TL;DR
One of the core upgrades of Dencun is the introduction of a new data structure blob through EIP-4844 to store the transaction data submitted by L2 to Ethereum, thereby significantly reducing the transaction cost of Ethereum L2, increasing the transaction throughput of L2, and benefiting the L2 ecosystem.
The Dencun upgrade also introduces a new instant storage operation code through EIP-1153, which supports smart contracts to read and call temporarily stored data, thereby reducing Ethereum’s storage costs and Gas consumption, improving the scalability of the main network, and benefiting the main network. Internet ecological applications.
According to the Shadowfork test report released on December 19 and the 178th Ethereum Core Developer Executive Meeting held on January 4, the current Ethereum Dencun upgrade test is in good condition, and the Dencun upgrade of the mainnet is expected to be completed by the end of February.
The Dencun upgrade will promote the prosperity of the L2 ecosystem and drive demand for Infra tracks such as decentralized storage, DA and RaaS. For the application layer, tracks such as Perps, LSD, ReStaking and FOCG will also benefit from the Dencun upgrade.
Cancun upgrade
Cancun upgrade background
On December 28, 2023, Vitalik published the article Make Ethereum Cypherpunk Again to talk about what he believes is the encryption vision. Among them, Vitalik emphasized that one of the core reasons why blockchain is currently limited to asset speculation is the increase in transaction fees. High network transaction fees have turned people from blockchain network users to blockchain network speculators. In order to realize the application value of blockchain, the transaction fees of blockchain network must be reduced by another order of magnitude. Even though the emergence of L2 has reduced network fees compared to the Ethereum mainnet, this is not enough.
