Original author: Xinwei Yimu
Summary of key points
Observing the historical trend, STX always lags behind the trend of BTC, and its rise and fall are greater than that of BTC. It is also relatively strong compared to other currencies in the BTC ecosystem.
The BTC halving is approaching, and the popularity of the BTC ecological concept continues to rise. Stacks, as the leading project in the BTC ecosystem, will usher in the Nakamoto upgrade in Q4. The fast block generation every 5 seconds and the trustless sBTC will bring DeFi possibilities to BTC, and it is expected to Make the Stacks ecosystem further prosperous.
Among the BTC ecological concept coins, STX has the largest number of listings and is listed on all mainstream exchanges including Upbit. It is also the most liquid target and can be used as a phenomenon-level indicator to observe the entire BTC ecosystem.
Stacks uses the Proof of Transfer (PoX) consensus mechanism to implement smart contracts and decentralized applications based on the Clarity language based on the security of Bitcoin. It mines and enhances its function as the second layer of Bitcoin by locking Bitcoin. Including fast processing of transactions and guaranteed Bitcoin finality.
The Stacks ecosystem currently has a TVL of more than 19 million US dollars, has deployed more than 120,000 smart contracts, and has more than 760,000 wallets. The ecological projects are relatively complete, including wallets, DeFi, NFT, DAO, DID, Social, etc.
introduction
Stacks (STX) is a Bitcoin smart contract layer designed to extend the functionality of Bitcoin to support smart contracts and decentralized applications.
Goals: The main goal of Stacks is to introduce smart contract functionality on the Bitcoin blockchain, allowing developers to build decentralized applications (DApps) and smart contracts to expand the uses of Bitcoin.
POX Consensus: Stacks 2.0 adopts the POX consensus. Participants are rewarded with a more stable, underlying chain cryptocurrency. Compared with the cryptocurrency of the new blockchain, the underlying chain cryptocurrency rewards are more motivating for early participants, which helps Attract early participants and the consensus is stronger.
Empower BTC: Increase the vitality of the Bitcoin economy by converting BTC into assets for building DApps and smart contracts.
Ecology: Currently Stacks has 79 projects with a TVL of US$24.95 million.
1. Team background

Image source: Linkedin
Stacks is a project comprised of multiple independent entities and communities, initially led by Blockstack PBC and later renamed Hiro Systems PBC. Based in NYC, the team currently has 49 people, according to the latest Linkedin information.
Main characters and responsibilities:
Muneeb Ali: Co-founder of Stacks and CEO of Hiro. He holds a PhD in computer science from Princeton University and focuses on the research and development of distributed applications. He has spoken at TEDx and other forums, spread the word about encrypted digital currencies and blockchain, and written There are a large number of academic publications and white papers on related topics. Muneeb is also the CEO of Trust machine.
Jude Nelson: Stacks Fund Research Scientist, former Hiro Engineering Partner, holds a PhD in Computer Science from Princeton University, and was a core member of PlanetLab, which received the ACM Test of Time Award for enabling planetary scale experiments and deployments.
Aaron Blankstein: Engineer who joined the Blockstack engineering team in 2017 after receiving his PhD. He studied computer science at Princeton University and MIT. His research covers a variety of topics, focusing primarily on web application performance, caching algorithms, compilers, and applied cryptography. His research on CONIKS won the Caspar Bowden Privacy-Enhancing Technology Award in 2017. Emacs has been used for more than 10 years.
Mike Freedman: Hiro technical advisor. He is a professor of distributed systems at Princeton University and provides technical guidance for the project. He has received the Presidential Early Career (PECASE) Award and the Sloan Scholarship. His research has spawned multiple commercial products and deployed systems with millions of daily users.
Albert Wenger: Director of Hiro and managing partner of Union Square Ventures (USV). Prior to joining USV, he served as President of del.icio.us and was an active angel investor in companies such as Etsy and Tumblr. Albert graduated in economics and computer science from Harvard University and holds a PhD in information technology from MIT.
JP Singh, director of Hiro, is a professor and undergraduate director at Princeton University. He mainly studies parallel computing systems and applications. He has won the Presidential Early Career (PECASE) Award and the Sloan Scholarship. He also co-founded the business analysis company, FirstRain Inc. He is a graduate of Princeton University and holds a graduate degree in electrical engineering from Stanford University and a Ph.D. He is also one of the founders of Trust machine.
In addition to Hiro, there are multiple independent entities in the Stacks ecosystem. Including Stacks Foundation, Diling Technology, Freehold, New Internet Labs, and Secret Key Labs.
