Original - Odaily
Author - Nan Zhi

UTXO
definition:UTXO (Unspent Transaction Output) is a common data model in blockchain technology. UTXO is a way of recording the state of a transaction output that keeps track of each unspent transaction output to determine which Bitcoins belong to which address.
Easy to understand:
Each UTXO is like a banknote, it has a specific denomination (number of Bitcoins) and has a lock attached to it that can only be opened by a private key (key). When you want to send Bitcoin, you need to select some banknotes, merge them into a new one, and relock it with the recipients lock. This is basically how a Bitcoin transaction works.
Example: If you have two UTXOs, one worth 10 Bitcoins and the other worth 20 Bitcoins, you can merge them into a new UTXO with a total value of 30 Bitcoins and then re-lock it with the recipients address. In this way, you complete a transaction, sending 10 Bitcoins and 20 Bitcoins to the recipient, and generating a new UTXO.
For example, Cathy in the picture below has obtained 10 BTC UTXO from Bob and 20 BTC UTXO from Alice. Its balance can be understood as 30 BTC, and Cathy can disassemble, combine and send these UTXO externally. .
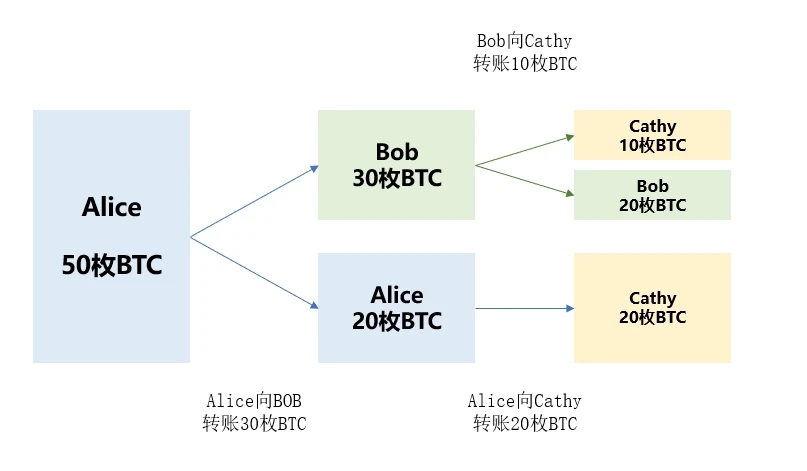
One thing to note here is that external transfers do not take out a portion of the funds from an individuals balance and transfer them out, but split them into one or more UTXOs.Transfer funds that are not transferred externally to yourself. This is crucial to understanding Ordinals.
Ordinals
serial number:
definition:There are 21 million Bitcoins in total, and each Bitcoin contains 100 million Satoshis (sats). The Ordinals protocol numbers these Satoshis according to the order of output and transactions.
The first block reward of the Bitcoin network is 50 BTC, which is 5 billion sats, and these 5 billion satos are numbered in sequence as sats No. 1, sats No. 2... until sats No. 5 billion. Afterwards, the Bitcoins and corresponding Satoshis produced in each block are also numbered sequentially.
Note that when first produced, each sats is homogeneous, and it is not possible to specify which sats are No. 1 and No. 2 until it is split by UTXO.
