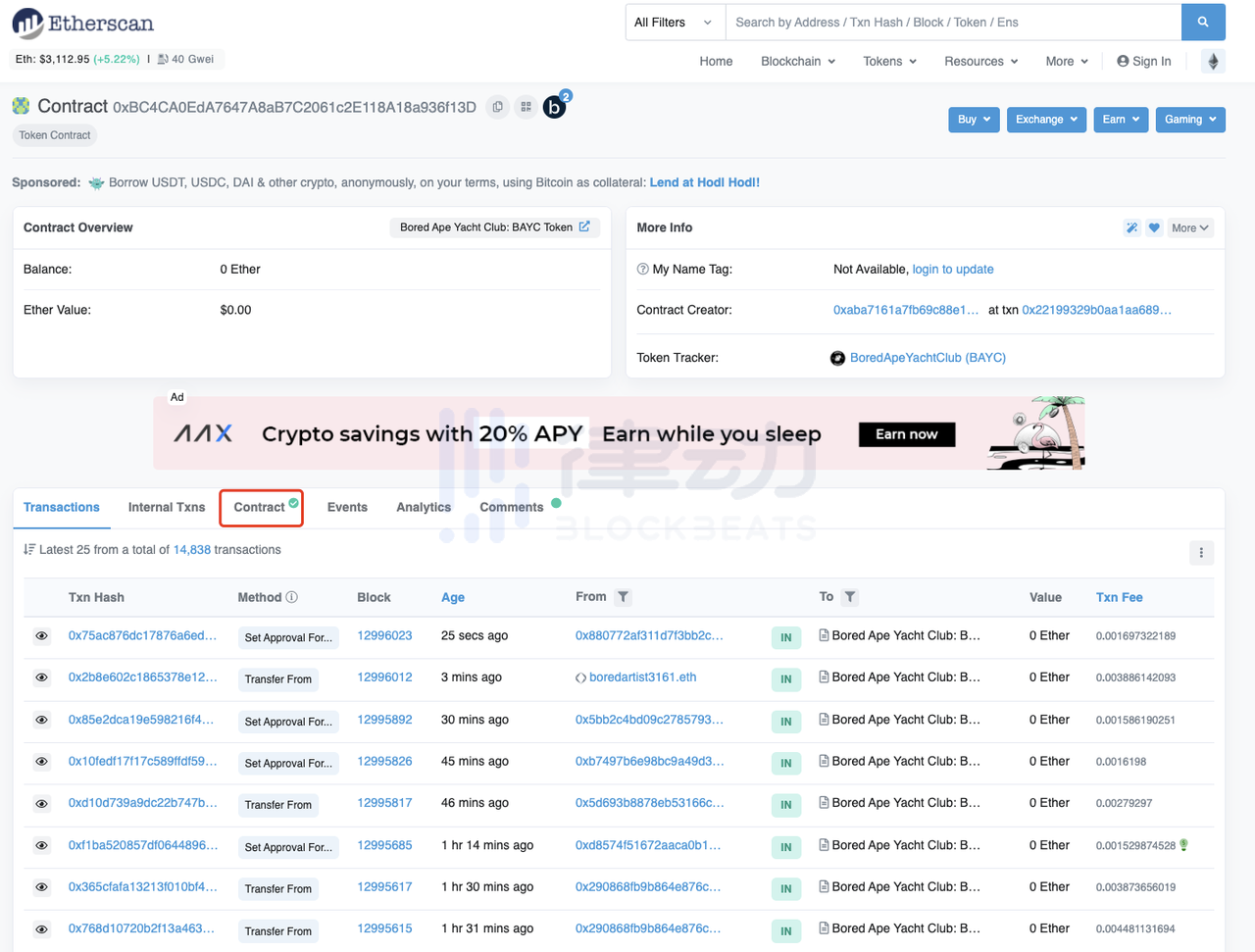
Click the Contract tab on the page to browse the underlying code of the contract.
We dont need to understand the specific meaning of the code, just click the Read Contract label in the above figure to browse the queryable functions in this contract.
