Original author: Lisa, LD Capital

1. Review of Hong Kong stock trends
Looking back at the trend of the Hong Kong stock market over the past ten years, the Hang Seng Index experienced two major rising periods from February 2016 to January 2018 and from March 2020 to February 2021.
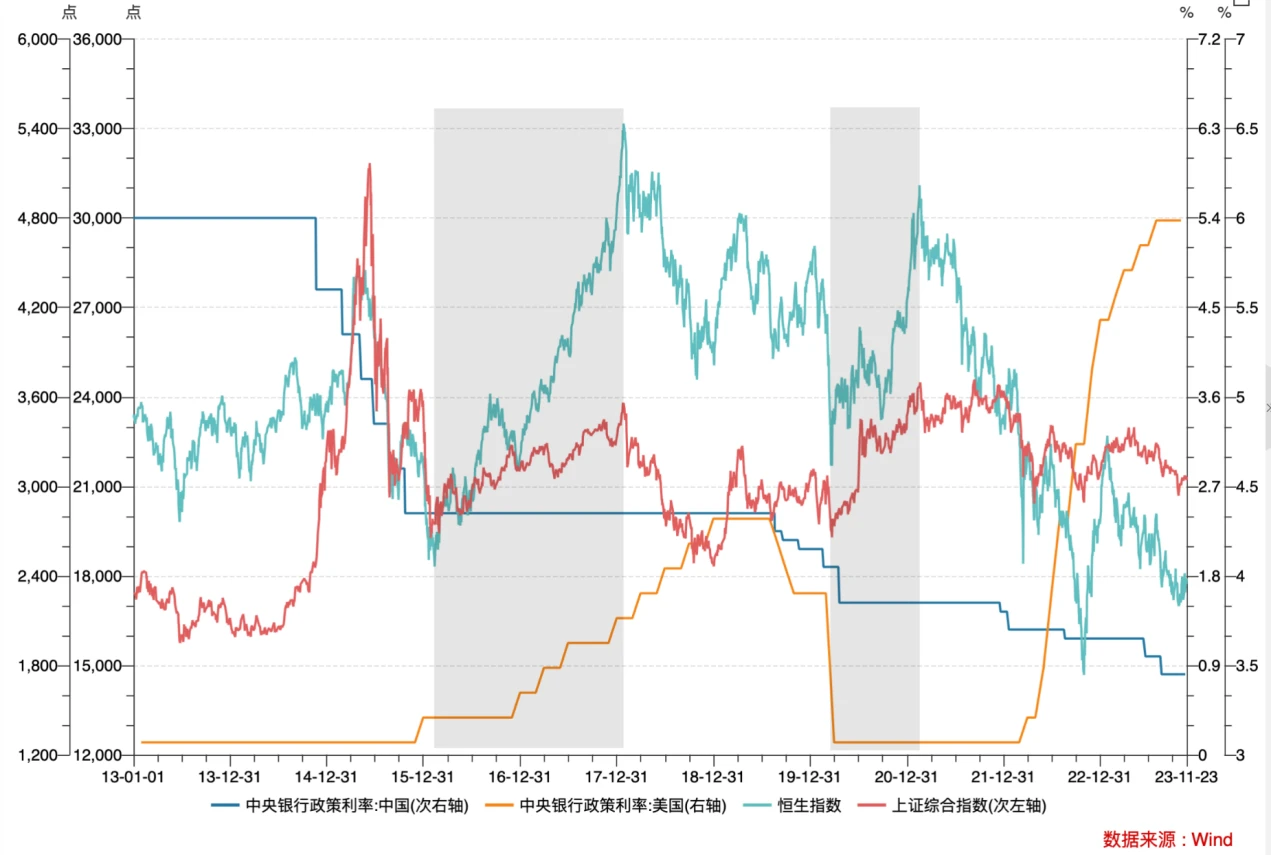
The first period of rising prices coincided with the Federal Reserve raising interest rates and shrinking its balance sheet. However, the Hong Kong stock market was not restricted by the tightening of external liquidity and continued to rise. The reason is that the supply-side reform and housing reform implemented by the central government in 2016 promoted the domestic investment and real estate cycle. open, driving strong growth of the domestic economy. From this wave of market conditions, we can see that the core factor that dominates the performance of the Hong Kong stock market is internal growth rather than the external environment.
In the second period of rising prices, under the backdrop of the global COVID-19 epidemic, the central government issued 1 trillion yuan of special government bonds to fight the epidemic. At the same time, due to the relatively small disruption to the domestic supply chain caused by the epidemic, external demand and exports increased, and the economy achieved rapid recovery. Stock markets performed strongly.
In the past year, the trend of the Hang Seng Index first rebounded and then fell. The market has bottomed out since November 2022, benefiting from expectations of economic recovery after Chinas epidemic relief and the Federal Reserves marginal easing. The Hang Seng Index continued to rise from 15,000 points on October 31, 2022 to a high of 22,700 points on January 23, an increase of more than 50%.
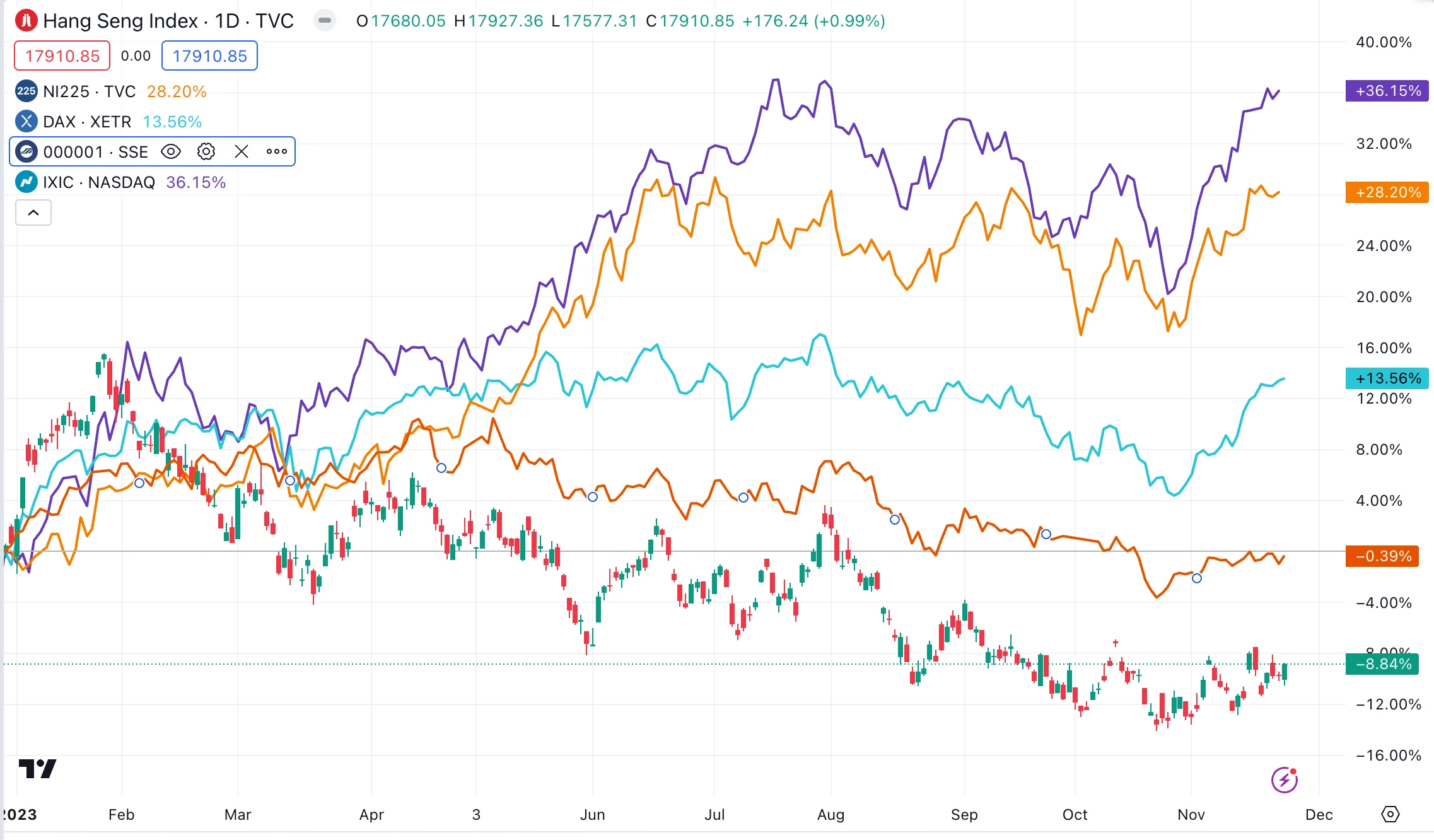
Later, affected by factors such as domestic growth falling short of expectations and U.S. inflation remaining sticky, the market ended its rebound. Hong Kong stocks have been at the bottom of global performance this year, underperforming major global indexes, including A-shares. Compared with the Nasdaq and Nikkei indices, which have risen 36% and 28%, the weakness is particularly obvious. The main reason is the withdrawal of foreign capital and the lack of support for domestic growth. Repair concerns.