Image source: stackschina
Hiro: Focus on providing and maintaining developer tools in the Stacks ecosystem
Stacks Foundation: Supports the development of the Stacks ecosystem through governance, RD, education, and funding
Daemon Technologies: Focus on supporting Stacks mining and staking business
Secret Key Labs: Focus on providing Chinese mobile wallets that can directly participate in Stacking
2. Capital relations
Stacks has raised a total of 5 rounds of financing, totaling $88M
Source: Rootdata
The specific time points and funding sources are as follows:
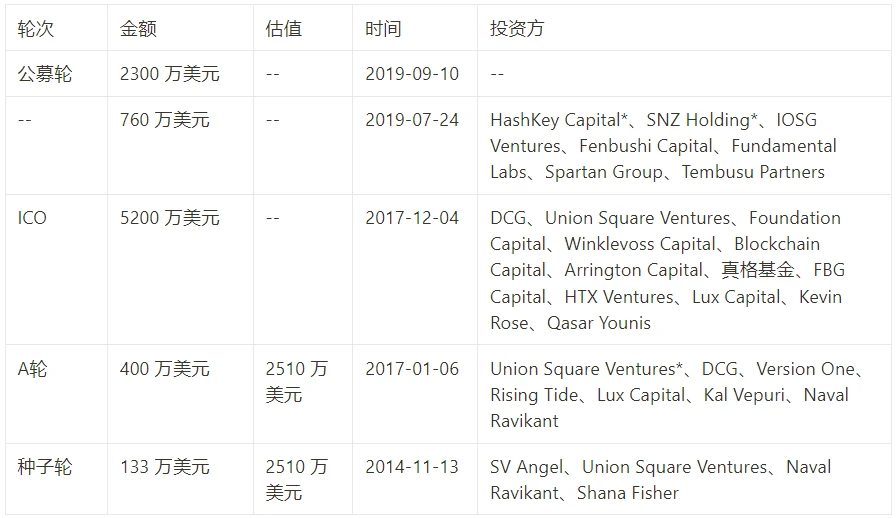
Source: Rootdata
Trust machine:
Trust Machine was founded by two Princeton computer scientists (Muneeb Ali, one of the founders of Stacks, and JP Singh, executive director of Hiro) who are both big believers in Bitcoin and believe that the Bitcoin layer can unlock a wide range of new use cases for Bitcoin. Trust machine was co-founded by Muneeb Ali, one of the founders of Stacks, and JP Singh, executive director of Hiro.
Trust Machines has three products: Leather (wallet, formerly known as Hiro wallet), Console (social platform), and LNswap
In April 2022, Breyer Capital, Digital Currency Group, GoldenTree, Hivemind and Union Square Venture announced an investment of $150M in Trust Machine[1]
Additionally, in March 2023, Trust Machine and Gossamer Capital announced a $2.5 million investment in Alex (the largest dex on Stacks).
Image source: combed by the author of this article
3. Development History and Current Situation
development path

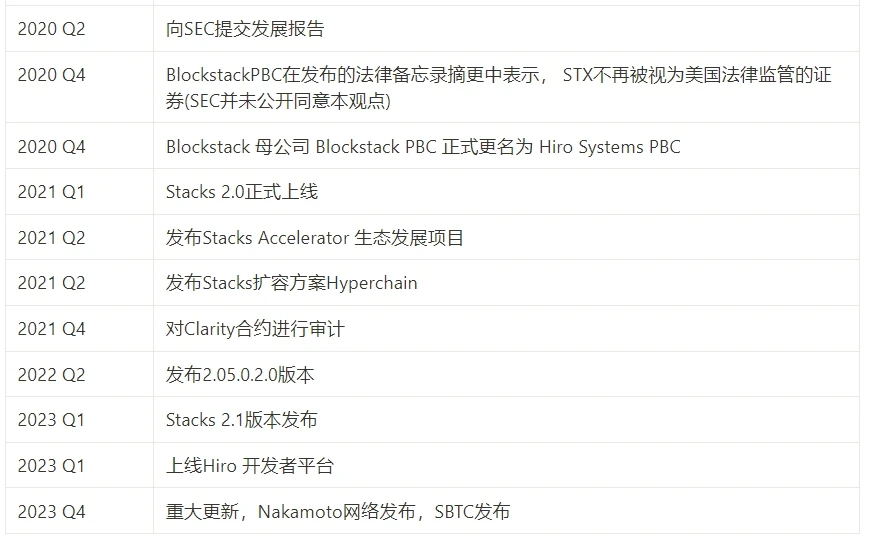
Source: This article is compiled based on public information
status quo
Stacks has carried out the latest v2.1 network upgrade in the first quarter of 2023, which includes updates to improve stacking functions, improve Clarity programming language, internal blockchain upgrades, and enhance reliability. . In addition, the Hiro developer platform has been launched, allowing developers to build and deploy smart contracts on Stacks through a managed experience.