Similarly, the take-off of the Solana ecological network at the end of 2023 is also closely related to its extremely low network transaction fees. Compared with Ethereum L2s gas cost of $0.5, Solanas gas fee is as low as 0.0005 and is almost negligible. The extremely low network gas promotes the prosperous Meme hype, DeFi application interaction and DePIN application migration on Solana. In particular, cNFT on Solana can reduce the casting cost by 1,000 times compared to NFT on Ethereum, which has also brought about the prosperity of some DePIN projects and creator economy projects with NFT as the core of the economy. It can be seen that low network transaction fees have a significant role in promoting the prosperity of network transaction activities and ecological applications.
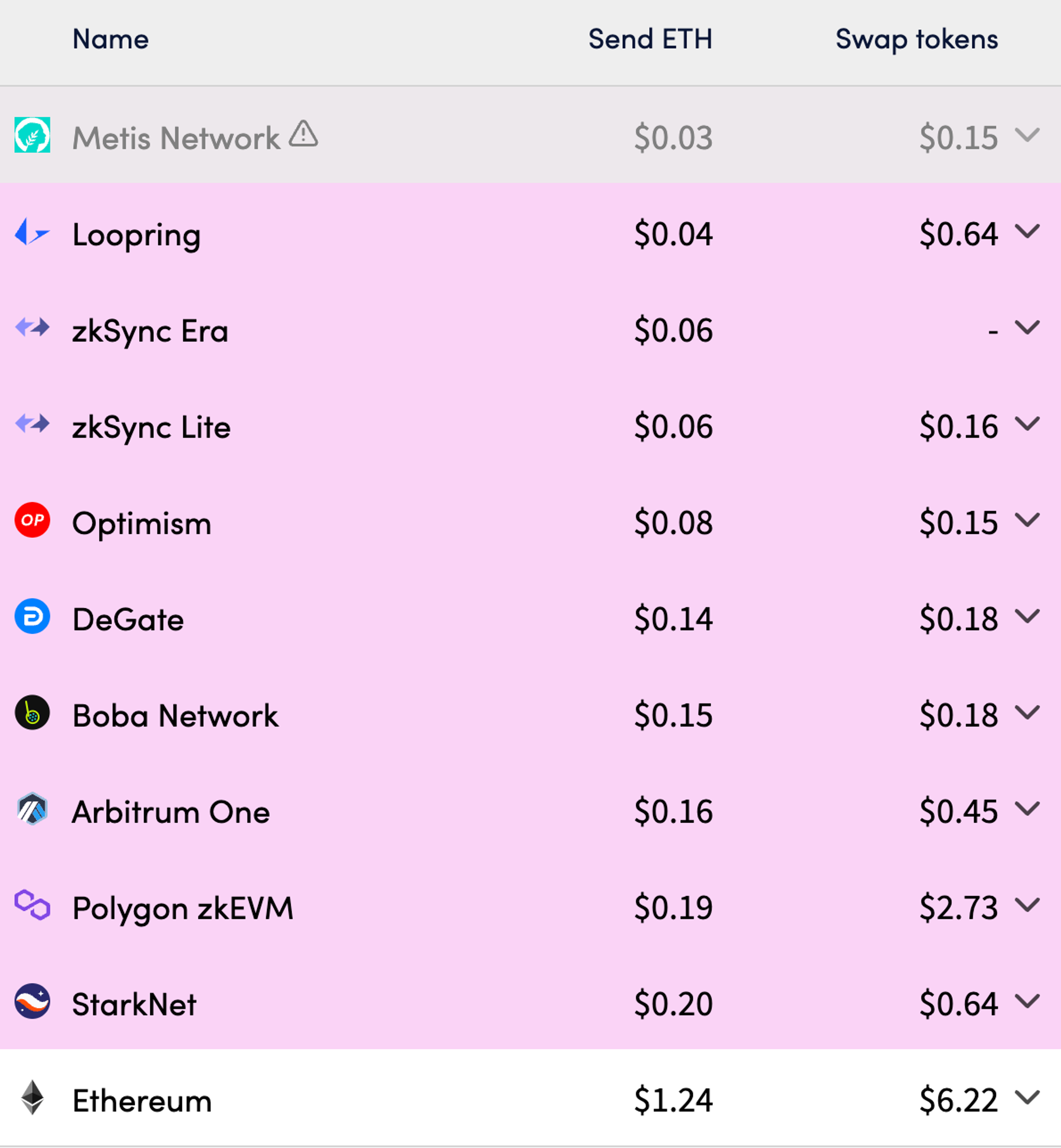
Ethereum L2 still has high gas fees
Of course, Ethereum has long been aware of this problem. In Ethereum’s upgrade roadmap, the next upgrade after the merger, “The Surge”, aims to improve Ethereum’s TPS and reduce the transaction fees of the Ethereum ecological network. Ethereum’s upcoming Dencun upgrade is part of “The Surge” and aims to further improve Ethereum’s transaction throughput and scalability through the introduction of Proto-Danksharding.
One of the core upgrades of Dencun is the introduction of the Proto-Danksharding module. Proto-Danksharding is also preparing for the final sharding expansion of Ethereum. The earliest expansion plan for Ethereum was to divide Ethereum into different shards and distribute the computing load of the main network to each shard. Each independent shard would store a subset of the transaction data that occurred on Ethereum. Process transactions in parallel, thereby increasing Ethereum’s TPS. The original ETH 2.0 plan eventually divided the main network into 64 shards to achieve 100,000+ TPS.
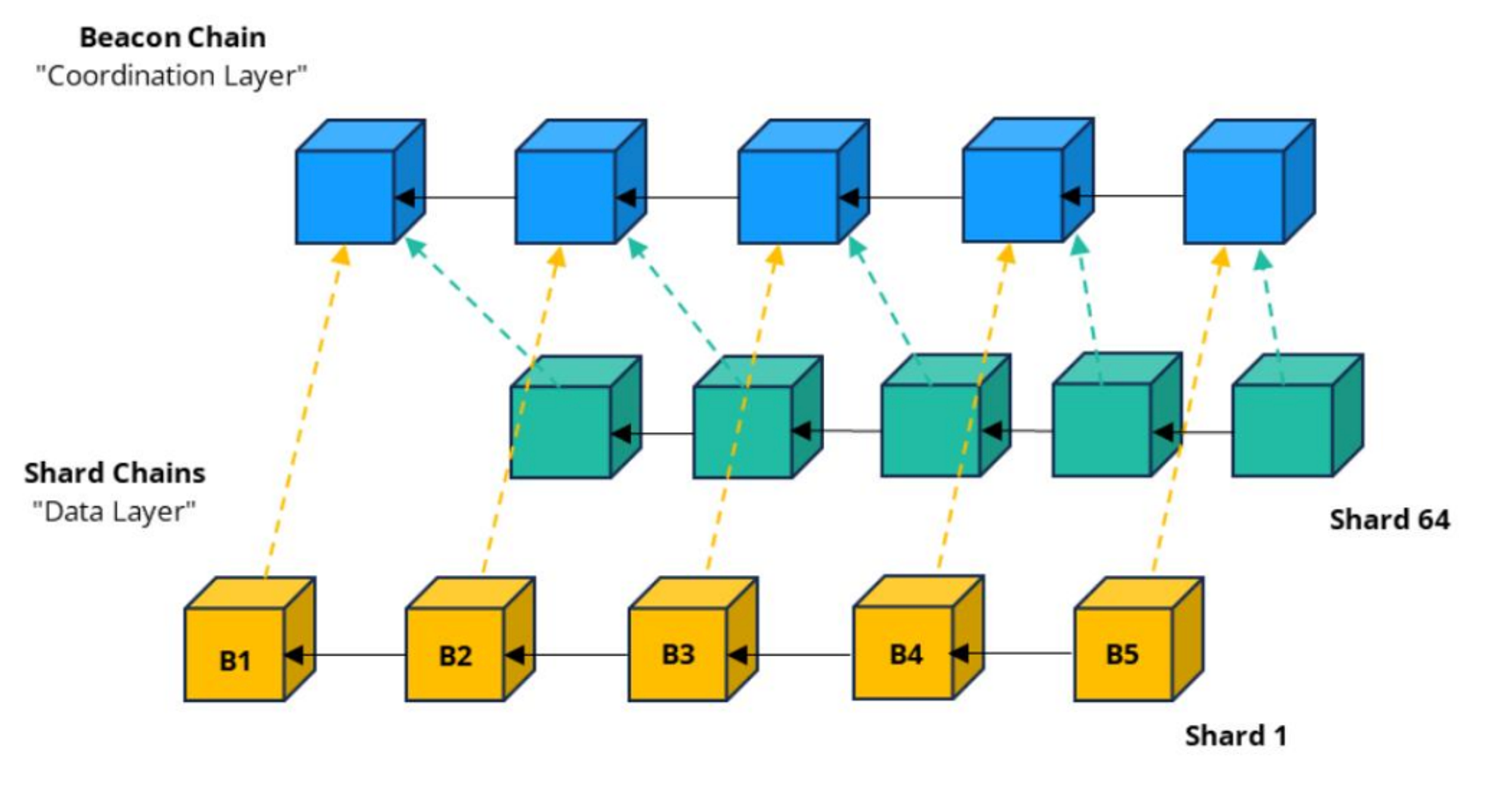
source:Crypto.com Research
However, the development complexity of shard expansion itself is high and the development progress is slow. In contrast, the Rollup expansion plan, which takes the transaction execution of Ethereum to the second-layer chain and relies on Ethereum for settlement, consensus and data availability, has developed at an extremely fast speed and has achieved In order to achieve lower transaction costs and higher throughput, it has met some of the expansion needs of Ethereum to a certain extent. This has caused Ethereum to gradually abandon the expansion path with sharding as the core and instead adopt data sharding for Rollup.