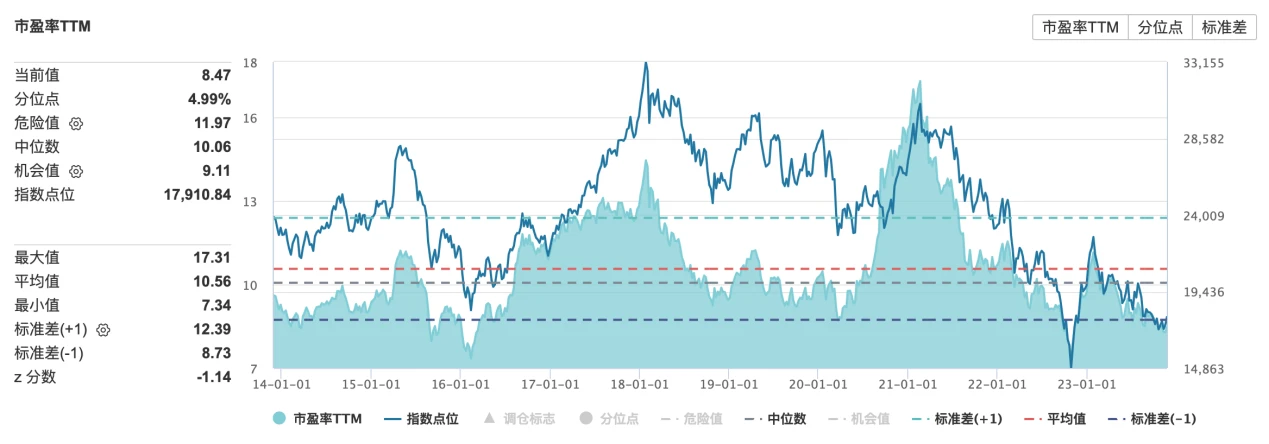
The earnings ratio of Hong Kong stocks shrank to 8.47 times, which is below 1 standard deviation of the long-term average.
Data source:wind
2. Main factors influencing Hong Kong stocks
1. External environment
Due to the open nature of the financial market, Hong Kong stocks are usually more susceptible to the impact of the external environment. The Federal Reserves monetary policy affects the Hong Kong stock market through liquidity and valuation (especially growth sectors represented by Internet technology, biomedicine and other industries).
In November, the FOMC Federal Reserve once again suspended interest rate hikes. Coupled with the weak economic data in October and the slowdown in fiscal bond issuance, it triggered widespread optimism in the market. U.S. bond interest rates fell rapidly, and have continued to fall since the high of 5% in mid-October. to about 4.4%.
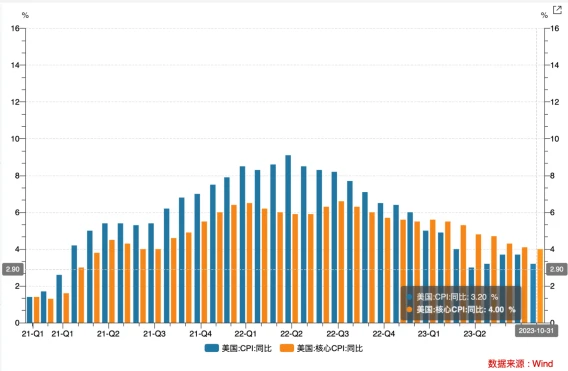
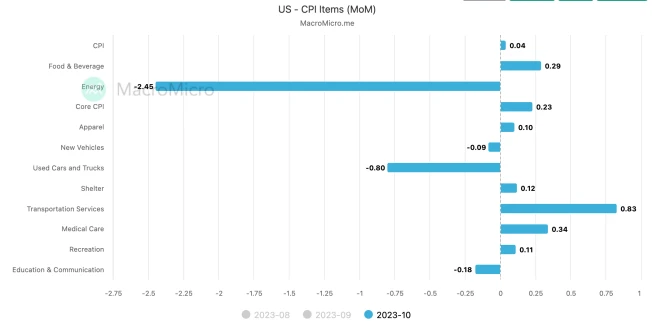
The overall CPI and core CPI fell more than expected in October. The U.S. CPI in October was 3.2% year-on-year, and the core CPI was 4.0% year-on-year, lower than market expectations. This was mainly due to the fall in energy and used car prices. As concerns about the impact on the crude oil market due to the Palestinian-Israeli conflict eased, crude oil prices fell and U.S. domestic gasoline prices fell.
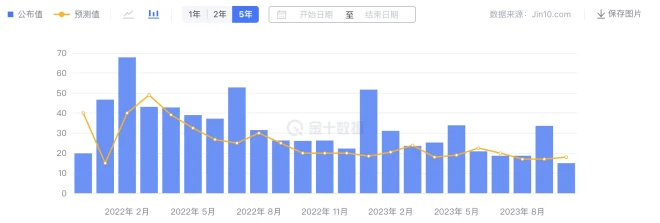
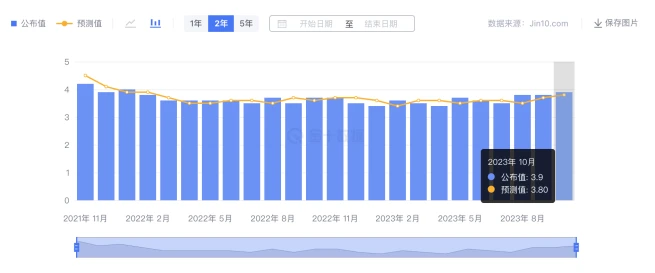
The non-agricultural sector has cooled significantly and the unemployment rate has slightly increased. On November 3, 2023, the U.S. Department of Labor announced U.S. non-farm employment data for October 2023, showing that 150,000 new non-farm jobs were created, lower than the expected 180,000 and only half of the previous value. The unemployment rate edged up 0.1 percentage point to 3.9%.