Currently, the community is actively preparing for the Nakamoto upgrade expected to occur in 2023 Q4.
The Nakamoto upgrade introduces a series of technological advancements that, combined with the introduction of sBTC, a 1:1 Bitcoin-backed asset, will soon enable Stacks to write to Bitcoin in a fully decentralized manner. sBTC is a trust-minimized way to move Bitcoin between L1 and L2. In addition, unlike early sidechain methods, threshold wallets are managed by a group of dynamically changing entities without permissions. These entities are economically motivated to maintain the peg, and they can join or exit the peg maintenance at will. Using this mechanism, an asset can be issued on the Bitcoin layer that always maintains a 1:1 pegged relationship with Bitcoin. In addition, the Nakamoto upgrade will significantly reduce execution time from minutes to seconds.
The community has previously opened trial applications for sBTC for developers, and has actively organized community members to learn the key points and use cases of this upgrade.
4. Consensus mechanism: POX
Stacks’ earliest consensus mechanism is POB (proof-of-burn), proposed by Jude Nelson and Aaron Blankstein at the end of 2018.
POB allows Stacks miners to compete by destroying cryptocurrency instead of consuming electricity. Compared to ordinary proof-of-work blockchains, miners on proof-of-burn chains do not require specialized hardware to participate and provide greater transparency to network participants. However, POW, proof-of-burn is also destructive, requiring miners to destroy value in exchange for the security of the blockchain.
Unlike PoS, PoB requires users to permanently destroy their tokens in exchange for mining rights. Users do this by sending their tokens to an address that cannot be retrieved"combustion"。
Mining rights are allocated based on a random selection process, and even if users have burned tokens, there is no absolute guarantee that they will be selected for mining.
This process may result in a reduction in the token supply for holders of the original token, but it does create an opportunity for competition with miners.
Since the BTC burned by POB is equivalent to permanent destruction, in order to better balance the interests between miners and currency holders while reducing the impact on the Bitcoin network, Stacks transitioned from the PoB consensus mechanism to PoX.
POX(Proof of Transfer)
POX (Proof of Transfer) is an extension of the burn proof mechanism. PoX uses the proof-of-work cryptocurrency of the established blockchain to secure the new blockchain. However, unlike POB, instead of burning cryptocurrencies, miners transfer committed cryptocurrencies to other participants in the network. Key Features and Benefits of PoX
Rewards based on underlying chain tokens: Participants are rewarded with more stable, underlying chain cryptocurrencies. Compared with new blockchain cryptocurrencies, underlying chain cryptocurrency rewards are more incentivizing for early participants, which helps attract Early participants, the consensus is stronger.
Initial value setting: It is thought to be linked to the underlying chain cryptocurrency, so the new token has an initial value that can be referenced.
Solve the dependent value spiral problem: PoX helps solve the dependent value spiral problem that may arise in new blockchains by providing participants with underlying chain cryptocurrency incentives.
Establishing a developer fund: PoX can also be used to establish a developer fund to support the development of new blockchain ecosystems. These funds can use another cryptocurrency, such as Bitcoin, without affecting the value of the new cryptocurrency.
POX design
participants
Miners: miners. Pledge BTC in the form of bidding to obtain the mining rights of the next block → Mining → Obtain the STX tokens produced by mining + platform transaction fees
Stackers: Users who lock in a certain amount of STX for a certain period of time. Set different periods to pledge STX → Build your own pool or join other pools → Provide an address to receive rewards → Obtain the miner’s BTC based on the amount of pledged STX
Miner mining mechanism
Image source: Stacks white paper
Participant (network maintainer) incentives Image source: Stacks white paper
Reward Period: During each reward period, miners transfer funds to the address that receives the reward. Each reward address receives only one Bitcoin from miners during the reward cycle.
Eligibility:
The Stacks wallet has no less than 0.02% of the total unlocked STX tokens, this threshold will be adjusted based on the level of participation in the Stacking protocol;
A signed message is broadcast before the start of the reward cycle, which includes the protocol to lock the corresponding STX tokens specifying the locking period, specifying the Bitcoin address to receive the funds, and voting for a certain block on the Stacks chain.
Address validity:Participants need to be able to verify the address receiving funds, as the reward address needs to be confirmed as valid each reward cycle.
Preparation phase and reward consensus:Before the reward cycle, participants go through a preparation phase where two key things are decided:
1) Anchored block: During the reward cycle, there is an anchor block that miners need to transfer their funds to the appropriate reward address. **This anchor block is valid throughout the reward cycle.
2) Reward Set: The reward set is the collection of Bitcoin addresses that will receive funds during the reward cycle. This set is determined by the Stacks chain state of the anchor block.