Find the function tokenURI ranked 20th on the page, which is the dedicated function for querying metadata of the NFT contract.
Of course, the functions used to query metadata are named differently in different smart contracts, but generally have URI, metadata and other fields, which need to be analyzed in detail. Fortunately, most recent new projects will basically name this function tokenURI, which saves users a lot of trouble.
After clicking on the tokenURI function, we can see the following interface. Enter the NFT number we want to query in the input box above, which is the Token ID number 6476 we just saw on Opensea, and then click the query button Query below.
It can be seen that after clicking the query button, the system returns a series of codes: ipfs://QmeSjSinHpPnmXmspMjwiXyN6zS4E9zccariGR3jxcaWtq/6476
This string of codes is the metadata stored in the smart contract of the NFT. It can be seen that the metadata of this NFT saves an ipfs storage link, so it can be judged that the NFT uses a decentralized storage method. Readers can use browsers such as Brave that support ipfs browsing to view, and this address returns the picture of the ape represented by the NFT.
The above is the entire process of querying NFT metadata through Etherscan. It can be seen that for users, the operation threshold is not too high. But the more critical question is, by understanding how an NFTs metadata is stored, how can it help future investment or purchase of NFT?
first level title
secondary title
1. Do not store
Yes, it is true that some NFT projects cannot find any information about the storage location of their pictures on the chain at all, and there is even no function to store metadata in the contract. This storage method was only adopted by some fossil-level projects in the early days of NFT, the most typical being CryptoPunks.
CryptoPunks
We queried the contract address of CryptoPunks in the way just now, and found that TokenURI or similar fields could not be found. But it can be seen that a string of hash values is returned in the fifth function imageHash, which is the hash value of a large image spliced from the entire 10,000 CryptoPunk images. This image is currently kept on the projects official website (image link), users can download the picture by themselves and calculate its hash value and compare it with the hash value on the chain to verify the authenticity of the picture.
From this we can conclude that the CryptoPunks project does not store any pictures on the chain, but only provides users with a picture verification method in its smart contract.It does not store pictures in essence, but only provides a way to verify on the chain.
Since there is no storage, why can the corresponding picture be accurately displayed on Opensea after we purchase a CryptoPunks NFT? In fact, this completely depends on the artificial adaptation of websites such as Opensea on the front end of the webpage. The CryptoPunks pictures do not exist on the chain, but in the centralized website cache. Therefore, the NFT of CryptoPunks must rely on a centralized organization before it can be displayed normally.
Therefore, the CryptoPunks NFT purchased by investors is just a number in a smart contract, without pictures or other practical functions. Peoples recognition of him and the content of the pictures displayed on the website rely more on the consensus of the community. For example, for the second CryptoPunks NFT, whether it is the second from left to right or the second from top to bottom, there is no clear judgment standard on the chain. Everyone just thinks that he is the representative a certain avatar.
This type of NFT project has almost disappeared in the current market, because its existence and value require extremely strong community consensus support. If there are new projects that still use this storage method, investors are advised to purchase cautiously.
CryptoKitties CryptoKitties
CryptoKitties is also an NFT project with a long history. We also couldnt find metadata in its contract, and the only metadata-like function returned a null value.
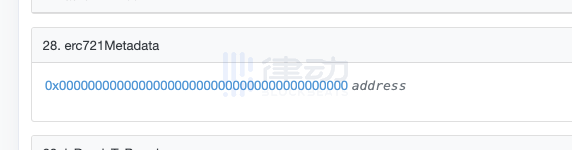
After analysis, we found that CryptoKitties also did not choose to store cat pictures on the chain, but stored the basic elements that make up cat pictures on a centralized official website. What is recorded on the chain is only the unique characteristic value of each cat, or it can be called the gene that determines the appearance of the cat. When a user purchases a CryptoKitty, the website responsible for the front-end display directly retrieves the characteristic gene of the NFT, and generates a cat picture displayed to the user according to the established rules.
Therefore, the storage method of the CryptoKitties project can be summarized as follows: the cats gene is stored on the chain, but the specific display content is synthesized by the server, and its display effect is completely dependent on the centralized server.