Here, we assume that Alice holds the 50 BTC from the genesis block, and the transfer situation is as follows:
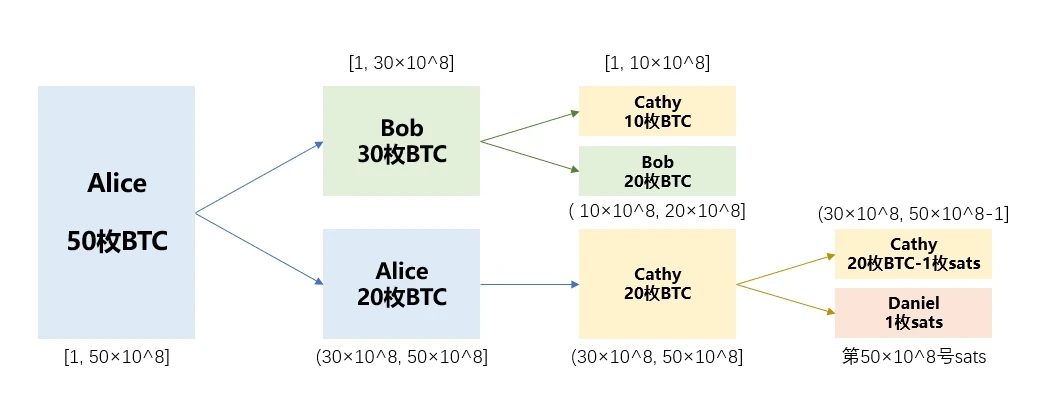
After Alice transfers BTC to Bob, the first three billion sats and the last two billion sats are distinguished, and then continue to be divided with new UTXOs; in the end, Cathy owns sats No. 1 to 1 billion, and Satoshi number 3 billion went to (5 billion-1) sats; and satoshi number 5 billion went to Daniels account.
Segregated Witness
Segregated Witness, often referred to as SegWit, is an upgrade to the Bitcoin protocol that aims to solve some problems related to Bitcoin transactions and network scalability. The main change to SegWit is the addition of signature data (also known as"witness", witness data) are stored separately from the transaction data itself, making Bitcoin transactions more efficient and secure, and improving the scalability of the network.
Taproot
Taproot is an important protocol upgrade for Bitcoin designed to improve the privacy, scalability, and smart contract capabilities of the Bitcoin network. This upgrade becomes active in November 2021. Taproot scripts have very few restrictions on their content and also receive witness discounts, making storage of inscription content relatively economical. Taproot is the latest stage of Bitcoin scaling after Segregated Witness, creating the conditions for the emergence of Ordinals.
inscription
In short, inscription is to store (engrave) content on the Bitcoin network through Segregated Witness and bind it to sats with a specific serial number, allowing it to be transferred and traded. In the early days, there were cases where key sats were mistakenly transferred and assets were lost (actually the sats were transferred to the recipient, although the original intention may have been just a BTC transfer), and the current tools have basically automated this process to avoid mistransfer of key sats.
Rare Satoshi
According to the order of production, the rarity of certain serial numbers is defined.
uncommon: the first satoshi of each block
rare: the first Satoshi of each difficulty adjustment cycle
epic: the first Satoshi of each halving period
legendary: the first satoshi of each cycle
mythic: the first Satoshi of the genesis block
BTC NFT
Inscription can upload any file of suitable size (4 MB) to the Bitcoin network. Currently, the main types include image, text, video and audio. The pictures form a BTC NFT. The main differences from traditional NFTs include:
BTC NFT is always immutable, and traditional NFT usually has modification and adjustment permissions;
BTC NFT creators must pay a fee proportional to the size of the content, while traditional NFTs are usually stored in IPFS at very low cost;
Early major BTC NFT projects include: TwelveFold, Bitcoin Punks, Bitcoin Wizards, etc.
The most popular series of BTC NFTs include: Bitcoin Frogs, Ordinal Maxi Biz, Goosinals, etc.