Reward address selection rules:Different rules apply to the selection of reward addresses, depending on whether the blockchain tip built by the miner is a descendant of the anchor block. If a miner builds a blockchain tip that is not a descendant of the anchor block, then all of that miners committed funds must be destroyed. If a miner builds a blockchain tip that is a descendant of the anchor block, then the miner must send committed funds to two addresses in the reward set.
5. Technical architecture
L1 or L2?
Stacks is described as a smart contract layer built on top of Bitcoin.
The initial version (released in 2021) of Stacks has a security budget separate from Bitcoin L1 and is treated as an independent layer (L1.5)
Future Nakamoto versions are planned to rely entirely on Bitcoin’s hashing power, making it a fully affiliated layer (L2) of Bitcoin, meaning that Stacks will have Bitcoin’s security determine the irreversibility of its transactions.
Sidechain?
Stacks is interoperable with Bitcoin to some extent, but it does not meet the definition of a traditional sidechain. Stacks’ consensus mechanism runs on Bitcoin L1 and is closely tied to Bitcoin’s finality, and data and transactions on Stacks are automatically hashed and permanently stored on the Bitcoin blockchain. This is different from traditional sidechains, whose consensus runs on the sidechain and does not rely on Bitcoin L1 and does not store data on Bitcoin L1. Therefore, Stacks does not meet the definition of traditional sidechains.
Smart contract language - Clarity
Clarity is a decision-making smart contract programming language designed specifically for the Stacks blockchain with the following features:
1) Security first: Clarity is designed with a focus on security and predictability to protect against common vulnerabilities and attacks in Solidity contracts. It is specifically designed for security and aims to avoid common problems in the smart contract world.
2) Interpretability: Clarity’s code is interpretive, which means that it will be interpreted and executed line by line when submitted to the chain, unlike other languages (such as Solidity) that need to be compiled into bytecode first. This reduces the vulnerabilities that compilers can introduce and keeps smart contracts readable because the code of a Clarity contract is the code that is executed, not compiled bytecode.
3) Decision-making: Clarity is a decision-making language, which means from the code itself, you can know exactly what the program will do. This avoids problems such as"Downtime issues". Clarity ensures that it will not be called during the call"Running out of fuel", because it guarantees that program execution will end within a limited number of steps.
4) Recursive calls are prohibited: Claritys design prohibits recursive calls, which is a situation that may lead to contract vulnerabilities, in which one contract calls another contract and then calls back to the original contract, which can trigger multiple extraction operations.
5) Prevent overflow and underflow: Clarity prevents numerical calculation overflow and underflow, which is a common type of vulnerability that may lead to abnormal behavior of smart contracts.
6) Built-in support for custom tokens: Clarity has built-in support for creating custom fungible and non-fungible tokens, which is one of the popular use cases for smart contracts. Developers dont need to worry about internal asset management, supply management, or the emission of token events because these features are already integrated into the Clarity language.
7) Transaction protection based on post-conditions: Clarity supports attaching post-conditions to transactions to ensure that the chain status changes in the expected way after the transaction is completed. If the postcondition check fails, the transaction will be reversed.
8) Forced return response processing: Public calls of the Clarity contract must return a response indicating success or failure. This helps ensure errors are not overlooked, increasing the security of the contract.
9) Composition over inheritance: Clarity adopts the principle of composition over inheritance instead of inheriting other contracts as in languages like Solidity. Developers can define features that are then implemented by different smart contracts, which provides greater flexibility.
10) Access the Bitcoin base chain: Clarity smart contracts can read the status of the Bitcoin base chain, which means you can use Bitcoin transactions as triggers in smart contracts. Clarity also provides a number of built-in functions to verify secp 256k 1 signatures and recovery keys.
Gaia storage system
Gaia is a unique decentralized storage system in the Stacks blockchain that emphasizes user ownership and control of data. Unlike some other immutable storage solutions on blockchain, such as IPFS and Arweave, Gaia focuses on user control over data rather than emphasizing immutability.
The Gaia storage system consists of Hub services and storage resources on a cloud software provider. The storage provider can be any commercial provider such as Azure, DigitalOcean, Amazon EC 2, etc. Gaia currently supports S 3, Azure Blob Storage, Google Cloud Platform, and local disks, but the driver model allows support for other backends.
Gaia stores data as a simple key-value store. Whenever an identity is created, the corresponding data store is associated with that identity on Gaia. When a user logs into a decentralized application (dApp), the authentication process provides the application with the URL of the Gaia hub, and Gaia then performs storage operations on the users behalf. There will be a pointer saved in Gaia to the Blockstack chain and the Atlas subsystem. When users use the Blockstack authentication protocol to log in to applications and services, this storage location information is passed to the application, and then the application interacts with the Gaia data at the specified location. That is, the cloud storage service provider cannot directly see the user data and can only See the encrypted data block.