However, since CryptoKitties is not a pure image-based NFT project, its reproductive function can be synthesized only by relying on the gene of the previous generation and the algorithm on the chain, and the rarity of the cats appearance depends solely on the composition of the genes, so this project The lack of metadata will not have a big impact on its game functionality and valuation.
The biggest advantage of the above two solutions to avoid the metadata storage problem and solve the NFT front-end display problem through other alternative methods is to save valuable storage space on the chain and reduce the complexity of project development. But the disadvantages are also obvious, because any website that wants to adapt or display related NFT must manually configure and cache its display effect, and its final display effect is completely dependent on traditional centralized organizations. Once a key node fails, it may cause the NFT purchased by the user to fail to display normally.
secondary title
2. On-chain storage
On-chain storage is also often habitually referred to aspermanent storage, because once the user submits the data to the chain, relying on the non-tamperable property of the blockchain, the data on the chain is theoretically permanently preserved. As long as we can expect the chain to run forever, then the corresponding data is equivalent to permanent preservation.
Projects that currently use on-chain storage can also be divided into two categories, one is to store metadata on the same public chain as the NFT smart contract, and the other is to store metadata on a dedicated storage public chain such as Arweave. At present, there are not many typical projects adopting the second scheme, so this article will not introduce too much, and only the typical projects stored on Ethereum will be analyzed below.
Autoglyphs
The Autoglyphs project is also developed by the same Larva Labs team that developed CryptoPunks. Compared with CryptoPunks, this product is not so well-known, and the elements of its appearance are relatively simple. The figure below shows some of the product forms.

We still use the method mentioned above to call up its metadata through Etherscan, and the returned result is as follows
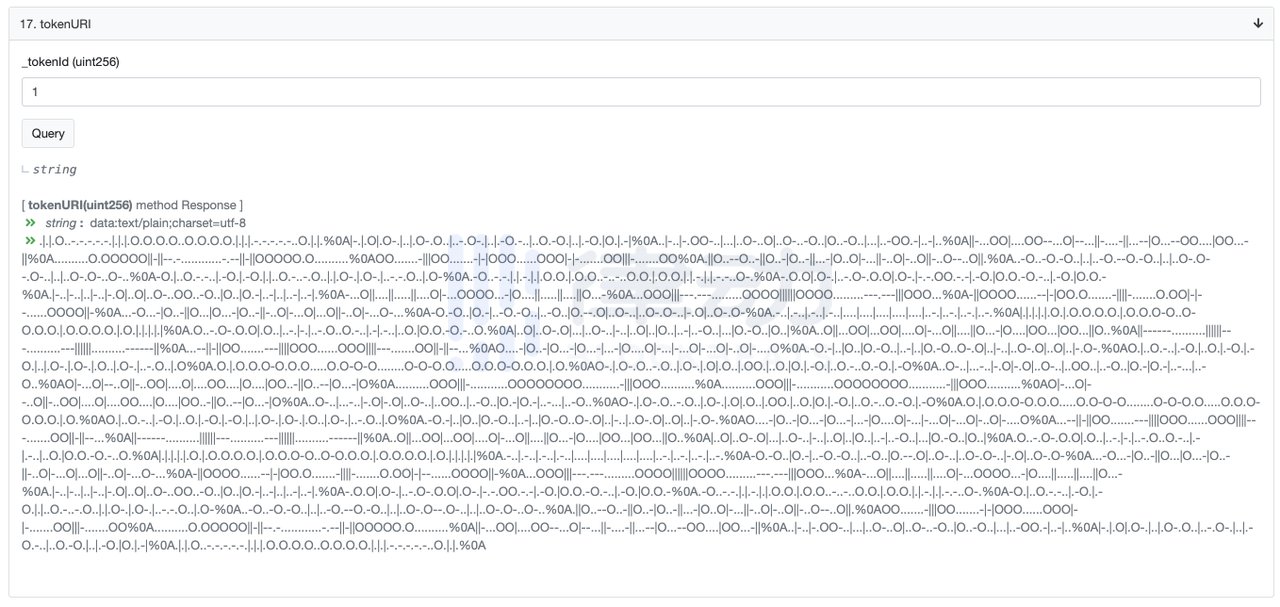
secondary title
3. Decentralized storage
The emergence of decentralized storage technology was much earlier than the invention of blockchain. Although decentralized storage has the same decentralized features as the blockchain, decentralized storage cannot be directly equated with on-chain storage.