U.S. non-farm employment population in October (10,000 people)
U.S. unemployment rate in October
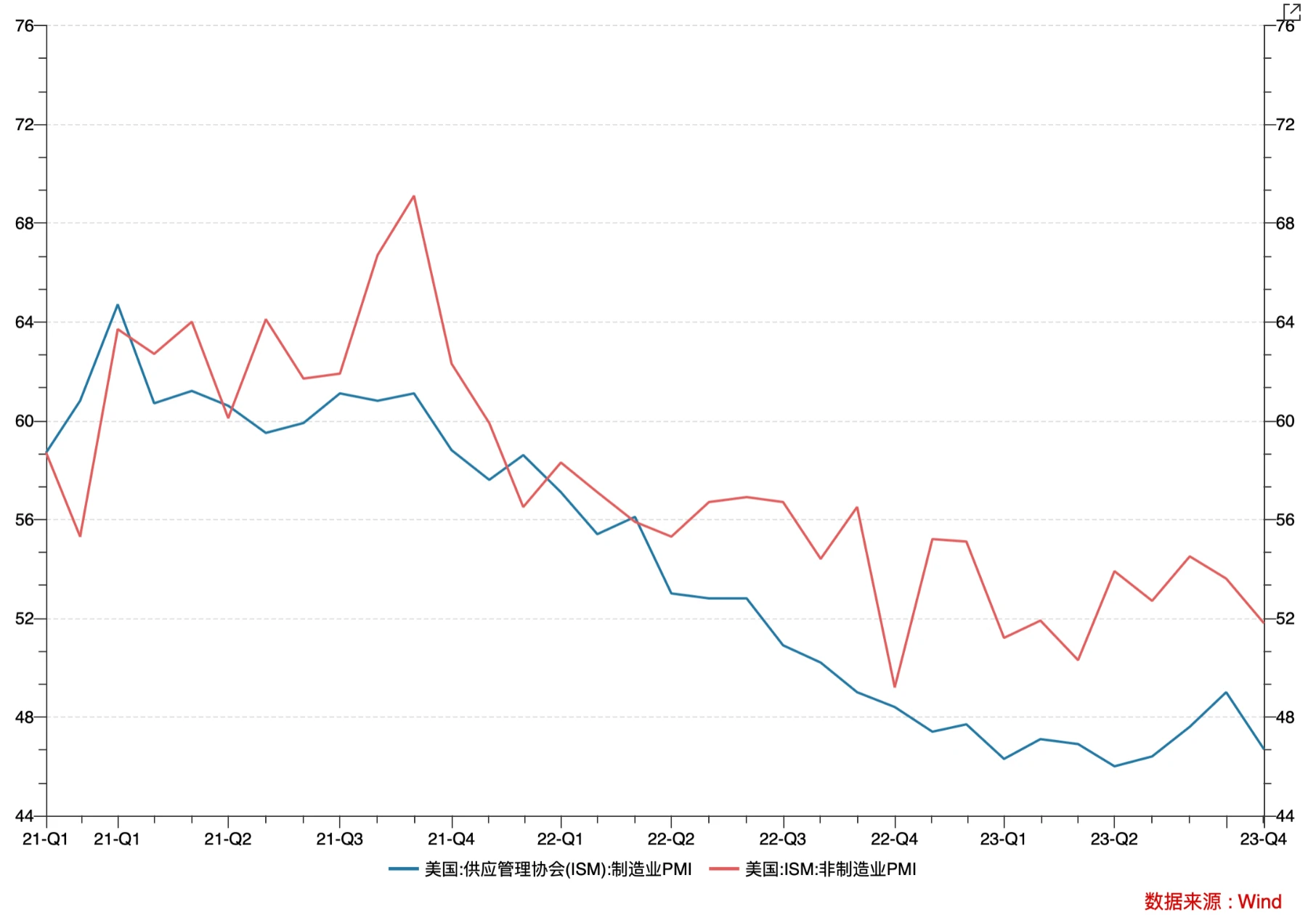
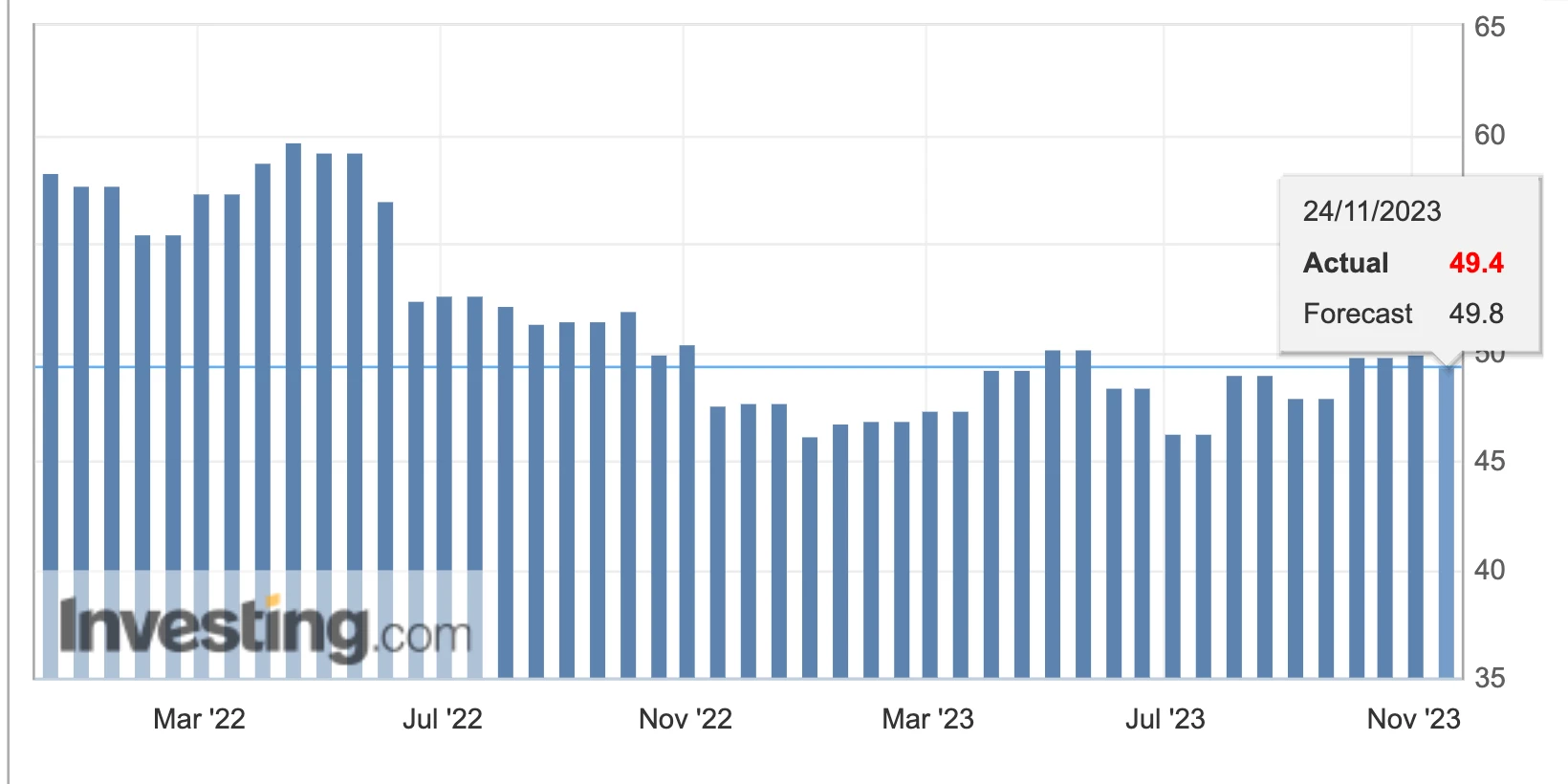
The U.S. ISM manufacturing and non-manufacturing PMI both fell, recording 46.7 and 56.8 respectively. Markits manufacturing PMI fell back into contraction territory again, while the services PMI rose slightly.