The Stacks blockchain only stores identity data, while data created by operations on identities is stored in the Gaia storage system. Each user has profile data, and when the user interacts with the decentralized dApp, the application stores the application data in Gaia on the users behalf. Because Gaia stores user and application data outside of the blockchain, Stacks dApps generally perform better than dApps on other blockchains.
Image source: stacks white paper
Here are some key features about Gaia:
User Ownership and Control:Gaia is designed with a focus on user ownership and control of their data. This means users decide where their data is stored and are able to modify or delete their data, unlike some other immutable blockchain storage solutions.
Connection to Stacks identity:Gaia connects access to data to a user’s identity on the Stacks blockchain. This connection enables users to better manage and access their data while being tied to their digital identity.
High performance and high availability:Storing user application data outside of the blockchain provides higher performance and availability because reading and writing data is not subject to the performance limitations of the blockchain.
6. Important upgrades
Stacks Nakamoto Upgrade
The Nakamoto upgrade introduces a series of technological advancements that, combined with the introduction of sBTC, a 1:1 Bitcoin-backed asset, will soon enable Stacks to write to Bitcoin in a fully decentralized manner. sBTC is a trust-minimized way to move Bitcoin between L1 and L2. In addition, unlike early sidechain methods, threshold wallets are managed by a group of dynamically changing entities without permissions. These entities are economically motivated to maintain the peg, and they can join or exit the peg maintenance at will. Using this mechanism, an asset can be issued on the Bitcoin layer that always maintains a 1:1 pegged relationship with Bitcoin. In addition, the Nakamoto upgrade will significantly reduce execution time from minutes to seconds.
sBTC: Provides a trustless, decentralized two-way anchor, introducing BTC liquidity into smart contracts
Bitcoin Finality: Stacks blockchain transactions are considered irreversible once confirmed under a PoX (Proof of Transfer) block
Faster Blocks: The Stacks blockchain implements faster block confirmation times, with a confirmation time of 5 seconds per block
7. Token Economy
The total supply of STX tokens is capped at 1.818 billion, and the current circulating supply is approximately 1.42 billion.
Stacks genesis block contains 1.32 billion STX tokens. These STX tokens were issued and distributed multiple times in 2017 and 2019. The price of the 2017 issuance is US$0.12 per STX, the price of the 2019 issuance is US$0.25 per STX, and the price of the 2019 SEC-compliant issuance is US$0.30 per STX.

Mining rewards are distributed as follows: 1000 STX per block for the first 4 years, 500 STX per block for the next 4 years, 250 STX per block for the next 4 years, and 125 STX per block permanently after that. STX allocated to founders and employees follows a 3-year unlocking schedule.
In October 2020, Stacks changed the minting and burning mechanism of STX tokens. Stacks did not implement STX minting and burning, but instead reduced the amount of tokens issued. By 2050, the total supply will reach approximately 1.818 billion coins.
8. Ecological situation
TVL situation
Wallet number trend
Smart contract quantity trend
ecological map

wallet
Xverse
Xverse is a crypto wallet built on Stacks and supports the Ordinals protocol. Users can manage both Bitcoin assets (including BTC and Bitcoin NFT) and Stacks-based assets through this wallet. At the same time, the wallet also has a built-in stack function, and users can earn Bitcoin income by stacking STX.
The UI of this wallet is simple, and the wallet creation process is similar to that of many EVM-compatible wallets. The wallet is also backed up and restored through mnemonic words. For EVM wallet users who are used to the little fox, this undoubtedly lowers the threshold for using the wallet. After the wallet is created, two addresses will be generated at the same time, one is a Bitcoin address, which is used to receive and send Bitcoin assets. The other is the Stacks network address, used to manage Stacks-based assets.
Leather
Leather was formerly known as Hiro Wallet. Hiro is a development tools company that supports developers on the Stacks blockchain. Hiro Wallet is one of the companys products. Leather is a wallet application built on Bitcoin. It currently supports Ordinals and will soon support the Lightning Network. Leather has many convenient built-in functions. Users can directly use credit cards, debit cards or even bank transfers to purchase STX in Leather, and then directly participate in staking in the wallet.
Currently, the wallet supports browser extensions for Chrome, Firefox, and Brave, as well as desktop versions for MacOS, Windows, and Linux systems.
The browser extension version can connect to applications, purchase STX, mint and NFT, and use Ledger hard wallet. The desktop version allows you to participate in staking to earn Bitcoins and protect assets using Ledger hard wallets.