At present, mainstream projects that use decentralized storage methods to store NFT metadata include the Bored Ape Yacht Club introduced earlier, which is also the storage method used by most art NFTs.
Adopting decentralized storage has the following significant advantages:
1. Non-tamperable modification: Since the domain name used to address and store files contains the hash value of the file, it has the same non-tamperable characteristics as the blockchain, and is more in line with the original spirit of encryption;
2. Lower storage costs: For most of the current image projects, basically a personal computer that can be connected to the Internet for a long time can guarantee long-term data storage. Even if a storage incentive layer such as filecoin combined with a blockchain incentive mechanism is adopted, its cost is still negligibly small compared to the cost of storage in Ethereum;
secondary title
4. Centralized storage
The so-called centralized storage here is to store the metadata in a centralized website server, and save the link to the URL in the metadata. Lets take the little penguin project that has exploded in the past two days as an example.
Pudgy Penguins
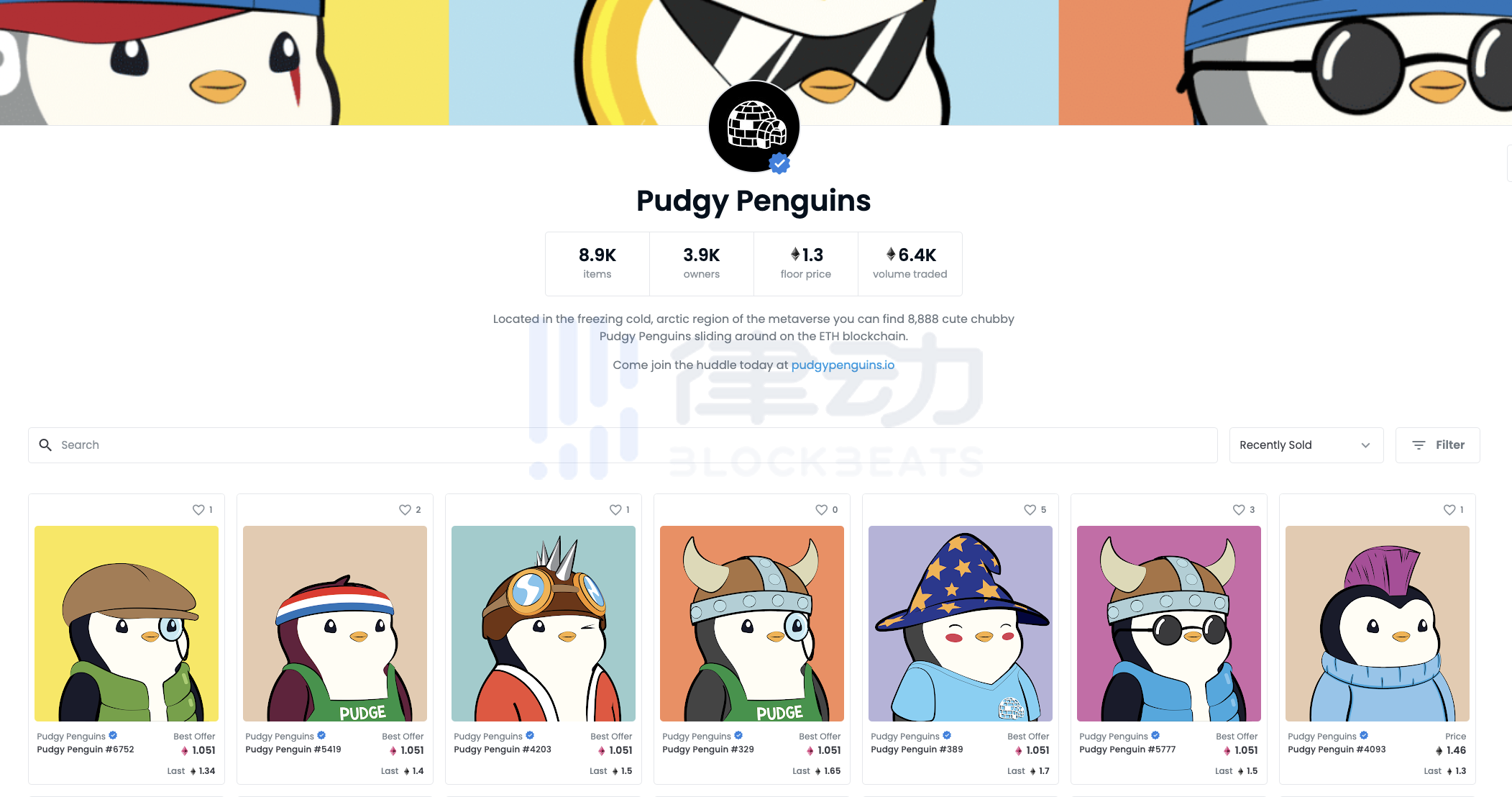
The figure below is a screenshot of the results returned by its tokenURI function query.
It can be seen from the query results that the metadata of this project returns a centralized URL link, indicating that the NFT image is directly stored on the server of the projects official website. This storage method will face two major risks in the long run. One is that the data can be tampered with by the owner of the website, and the other is that the website may lose maintenance one day and the link cannot be accessed.
Therefore, for such image NFT projects that use centralized storage, investors need to carefully evaluate the strength of the project party and the willingness to maintain the operation of the project for a long time when purchasing. Since this type of NFT has no application value other than the image itself, once the image returned by the corresponding link is changed, the item may be reset to zero at any time.