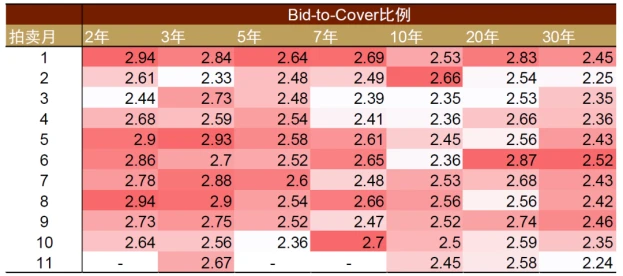
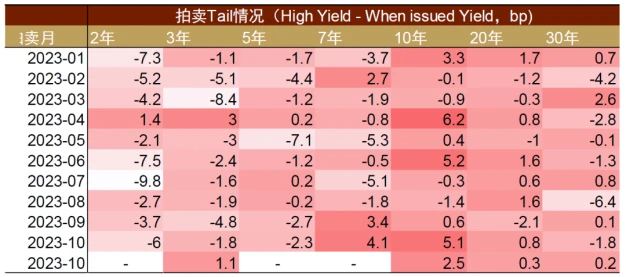
Due to the unsatisfactory results of long-term debt auctions and the possible phased improvement in the U.S. fiscal deficit in the fourth quarter, the U.S. Treasury Department slowed down the pace of U.S. debt issuance at the fourth-quarter refinancing meeting. Based on the recommendations of the Treasury Borrowing Advisory Committee (TBAC), the Treasury Department’s net debt issuance in the fourth quarter was US$776 billion, a decrease of US$76 billion from the expected size at the August refinancing meeting, excluding the US$171 billion from the Federal Reserve. After net redemptions, actual net issuance in the fourth quarter is expected to fall to $605 billion. After the news was announced on November 1, the market reacted positively, with the 10-year U.S. Treasury yield falling significantly. However, the actual situation of the Treasury bond auction in November still showed insufficient demand, and fiscal pressure has not been completely relieved. The long-term bond auction bidding coverage ratio (Bid-to-cover ratio) fell simultaneously, and the highest interest rates (high yield) of the 3-year, 10-year, 20-year and 30-year U.S. bond auctions were all higher than the market interest rate of the day (when-issued yield) .
Source: Bloomberg, CICC Research
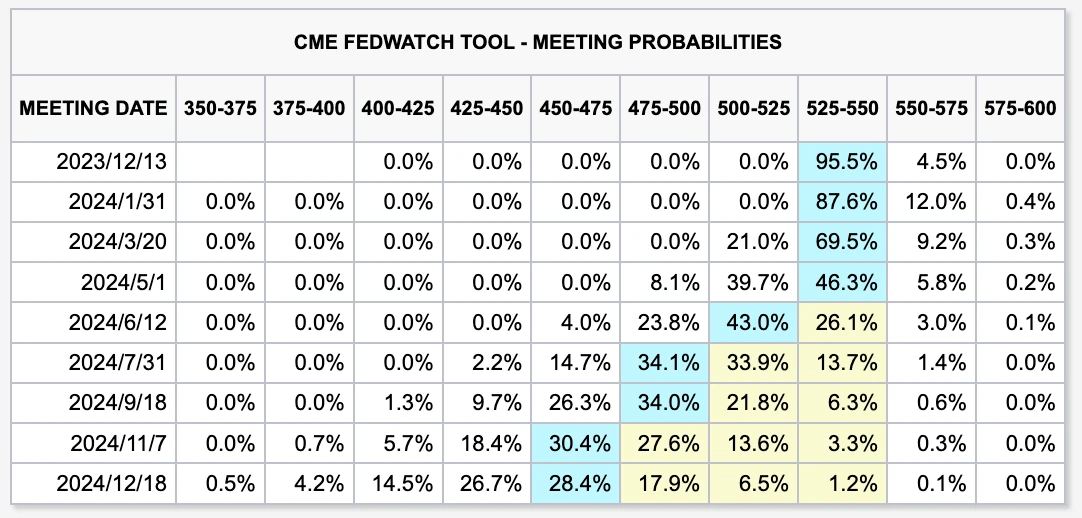
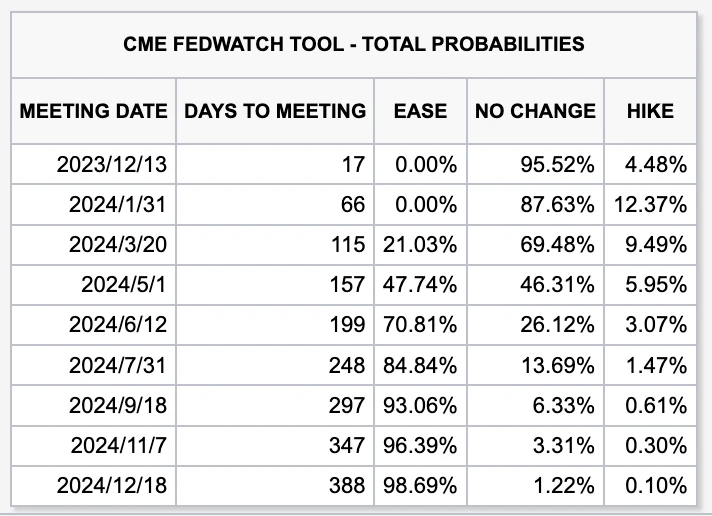
Falling inflation, slowing growth and partial relief of concerns about fiscal expansion have led the market to believe that there is a high probability that interest rates will be stopped in December. The current CME interest rate futures imply a probability of no interest rate hikes in December of 95.5%. Looking forward, the downward trend in U.S. bond interest rates is the general trend, and the pace may fall in a step-by-step manner.
2. Domestic economy
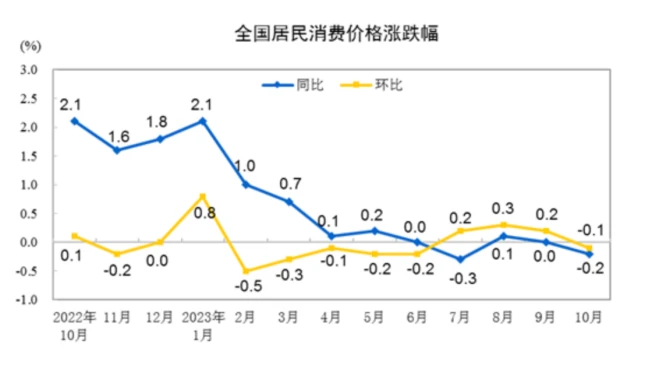
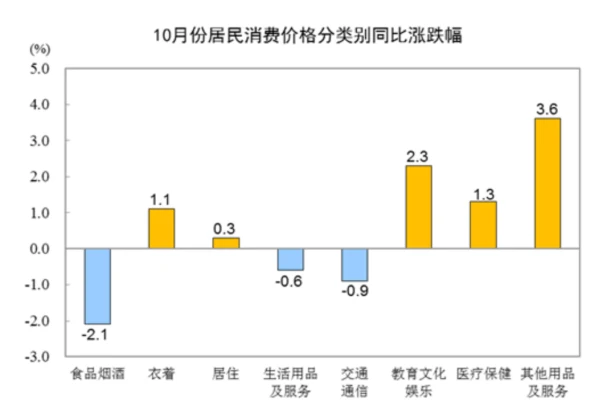
Price levels show that the momentum for domestic inflation to pick up is generally weak. On November 9, the National Bureau of Statistics released price data for October 2023. The national consumer price dropped by 0.2% year-on-year and 0.1% month-on-month. The fall in CPI was mainly affected by the fall in food prices, mainly pork, and the fall in consumer demand after the holidays. The price of livestock meat fell by 17.9%, affecting the CPI to fall by about 0.66 percentage points, of which the price of pork fell by 30.1%, affecting the CPI to fall by about 0.55 percentage points; the price of eggs fell by 5.0%, affecting the CPI to fall by about 0.04 percentage points; the price of fresh vegetables fell 3.8%, affecting the CPI to fall by about 0.08 percentage points.