Compared with the traditional sharding chain sharding expansion method, Dankshardings expansion implementation path is relatively simpler. One of the core contents of the upcoming Dencun upgrade is the introduction of Proto-Danksharding, which is the first to introduce blobs into the block space, optimize data availability costs through blobs, and improve the scalability of L2. The Proto-Danksharding introduced by Dencun will also become the first step in the comprehensive expansion of Ethereum, laying the foundation for the subsequent realization of complete Danksharing, the introduction of separation of block proposers and builders, and the realization of data availability sampling.
Cancun upgraded kernel
Proto-Danksharding
Proto-Danksharding, also known as EIP-4844, is the most critical module in Dencun upgrade. Proto-Danksharding is named after the two researchers who proposed the expansion idea: Proto Lambda and Dankrad Feist. Take part of their respective names as the naming of the upgrade content. Proto-Danksharding reduces L2 costs and optimizes L2 performance by introducing a new data storage structure, blob.
Transaction type carrying blob:
Previously, all transactions in Ethereum L2 were stored in the Calldata of L1. The space size of Calldata itself is relatively limited, and all data on Calldata will be processed by Ethereum nodes and permanently stored on the chain, which results in high data availability costs. Theoretically, L2 transaction data does not need to be permanently stored on the expensive Ethereum L1. It only needs to be stored for a certain period of time to meet verification requirements such as fraud proof. In other words, Ethereum L2 transaction data lacked suitable storage space in the past. From the data point of view, 80% of L2s transaction costs and Gas fees come from the expensive data storage costs in Calldata.