It is often said that the immutability of the blockchain is only reflected in the website links stored in the metadata. As for where this centralized website link points to, the blockchain has no knowledge of it and cannot control it at all. Therefore, this type of NFT is still centralized structurally.
We can summarize it in one law, which is:The degree of decentralization of a product depends on the most centralized link of all its components. As long as one link adopts a centralized technology stack, the entire product is a centralized product.Therefore, image-like NFTs that use this type of storage no longer have the basic characteristics of a decentralized and tamper-proof blockchain.
secondary title
5. It does not matter where it is stored
The reason why it is called indifferent where it is stored is because the value of this type of NFT is not directly related to the storage method of its metadata. Value has a significant impact. Below we take two well-known NFT-applied projects as examples.
NFTs in the Axie Infinity game
The figure below is the content returned by querying the metadata of an Axie NFT. It can be seen that its metadata stores only a centralized URL link, so the front-end display image is at risk of being tampered with.
But unlike picture NFTs,As a character or prop in the game, the main value of NFT does not come from the pictures it can display on the front end of the webpage, but its functions and attributes in the game.For example, the higher the attack power of a game character represented by an NFT, the more likely it is to win the battle, so its value is higher. The information stored in this NFT metadata is only similar to the skin of a game character, even if it is modified, it will not affect its game attributes.
This is similar to that in Glory of Kings, changing the skin of the game character will not have a significant impact on the operation of the game. Therefore, the NFT used in the game is more important to the actual function of the NFT in the game, or its intrinsic value, rather than the skin properties displayed on the front end of the web page.