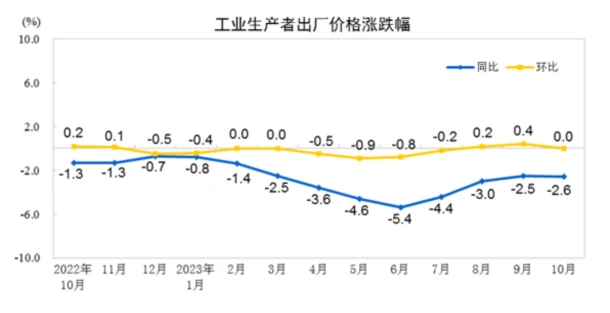
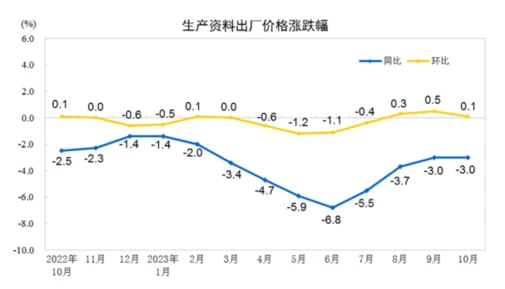
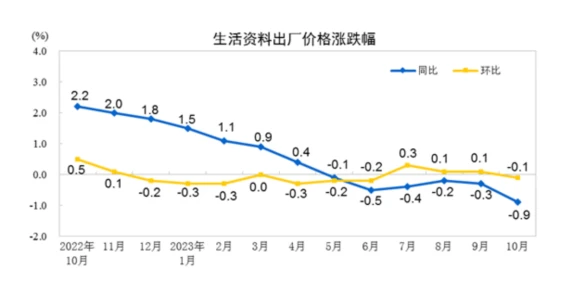
In October 2023, the national industrial producer price fell by 2.6% year-on-year and remained unchanged month-on-month, mainly dragged down by production materials. Year-on-year, the price of means of production fell by 3.0%, affecting the overall level of factory prices for industrial producers to fall by approximately 2.35 percentage points. Among them, the price of the extractive industry fell by 6.2%, the price of the raw material industry fell by 2.3%, and the price of the processing industry fell by 3.0%; the price of daily necessities fell by 0.9%, affecting the overall level of the factory price of industrial producers to fall by about 0.24 percentage points. Among them, food prices fell by 1.2%, clothing and general daily necessities prices increased by 0.4%, and durable consumer goods prices fell by 2.0%.
On a month-on-month basis, the price of means of production increased by 0.1%, affecting the overall level of industrial producer prices to increase by approximately 0.08 percentage points. Among them, the price of the mining industry increased by 2.4%, the price of the raw material industry increased by 0.4%, and the price of the processing industry decreased by 0.2%. The price of daily necessities fell by 0.1%, affecting the overall level of factory prices for industrial producers to fall by about 0.04 percentage points. Among them, food prices fell by 0.3%, clothing prices increased by 0.1%, general daily necessities prices remained unchanged, and durable consumer goods prices fell by 0.1%.
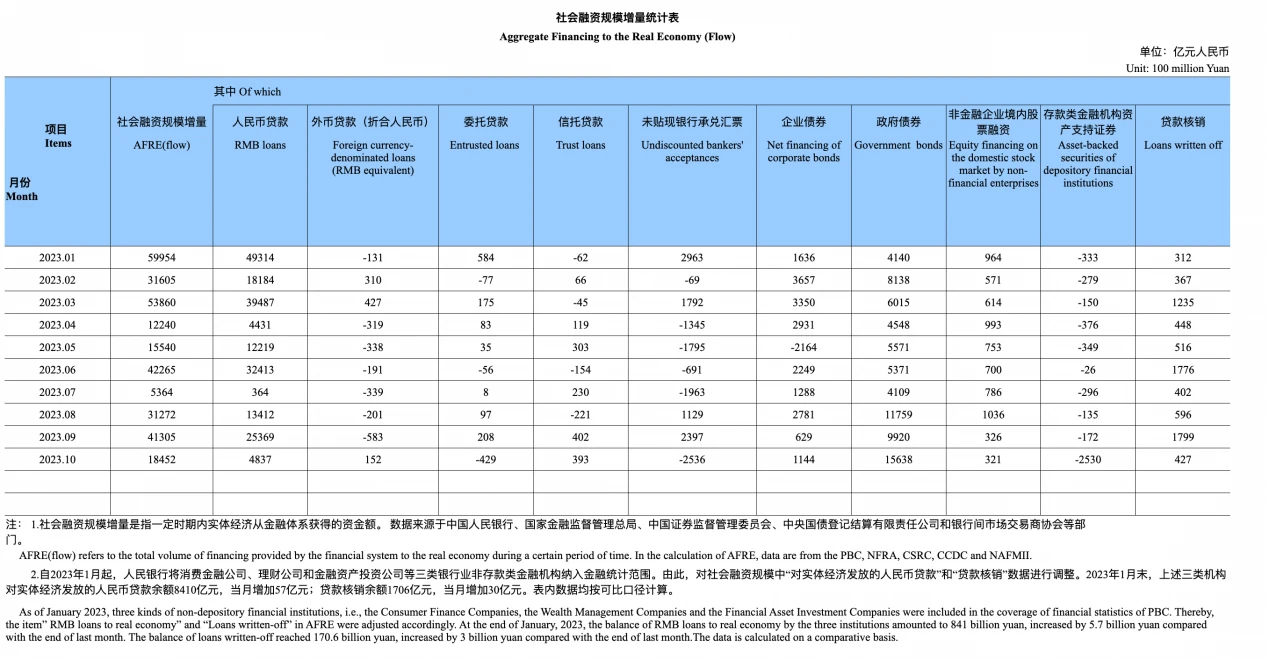
At the end of October 2023, the stock of social financing was 374.17 trillion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 9.3%. New social financing in October was RMB 1.85 trillion, an increase of RMB 910.8 billion year-on-year. The financing needs of residents and enterprises were weak. The growth in social financing mainly came from government sector financing. In October, new financing from government bonds amounted to RMB 1.56 trillion. Accounting for 85% of the total new social financing of 1.86 trillion. Most other subdivisions fell back. The balance of RMB loans was 235.33 trillion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 10.9%. The growth rate was the same as the end of last month and 0.3 percentage points lower than the same period last year. The new number of RMB loans was at a relatively historical low.