Proto-Danksharing will introduce a new data storage structure in the Ethereum block: blob. The blob will be used exclusively to store transaction data submitted by L2 to L1.
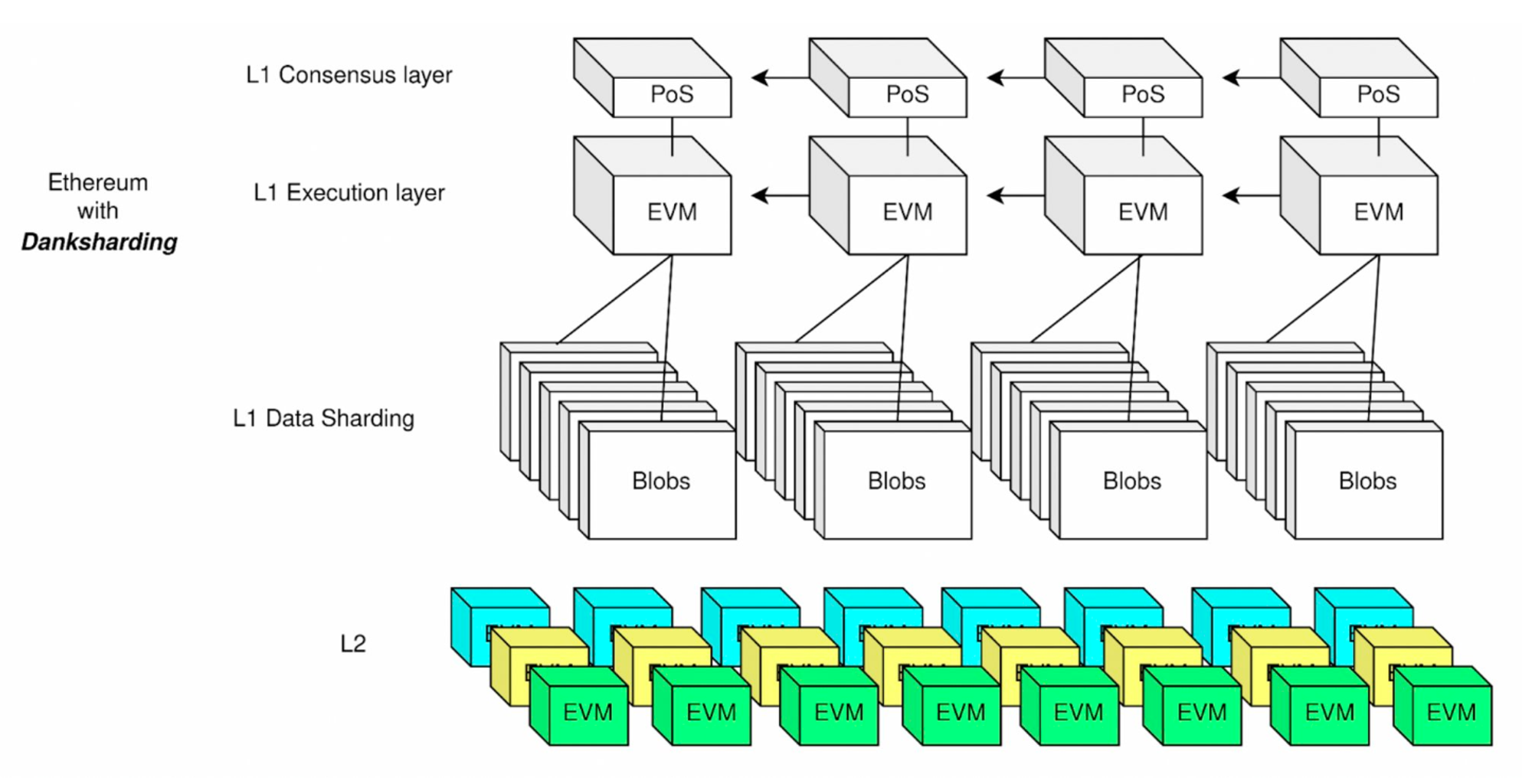 Each blob introduced by Proto-Danksharing is 128 KB in size. Each Ethereum block is planned to contain 3-6 blobs (0.375 MB - 0.75 MB), and will be gradually expanded to 64 in the future.