Uniswap V3 Position NFT
The storage method of Uniswap NFT metadata is extremely unique, and it is worth explaining in detail. We still query the data on the chain through Etherscan first, and the returned results are as follows:
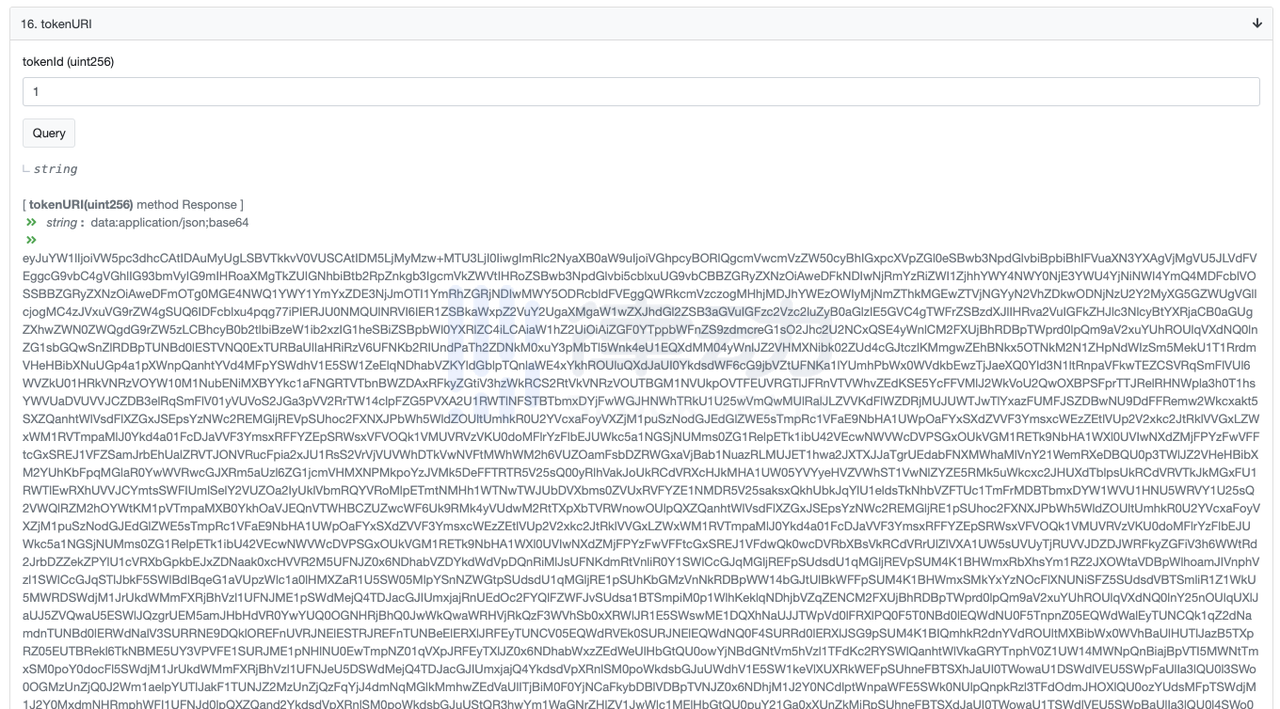
It seems that the returned data is undecipherable garbled characters, but the comment at the top provides us with the encoding method used: base64. We randomly search for an online base64 decoding tool, which can parse the garbled characters into the following readable results (only part of the data is intercepted because it is too long):

It can be seen that the token pair of the market-making position, market-making price range, token address, statement and other information are marked at the forefront of the metadata. In the rear image field, the NFT image information stored in svg format is saved.
Here is a little explanation of the svg format. svg is a picture saving format, its full name in Chinese isScalable Vector Graphics. We know that the commonly used picture saving format is based on pixels. For example, our mobile phone photo saving format is to save the color of each pixel collected by the lens in the file one by one, so the higher the pixel, the clearer the picture. At the same time, the larger the storage space occupied, the more difficult it is to save on the chain.
The svg format does not store pictures by saving pixels, but saves the shape of graphics. For example: save a rectangle with an aspect ratio of 2:1, the background color is red, the name of the token pair is displayed in the upper left corner, etc. The advantage of this way of storing images is that once the shape is determined, it can be zoomed in and out infinitely, and the storage space it occupies is not affected by the size of the graphic, but only related to the complexity of the graphic. Therefore, this storage form can help to store vector images with a relatively simple structure at low cost on Ethereum.
And because Uniswaps NFTs all use the same vector diagram template, the picture style of this NFT only needs to be stored once when deploying the contract, and then each newly minted NFT only needs to update the core information of token peers in the graphics. New NFT images can be generated. Therefore, users do not need to pay storage costs for storing this picture.