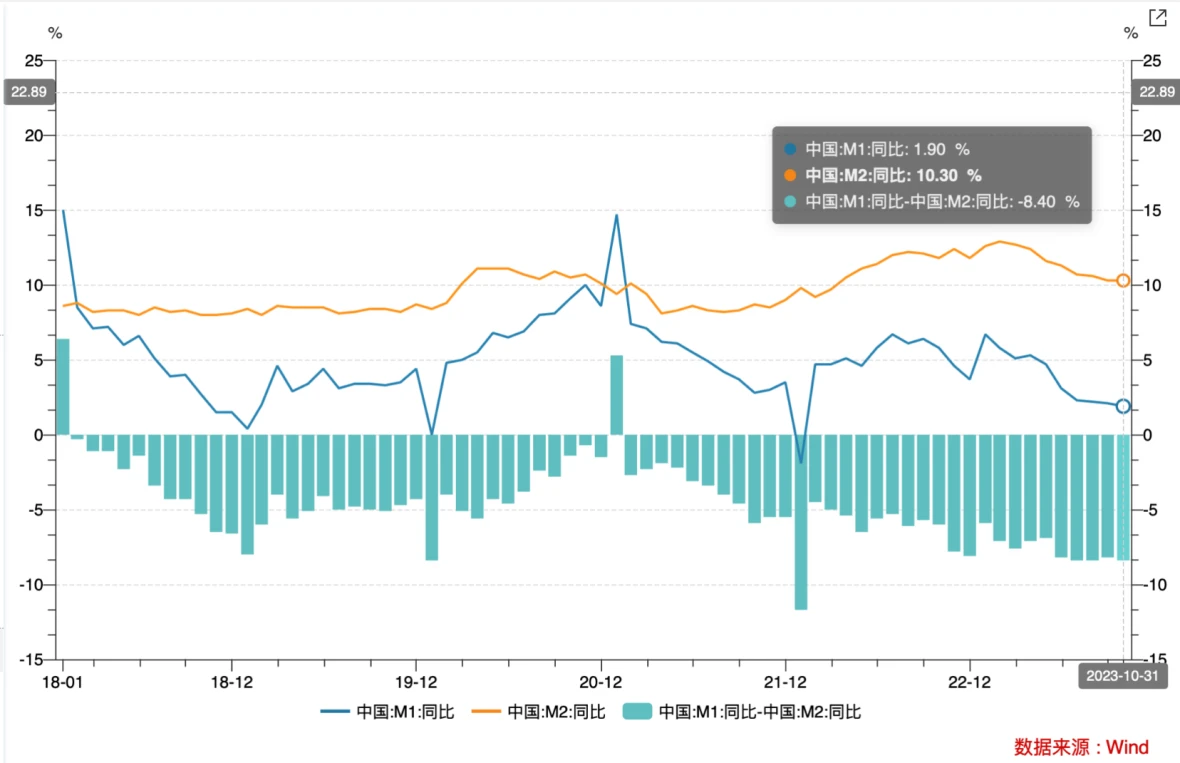
At the end of October, the balance of broad money (M2) was 288.23 trillion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 10.3%. The growth rate was the same as the end of last month and 1.5 percentage points lower than the same period last year. The balance of narrow money (M1) was 67.47 trillion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 1.9%, and the growth rate was 0.2 and 3.9 percentage points lower than the end of last month and the same period last year respectively. The balance of currency (M0) in circulation was 10.86 trillion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 10.2%. Net cash withdrawals for the month were 68.8 billion yuan. The M 1-M 2 scissor gap was -8.4%, down 0.2% from September, indicating that the overall saving tendency has not been alleviated, the degree of capital activation is still at a low level, and the economic performance is weak.
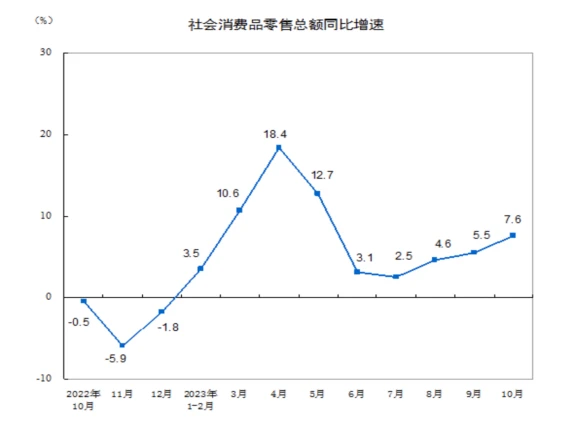
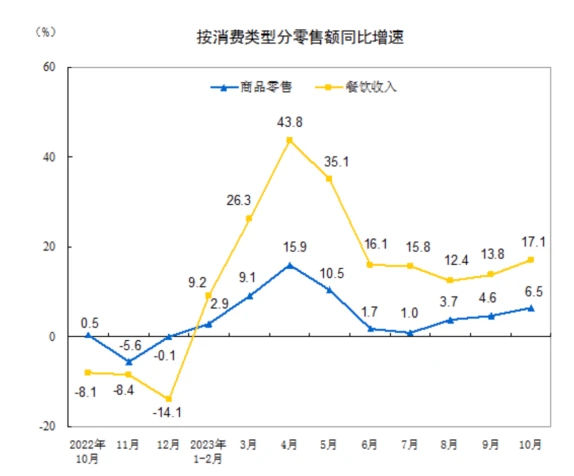
In terms of consumption, the total retail sales of consumer goods in October, supported by factors such as a low base and the Double Eleven Shopping Festival, recorded a year-on-year increase of 7.6% to 4,333.3 billion yuan, and the growth rate was 2.1% higher than that in September. By consumption type, retail sales of goods in October were 3,853.3 billion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 6.5%; catering revenue was 480 billion yuan, an increase of 17.1%, mainly related to the National Day holiday and increased demand for dining and travel.
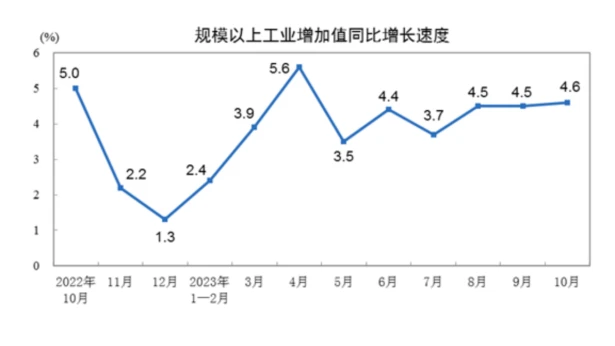
In October, the added value of industries above designated size actually increased by 4.6% year-on-year and 0.39% month-on-month. From January to October, the total profit of industrial enterprises above designated size nationwide was 6.11542 billion yuan, a year-on-year decrease of 7.8%. The decline was 1.2 percentage points narrower than that from January to September. The recovery of corporate profits has slowed down.
Since August, measures such as the reduction of down payment ratios and interest rate adjustments for existing first-home loans have been implemented frequently. Policies in various provinces and cities have continued to exert their efforts, and there have been a number of important developments recently:
(1) On November 17, the Peoples Bank of China, the State Administration of Financial Supervision, and the China Securities Regulatory Commission jointly held a symposium on financial institutions and proposed 1. Three no less than, that is, the growth rate of real estate loans of each bank shall not be lower than the average growth rate of banks. The growth rate of corporate loans to non-state-owned real estate enterprises shall not be lower than the Banks real estate growth rate, and the growth rate of personal mortgage loans to non-State-owned real estate enterprises shall not be lower than the Banks mortgage growth rate. 2. The regulatory agency is drafting a white list that may include 50 state-owned and private real estate companies. The listed companies will receive support from various aspects including credit, debt and equity financing. The list has been expanded from the beginning of the year; 3. It is planned to Modify the measures for development loans, commercial property loans, and personal housing loans, etc.
(2) On November 22, Shenzhen officially announced that the minimum down payment ratio for personal housing loans for second homes will be adjusted from the original 70% for ordinary housing and 80% for non-ordinary housing to 40%, and the standards for ordinary housing will be relaxed. (3) China’s Monetary Policy Implementation Report for the Third Quarter of 2023 released by the People’s Bank of China on November 27 pointed out that macro-prudential management of real estate finance should be improved, reasonable financing needs of real estate enterprises of different ownerships should be met equally, and real estate enterprises operating normally should not hesitate to lend or withdraw funds. Loan, break loan.