Each blob introduced by Proto-Danksharing is 128 KB in size. Each Ethereum block is planned to contain 3-6 blobs (0.375 MB - 0.75 MB), and will be gradually expanded to 64 in the future.

In comparison, the current data size that each Ethereum block can accommodate is less than 200 KB. After the introduction of blobs, the amount of data that Ethereum blocks can accommodate will be significantly increased.
After the introduction of blob, the transaction data submitted by L2 will no longer need to compete for the storage space of Calldata, but will be directly submitted to the blob for storage. Moreover, the blob data will be automatically deleted after about a month, further reducing unnecessary storage burden. The introduction of blob means that L2s transaction fees will be greatly reduced (~90% reduction), and since blob is equivalent to additionally expanding the block space for L2, the transaction throughput that L2 can submit simultaneously will also be significantly improved. If Dencun successfully achieves the average target of 3 blobs per block after the upgrade, L2 throughput will be increased by nearly 2 times. If the goal of adding 64 blobs to a block is finally achieved, the throughput of L2 will be increased by nearly 40 times.
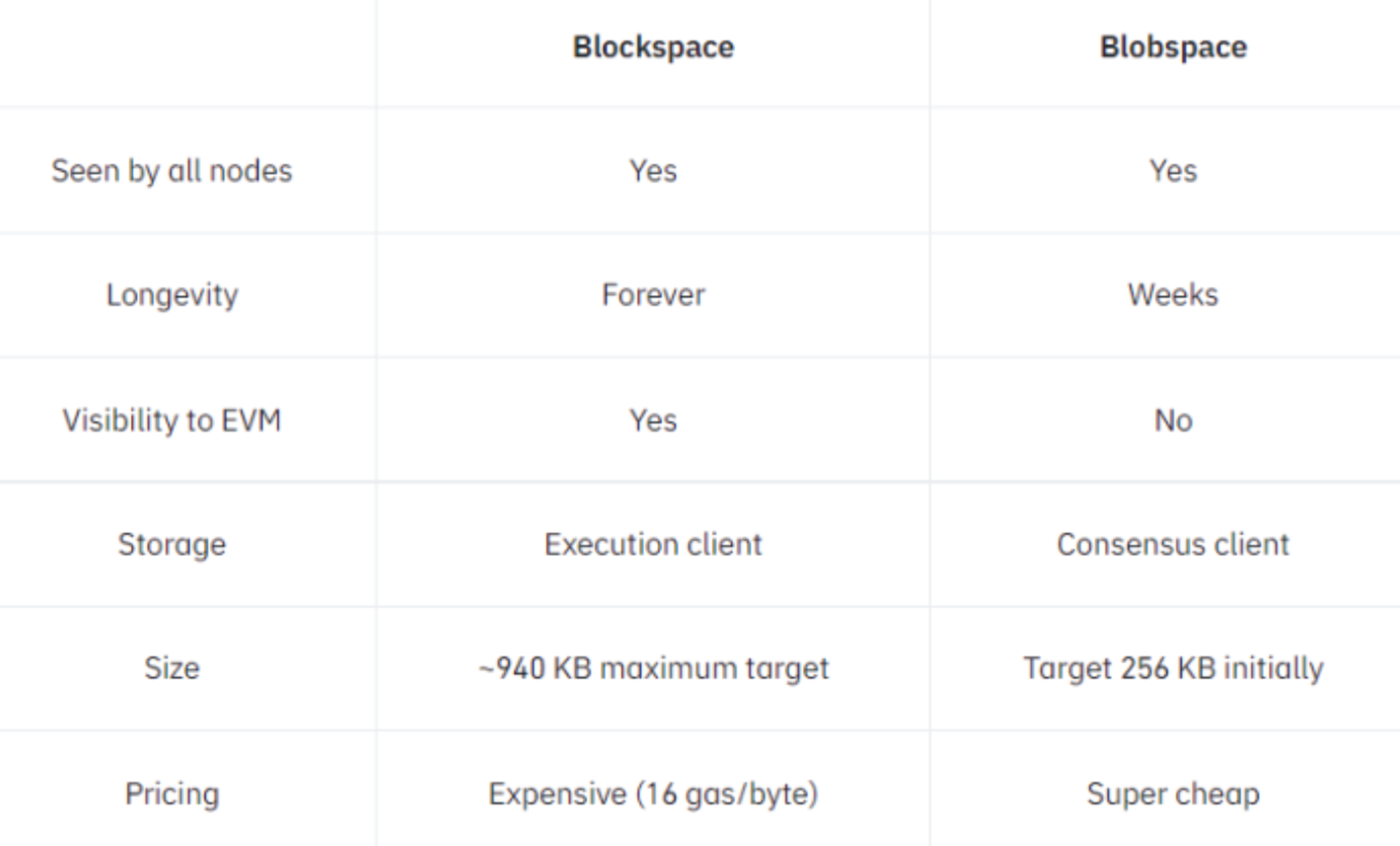
In addition, blob also has an independent fee market. Proto-Danksharing also introduces a new type of Gas called blob Gas. The Blob Gas fee mechanism in EIP-4844 is rooted in the previously introduced EIP-1559 mechanism, in which blob storage space will be auctioned according to its own fee market. This means that the blob fee market is completely independent of the demand for block space, thereby improving the flexibility and efficiency of network resource allocation. The cost of data storage in blob is approximately one data-gas per byte, while Calldata is priced at 16 data-gas per byte. In comparison, the data storage cost of Blob is significantly lower than that of Calldata.