DeFi
ALEX
ALEX is a DeFi protocol built on the Bitcoin network through Stacks smart contracts, and draws on the design of Balancer V2 during development. The current mainnet version of the platform features Swap, lending, staking, revenue mining and Launchpad. In addition, as BRC 20 becomes popular, ALEX also launched the BRC 20 order book exchange.

Arkadiko
Arkadiko is an open source, non-custodial liquidity protocol built on Stacks smart contracts, where users can mortgage assets to mint the stablecoin USDA, earn deposit interest and borrow assets on Stacks. Arkadikos governance token is DIKO, which can be obtained by pledging assets to add liquidity to the pool.

LNSwap
LNSwap is an atomic swap protocol that embodies the foundation of Bitcoin and the security, decentralization, and stability it provides.
Lnswap is composed of three parties: users, liquidity providers and aggregators.
Users are those who want to exchange assets. Their funds are locked in a very basic Hash Time Lock Contract (HTLC) only for the duration of the exchange, and through the use of smart contracts, direct transactions can be made between the two parties without the involvement of a third party.
Liquidity providers are those who use the assets they own to provide funds to the LNSwap protocol to facilitate swaps on our exchange. In return for providing assets, liquidity providers will be rewarded with fees generated by swaps that occur on the platform.
Aggregators essentially collect the data and information exchanged on a protocol and consolidate them for easy reference and access. Currently, LNSwap’s aggregator is a router that forwards exchange information between users and liquidity providers. But in the future, the aggregator will actually be an on-chain contract, which effectively means that anyone can become an aggregator on the platform through a simple front-end. Additionally, liquidity providers will be able to register to multiple aggregators.

NFT
Gamma
Gamma, the NFT market on Stacks, was originally named STXNFT. On April 27, 2022, it was announced that it would be renamed Gamma. Gamma is the third letter of the Greek alphabet and represents the third phase of the web: Web 1.0, Web 2.0 and now Web3.
The platform aims to bring collectors, creators and investors together to explore, trade and showcase NFTs within the Bitcoin ecosystem. The Gamma platform consists of three core products: NFT market, Launchpad and social platform.Gamma.ioAt the same time, it supports the primary market and secondary market of Bitcoin NFT.
Users can use Gamma bot to create their own unique digital works, collect them or sell them. Users can use the code-free Bitcoin NFT creation tool to successfully create it in minutes.Gamma.ioIt solves the technical, complex and time-consuming pain points of creating NFTs on the Bitcoin network. However, the secondary market still accounts for the majority of platform sales. Each sale includes artist royalties as well as marketing commissions, with percentages varying by artist and collection.

Boom
Boom is Stacks native NFT platform, supports Stacks ecological token transfer, and will support Stacks NFT transactions in the future.
9. Competitors
Unlike Lightning Network, which focuses on improving Bitcoin’s scalability, Stacks focuses on introducing new smart contract features. Unlike RSK, Stacks has its own miners and mining process, rather than relying on Bitcoin miners. Unlike Liquid, Stacks is an open, decentralized network that doesn’t just focus on financial applications. Unlike Rollups, Stacks is a solution built on top of Bitcoin rather than a new network outside of Bitcoin.
Why was the value of the BTC ecosystem suddenly discovered this year?
Two important technical updates need to be mentioned here:
The first is the 2017 Segregated Witness upgrade, which is equivalent to expanding BTC’s block data from 1 MB to 4 MB, but the expanded part can only be used to store signatures. Until the Taproot upgrade at the end of 2021, advanced scripts can be written in Segregated Witness for the first time, and complex data can be written on BTC. Since then, BTC has made great progress in programmability and scalability. Some protocols containing complex logic have begun to appear. The BTC ecosystem has finally begun the next phase of milestones. This is the main opportunity for the explosion of the BTC ecosystem in 2023. .
Ordinals & BRC 20
The emergence of the Oridnals protocol has completely ignited the BTC ecosystem, and its rapid development has also promoted each other with the adoption of Taproot. People can encode the NFT data and write it into the SegWit extended space (4 MB per block).
Soon, new developers improved Ordinals, imitating ERC 20 and writing the full functionality of Token into the BTC output script, and BRC 20 was born.
Atomicals & ARC 20
Atomics is another derivative protocol that engraves data on UTXO to implement Token.
Different from Oridnals, which was originally designed for NFT, it rethinks how to issue tokens on BTC in a centralized, tamper-proof and fair manner from the bottom up.
When verifying an Atomics transaction, you only need to query the corresponding sat UTXO on the BTC chain. The atomicity of ARC 20 Token is consistent with the atomicity of BTC itself, and the calculation of ARC 20 transfers is completely handled by the BTC basic network.
The design of Atomics binding UTXO cleverly avoids the complexity faced by BRC 20, making it more decentralized, more BTC native, and most importantly, more in line with the culture of the BTC community.