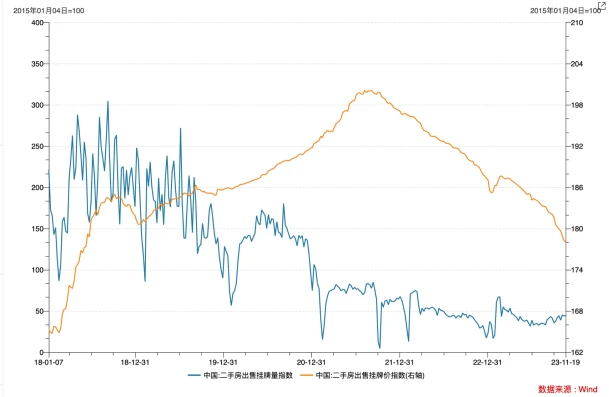
However, under the weak expectations of housing prices, there is no significant improvement in the current data. As of now, the effects of local policies are limited. The transaction area of commercial housing in 30 large and medium-sized cities is at the lowest level in the same period in the past five years. The number of second-hand housing listings has stabilized recently, but the listing price The index continues to decline.
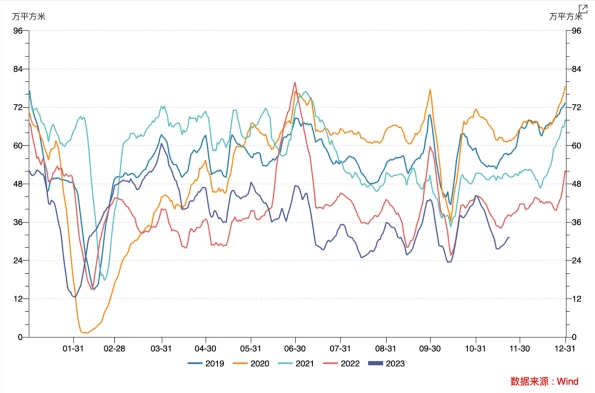
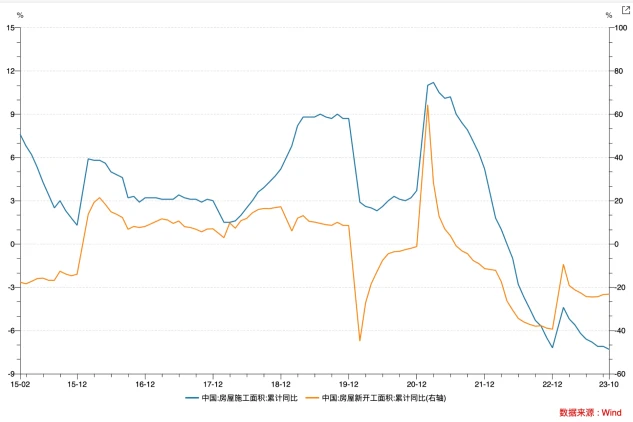
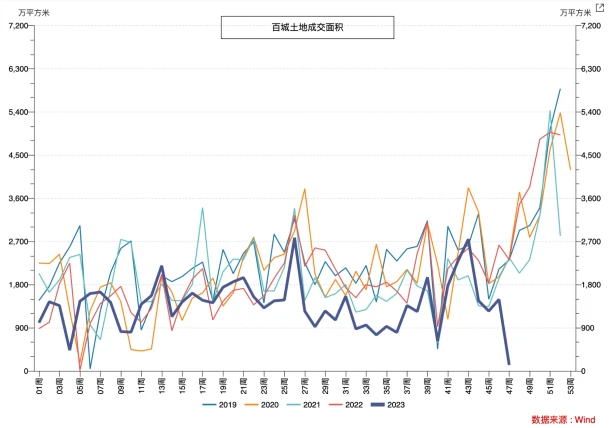
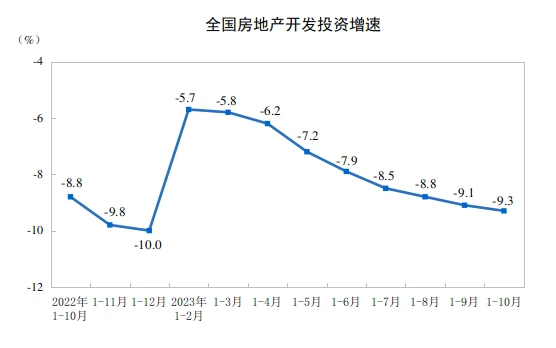
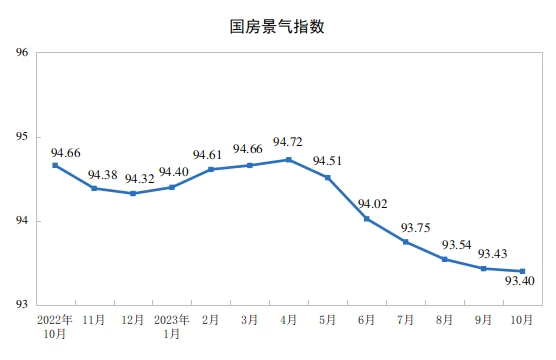
In recent years, sales and the willingness of real estate companies to acquire land have been sluggish. From January to October, the national real estate development investment was 9.5922 billion yuan, a year-on-year decrease of 9.3%, of which residential investment was 7.2799 billion yuan, a decrease of 8.8%. The housing construction area has continued to show negative growth year-on-year since May 2022, and there has been no obvious turning signal as of October. In October, the real estate development boom index (referred to as the national real estate boom index) was 93.40, declining for the sixth consecutive month.
The central government will issue an additional 1 trillion yuan of 2023 treasury bonds in the fourth quarter of this year. All the additional treasury bonds will be arranged to local governments through transfer payments to focus on supporting post-disaster recovery and reconstruction and making up for shortcomings in disaster prevention, reduction and relief, and overall improving our countrys ability to withstand natural disasters. . It is planned to use 500 billion yuan this year and carry forward 500 billion yuan to next year. The national fiscal deficit will increase from 3.88 trillion yuan to 4.88 trillion yuan, and the deficit rate is expected to increase from 3% to about 3.8%. Fiscal expansion is expected to become an important driver of corporate and household loans to boost the market.