Uniswaps NFT metadata storage method can be said to be the most eye-catching solution among many NFT projects. He juggled several important needs at the same time. First, it is stored on the entire chain, which is completely decentralized and cannot be tampered with; second, all information can be read directly from the chain without relying on the cached data stored on the front end of the web page; third, it will not involve the risk of cross-chain call data , dont worry about the failure or attack of the protocol using off-chain storage, as long as you trust the security of Ethereum, you can fully trust the security of the NFT. Fourth, it can save complex images, unlike the Autoglyphs project, which can only display simple graphic information.
Of course, after talking so much, we still have to return to the source of value of NFT. In fact, for the value of Uniswaps NFT, where its metadata is stored, or even whether the metadata is stored, does not affect its value at all. Because the value of Uniswaps NFT only depends on the value of its assets that can be retrieved from the fund pool. Just like the bank certificate of deposit you hold, it doesnt matter whether the certificate of deposit itself is beautiful or not, as long as the equivalent currency can be retrieved, no matter whether the printing quality is fine or rough.
first level title
The source of value of NFT assets
There was a research report that summarized NFT asMetadata container, this extremely incisive summary better explains the source of value of the current art collection NFT. But for the application-type NFT mentioned above, it is difficult to give a reasonable explanation for this conclusion.
We believe that the current value sources of NFT assets are mainly divided into two different types. One is to rely on the application value of NFT itself. For example, holding NFT can be exchanged for certain assets, or it has certain attributes in the game that can increase the winning rate, or it can be used as an admission ticket for off-chain activities, etc. The value of these NFTs comes from the use value they can bring to holders.
The other is the value acquisition method of mainstream NFT projects. That is, NFT itself has no actual use value, and only relies on the display content such as pictures stored in metadata to obtain a certain consensus (of course, some NFT projects do not even do this). This type of NFT has obvious air characteristics in the long run, and we dont think it will become the mainstream NFT asset class in the future.
The large number of image-based NFT products that are currently popular make people inevitably recall the many air coin projects that flooded in 2017. The project party only needs to copy and simply modify a version of the white paper, and they can harvest a lot of wealth by issuing coins. The rise and fall of the Aircoin price mainly depends on hype, not its intrinsic use value.
Similar problems have also appeared in many current NFT projects. The project party only needs to use algorithms to generate thousands of simple pictures, and then it can obtain a large amount of funds through sales. There is almost no threshold for the operation of this kind of project, and there will only be more and more similar projects in the future, which will eventually make this round of NFT hype completely empty.
Although the current hype phenomenon has improved ordinary users understanding of the concept of NFT, it has promoted the improvement of NFT-related infrastructure. However, due to its lack of long-term intrinsic value, except for a few early head projects, more image NFT projects will have a very high risk of zeroing in the long run.
At the same time, users who purchase this kind of image NFT need to pay special attention. Due to the way its metadata is stored,What you see for many NFT products is not equal to what you get. A large number of image-based NFT projects need to rely on a relatively centralized trading platform to manually brain supplement the images displayed on them. Once the maintenance of a platform like Opensea is lost, the NFT bought by many users will only have a string of URL links instead of pictures.
The future of NFT should rely more on application-type NFT that is not affected by metadata. It can be seen that there are more and more explorations of such applications in the near future. For example, a project has recently cast a market-making algorithm into an NFT. If users who use this algorithm can pay a certain percentage of handling fees to this algorithm NFT in the future, the value of the NFT can be equal to the discounted future cash flow, making it inherently Value is strongly supported. As for whether its metadata stores a cool picture, I am afraid no one will care anymore.
Currently, applied NFTs with intrinsic value mainly exist in two tracks. One is financial NFT, and the other is game asset NFT. Both of these NFT assets have better long-term intrinsic value support, and their value no longer depends on the skin displayed on the front end of the webpage, such as metadata, but the actual use value brought to the owner. Compared with the currently hotter picture NFT, this application-type NFT is more likely to outperform the current hype cycle in the long run.