Rune & Pipe
Under the general trend of hype, Casey also proposed an inscription implementation specifically for issuing FT, namely Rune.
The idea of Rune was just an idea, and the founders of #Trac wrote the first usable protocol based on it and issued $PIPE. Due to Caseys high popularity, $PIPE took over the hype that continued from BRC 20 and quickly completed the first wave of hype.
Runes legitimacy is stronger than BRC 20, but it is still difficult to be accepted by the BTC community.
Lightning Network
The Lightning Network is the king of legitimacy in the BTC community. Starting in 2016, more than half of the developers in the BTC ecosystem have been engaged in the development of the Lightning Network for a long period of time.
The basis of the Lightning Network is a payment channel. This concept was first proposed by Satoshi Nakamoto. Both parties to the transaction lock BTC through multi-signatures, and both parties maintain an off-chain ledger to record the transaction.
Payment channels connected in pairs form a network, and two parties who are not directly connected can also jump to the channel to complete transactions. The Lightning Network does expand the performance of BTC transfers, giving users a better experience.
The final BTC settlement can only be carried out on the BTC main network, and all coins are still saved by the public and private key system.
Taproot Assets (Taro)
Different from BRC 20 and others, Taproot Assets only writes the Token information in the UTXO output script of the BTC main network, and does not store the transfer, mint and other functional codes of this Token.
Taproot Assets only regards the BTC main network as a registry of Tokens and does not completely rely on the BTC main network to operate, so these assets must be deposited into the Lightning Network before they can be traded.
Therefore, the Token of Taproot Assets must rely on a third-party storage indexer. Without the storage indexer, these tokens will be lost forever.
RGB
RGB is a smart contract system based on BTC and Lightning Network. It is the ultimate expansion method, but its progress is slow due to its complexity.
RGB converts the state of a smart contract into a short proof, engraving the proof into the BTC UTXO output script.
Users can check the status of the smart contract by validating this UTXO. When the smart contract status is updated, a new UTXO is created to store the proof of this status change.
RGB can be regarded as the L2 of BTC. The advantage of this design is that it uses the security of BTC to guarantee smart contracts. However, as the number of smart contracts increases, the demand for UTXO encapsulated data will also increase, which will eventually become unavailable. Avoid creating a lot of redundancy in the BTC blockchain.
RSK & RIF
RSK can be regarded as the L2 of BTC, which is essentially a smart contract chain with an EVM structure.
RSK just cross-chains the mainnet BTC to its own face through the Hash lock and uses it as network gas.
At the same time, RSK adopts the same POW consensus algorithm as BTC, so BTC miners can also mine RSK at the same time and earn transaction fees of $RBTC.
BitVM
BitVM is currently the most BTC-native, most potential, and most technically hard-core smart contract expansion solution.
Without modifying the BTC network, a VM virtual machine that supports calculations is run through Optimistic Rollup to implement BTC smart contracts. The BTC network is used to run Optimistic Rollup’s fraud proofs.
Using the most basic Hash lock and BTC script operations OP_BOOLAND and OP_NOT, a simple logic gate is implemented. By combining BTCs logic gates, a circuit that can perform operations is formed, through which fraud proofs are processed on the BTC chain.
10. Innovation and Risk
Innovation
S (Secured by the entire hash power of Bitcoin): The security of the Stacks smart contract layer is supported by the entire hash power of Bitcoin, which means that it is subject to the high security and decentralized nature of the Bitcoin network Protect.
T (Trust-minimized Bitcoin peg mechanism; write to Bitcoin): Stacks adopts a minimum trust Bitcoin peg mechanism that can write information to the Bitcoin blockchain. This ensures interoperability between Bitcoin and Stacks while minimizing trust requirements.
A (Atomic BTC swaps and assets owned by BTC addresses): Stacks allows for atomic Bitcoin (BTC) swaps while ensuring that assets in smart contracts belong to Bitcoin addresses. This means assets can be securely transferred from the Bitcoin network to the Stacks blockchain and vice versa.
C(Clarity language for safe,decidable smart contracts: Stacks uses the Clarity programming language, a language designed for writing secure, decidable smart contracts. The Clarity language features the ability to reduce errors and uncertainty in smart contracts.
K (Knowledge of full Bitcoin state; read from Bitcoin): The Stacks smart contract layer has knowledge of the complete state of Bitcoin and can read information from the Bitcoin blockchain. This allows Stacks smart contracts to stay connected to the Bitcoin network, understanding and validating data on the Bitcoin chain.