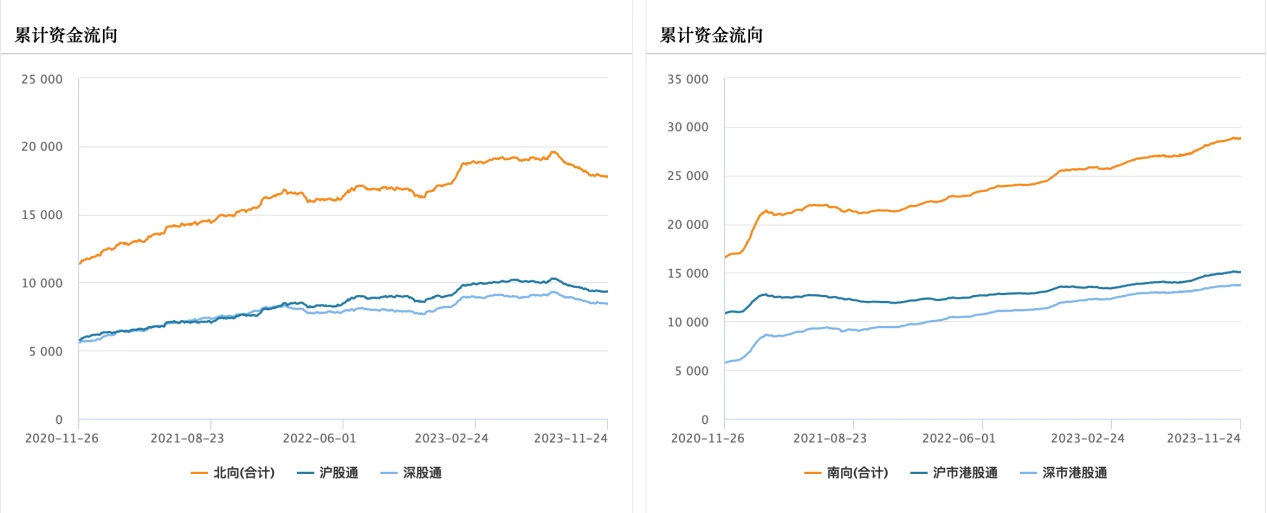
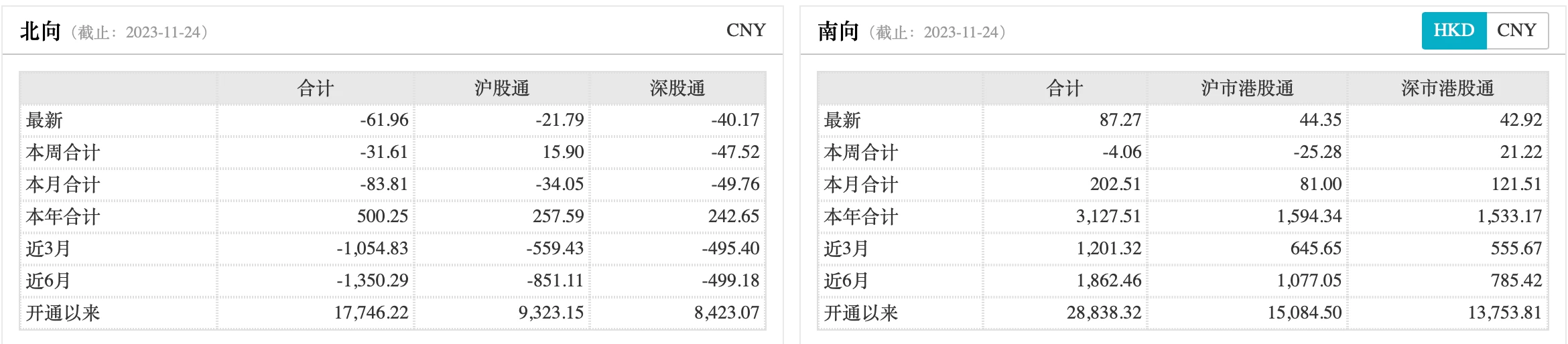
3. Fund flow
Both north and southbound funds showed net outflows last week. Southbound fund outflows totaled HK$406 million last week.
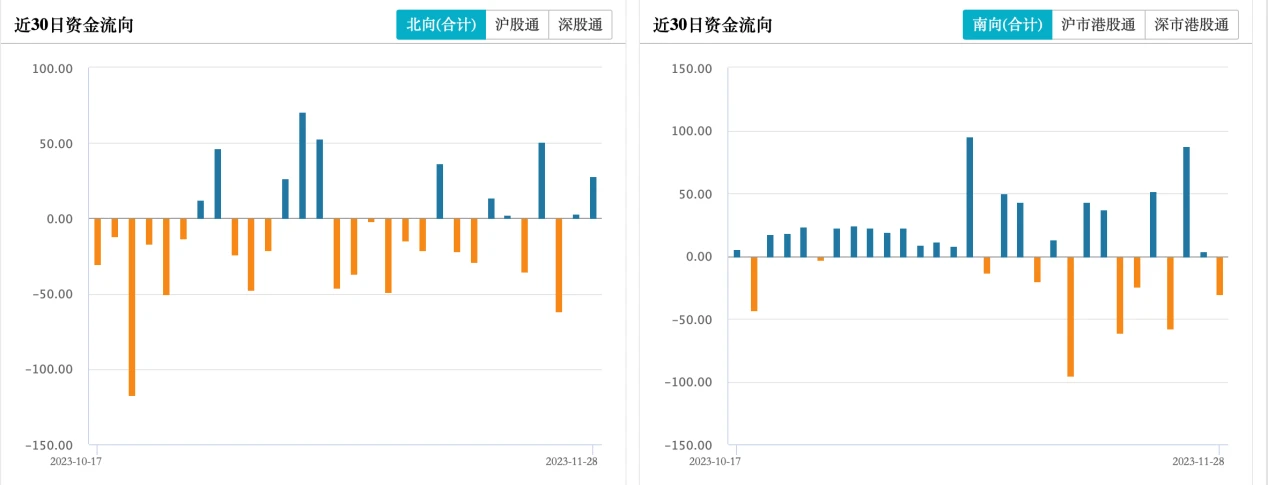
EPFR data shows that overseas active funds have continuously flowed out of the overseas Chinese stock market in the past 21 weeks.
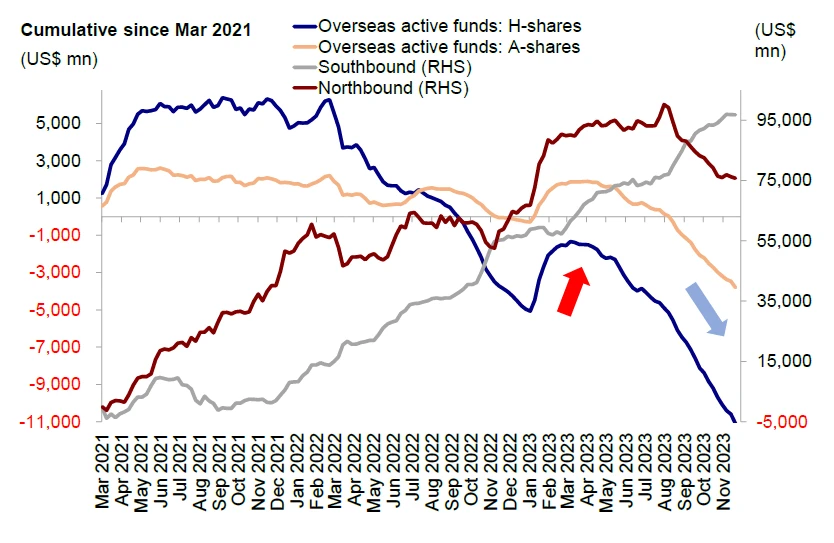
Source: EPFR, CICC Research
4. Summary
Against the background that the Federal Reserve has stopped raising interest rates, major regional funds around the world have reduced their allocation to Chinese stocks to underweight, and domestic stimulus policies have been introduced, there are still no signs of foreign capital returning to the Hong Kong stock market, and the Hang Seng Index remains weak. Judging from historical conditions, fundamental factors are still It is the key to leading the direction of funds. While economic data is still weak, Hong Kong stocks are still in the process of gradually bottoming out as a whole, and a sharp rebound depends on increased confidence in improving fundamentals. At present, the willingness of various departments to increase leverage is weak, the recovery process is slow, and the transmission of monetary easing to credit easing is not smooth. The key to reversing the decline lies in the continued efforts of fiscal and monetary policies to promote the opening of the credit cycle. The most important measures may be to stimulate the property market and increase central fiscal leverage. It can be seen that the government is also moving in this direction. When the turning point occurs, we need to pay close attention to the following fundamental data and the continued transmission and increase of policy support.