BRC-20
BRC-20 is a token standard proposed by Domo on March 9, 2023, which inscribes a specific piece of text onto the blockchain and treats it as a token. Its standard format is as follows:
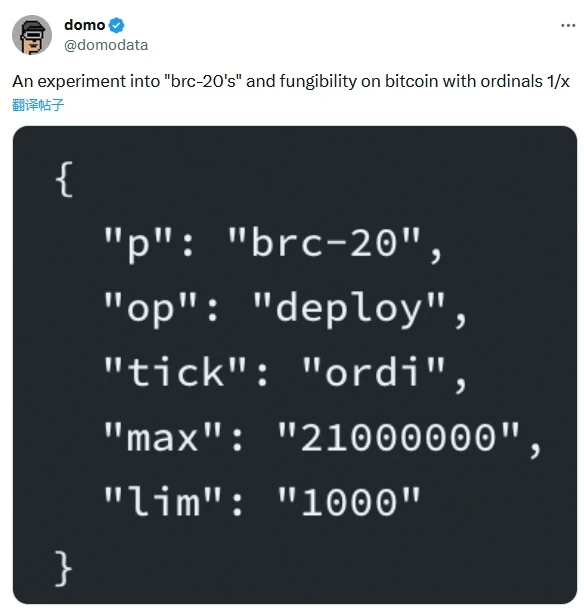
BRC-20 can be understood as a paper recorded on the chain. Users record what operations they have performed on the paper, such as deploying tokens, transferring tokens, etc. The slips are then collected, organized, and calculated by a centralized (or decentralized) organization to ultimately derive token holdings and transaction data.
The value of BRC-20 tokens comes more from consensus than utility. When more users recognize its value, the paper is upgraded to banknotes. Just like the birth process of BTCs value, data that was also considered penniless in the initial stage has increased its value through the gathering of consensus.
recursive inscription
A major limitation of Bitcoin inscriptions is that the single storage capacity is only 4 M. For example, the BRC-721 protocol uses third-party storage to solve this problem (refer to traditional NFT). Recursive inscriptions were proposed by Ordinals founder Casey, which allows the use of special syntax to reference The contents of other inscriptions can form complex and large files, and a new NFT series can be created with just a few lines of code modifications.
Current popular protocols
Taproot Assets
Taproot Assets (formerly Taro) is a protocol powered by Taproot for issuance of assets on the Bitcoin blockchain. It can be used to create assets that can be transferred on the Lightning Network, thereby enabling instant, high-volume and low-fee transactions.
Lightning Labs developed “Taproot Assets” to enable Bitcoin to become a multi-asset network in a scalable way while staying true to Bitcoin’s principles. Taproot Assets relies on Bitcoins latest upgrade, Taproot, to implement a new tree structure that allows developers to embed arbitrary asset metadata in existing outputs. It uses Schnorr signatures to improve simplicity and scalability, and importantly, it can handle multi-hop transactions over the Lightning Network.
Atomicals Protocol
The Atomics protocol is a simple and flexible protocol for creating, transmitting and updating UTXO blockchains (such as the Bitcoin network)digital object(Traditionally known as NFTs). Atomic (or ATOM) is a method of controlling the creation, transfer, and update of digital objects.
Unlike Ordinals originally designed for NFT,It rethinks how to issue tokens on BTC in a centralized, tamper-proof and fair manner from the bottom up.。
Atomics uses sat, the smallest unit of Bitcoin, as the basic atom. The UTXO of each sat is used to represent the Token itself, 1 token = 1 sat.
When verifying an Atomics transaction, you only need to query the UTXO corresponding to sat on the BTC chain. The atomicity of ARC 20 Token is consistent with the atomicity of BTC itself, and the calculation of ARC 20 transfers is completely handled by the BTC basic network. Therefore, compared with BRC-20, ARC-20 transactions have greatly reduced the demand for third-party sequencers, which greatly improves the decentralization of the entire system.
BRC-420
Official Documentation: The BRC-420 protocol introduces a method of digital asset management in the Metaverse, providing creators with a comprehensive system to manage, share and monetize their creations through recursion, licensing and royalties. Features include:
Based on the recursive function, complex and recursive digital asset formats can be implemented and various recursive asset formats (2D, 3D) are supported.
Integrate with blockchain for automated royalty transfers, linking usage rights to royalties to benefit creators.
There are many new things emerging in the Bitcoin ecosystem, and Odaily will continue to pay attention. Readers who are interested in Bitcoin ecology are also welcome to add the official WeChat account (Odaily 2018 or odaily 001) to join the community.