S(Scalable,fast transactions that settle on Bitcoin): The Stacks smart contract layer enables scalable, fast transactions that settle on Bitcoin. Despite its faster transaction speeds, Stacks still benefits from Bitcoin’s finality and security. risk
Security: Although Stacks transactions are processed in batches and hashed on the BTC main network, there is no doubt about the security of BTC. However, like other blockchains, the Stacks network itself may face security threats, such as security holes and hacker attacks. Some people also question Stacks The degree of decentralization of the network. These situations can result in financial losses and compromise the security of the network.
Complexity: Although Stacks provides developers with an evolving infrastructure, the Clarity language has blocked many talented developers, and this complexity can lead to potential errors and inefficiencies.
Interoperability: Although Stacks and BTC are tightly bound, Stacks and other BTC ecological projects are still unable to interoperate efficiently. The ability of blockchain networks to work together seamlessly is critical to the adoption and efficiency of the technology. A lack of interoperability can lead to inefficiencies and hinder innovation. 11. Secondary market liquidity
The k line is STX/USDT, and the orange line is BTC/USDT. It can be seen that no matter whether it rises or falls, the performance of STX always lags behind that of BTC, and rises and falls with BTC.
It can be seen from STX/BTC that STX is equivalent to BTC with leverage.
To sum up, STX always lags behind the trend of BTC, and its rise and fall are greater than that of BTC.
Orange is REN, yellow is BADGER, cyan is RIF, purple is ORDI
It can be seen that the currencies in the BTC ecosystem are strongly related to BTC, often rising and falling at the same time. STX is relatively resilient, and ORDI is more flexible because it is a new currency.
Summarize
Stacks is a second-layer solution built on top of Bitcoin that provides innovative approaches to address scalability challenges and drive the development of new applications. It enhances the functionality of Bitcoin by introducing smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps) while leveraging Bitcoin’s security and consensus mechanisms. The platform provides a trustless two-way Bitcoin peg and uses Clarity, a smart contract language designed for security and transparency. Stacks provides a programmable asset layer for Bitcoin, unlocking its potential in multiple use cases.
Key developments like the upcoming Nakamoto upgrade position Stacks as a pioneer in the cryptocurrency space. As the broader crypto community recognizes the importance of second-layer solutions to Bitcoins future, Stacks is poised to play a key role in the growing industry. Collaboration, technological innovation, and the exploration of new use cases are shaping the Stacks ecosystem, with the goal of releasing $600 billion in Bitcoin liquidity into decentralized finance (DeFi), providing cheaper and faster ways to trade Bitcoin, and continuing to Develop DApps and integrate cutting-edge technologies. This shows how much potential there is in the development of Nakamotos version of Stacks.
About MT Capital
MT Capital, headquartered in Silicon Valley, is a crypto-native fund focusing on Web3 and related technologies. We have a global team, and our diverse cultural backgrounds and perspectives allow us to have an in-depth understanding of the global market and to seize investment opportunities in different regions. MT Capitals vision is to become the worlds leading blockchain investment firm, focused on supporting early-stage technology companies that can generate significant value. Since 2016, our investment portfolio covers Infra, L1/L2, DeFi, NFT, GameFi and other fields. We are not just investors, we are the driving force behind the founding team.
Official website:https://mt.capital/
Twitter:https://twitter.com/MTCapital_US
Medium:https://medium.com/@MTCapital_US
Reference:
[ 2 ]Trust machine: https://trustmachines.co/blog/hello-trust-machines/
[ 3 ]https://decrypt.co/82019/bitcoin-defi-thing-says-stacks-founder-muneeb-ali
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/eJ36c6kBV1 8 fgH 259 XDiMghttps://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/u-i-oZf2b FAuItTUBYxosAhttps://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/ vFyz 4 kylLJ 2 S 1 yVohbzXTQ https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/uxaPnzjPjJlCLmwakPIY_A
https://www.stackschina.com/stacks-ecosystem-map
https://www.blocktempo.com/the-bitcoin-scalability-solution-stacks/https://mirror.xyz/arsenal-fc.eth/ ujrApyfn 40 YOBKAZ 9 mz 5 sWNCZjWig 2 x 1 IZESAn 0 QvFg ](https://mirror.xyz/0x0bF07321af1bF1F77b3E96C63628192640A38206/cQl_kK3ETuLaAvo9Gn9mcuI04043GS9bCO7PVFLkTrkhttps://www.stackschina.com/stacks-ecosystem-maphttps://www.blocktempo.com/the-bitcoin-scalability-solution-stacks/https://mirror.xyz/arsenal-fc.eth/ ujrApyfn 40 YOBKAZ 9 mz 5 sWNCZjWig 2 x 1 IZESAn 0 QvFg )
https://gaia.blockstack.org/hub/1Eo6q4qLMcSSpkhoUADxRAGZhgUyjVEVcK/stacks-zh.pdf