After the introduction of blobs, the operating processes of the L1 and L2 block networks will also change. First, L2 needs to publish its commitment to transaction data on-chain. L2 then needs to submit the actual transaction data into the blob. At the same time, nodes can check whether the commitment is valid and verify the data. Consensus layer nodes prove that they have seen the data and that the data has been propagated on the network. After a month or so, the node will delete the data in the blob, and this part of the data can be stored in other DAs.
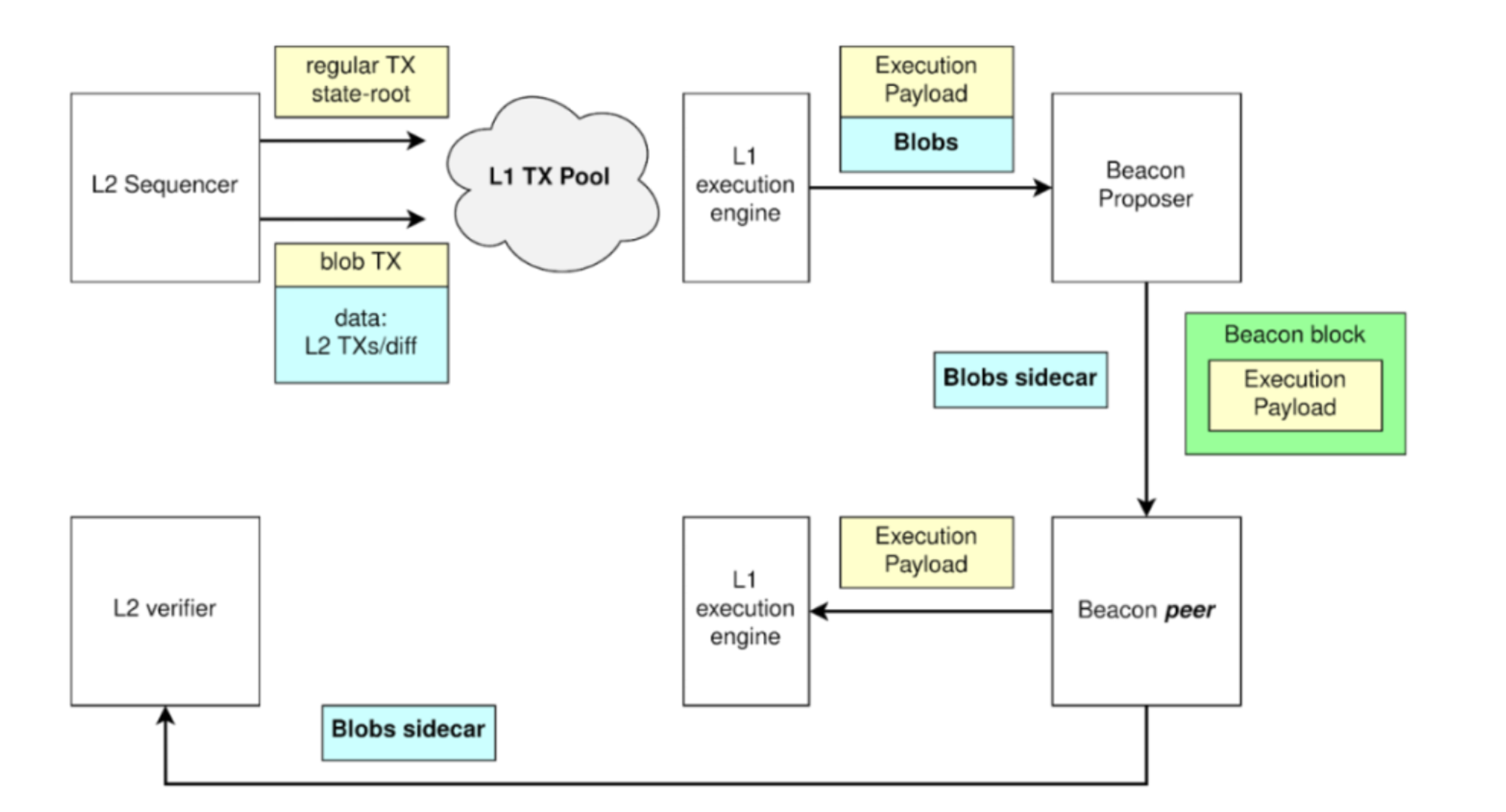
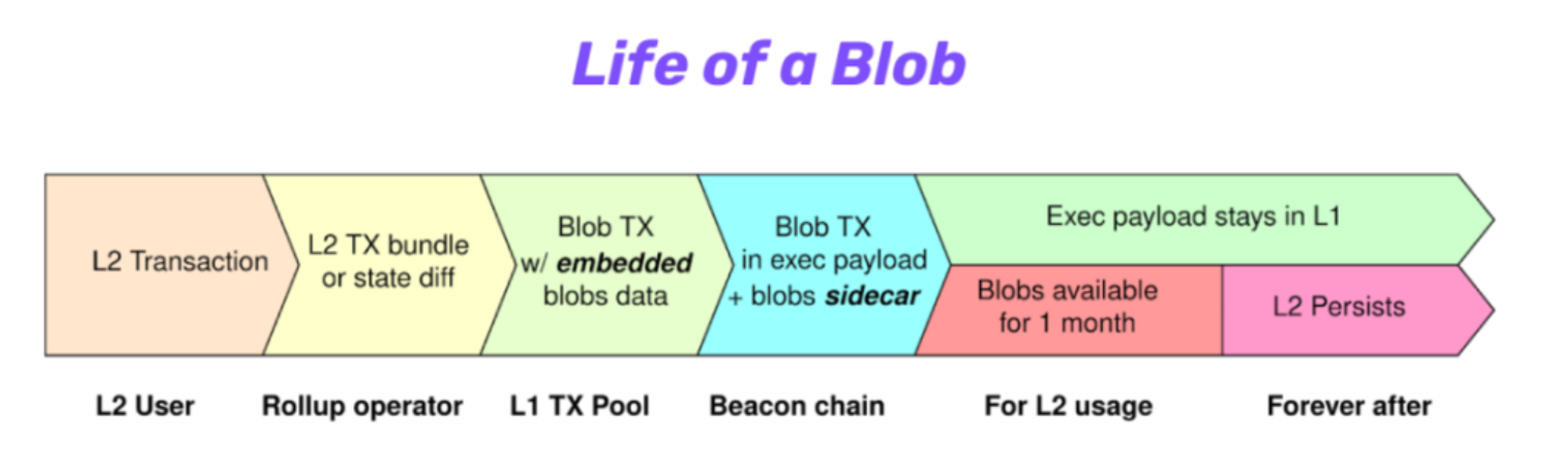
source:OP in Paris: OP Lab's Protolambda walks us through EIP-4844
KZG Commitment
EIP-4844 also introduces the KZG (Kate-Zaverucha-Goldberg) commitment scheme as part of the blob verification and attestation generation process. KZG commitment is a polynomial commitment scheme that enables submitters to use a short string to commit to polynomials, and supports verifiers to use short strings to confirm stated commitments. Simply put, KZG can simplify the verification of large amounts of data into the verification of small cryptographic commitments.
Blocks of data can be represented as polynomials and then used with a polynomial commit scheme to commit the data. Leveraging a polynomial commitment scheme to generate commitments on data allows you to efficiently verify specific properties of a data blob without having to read its contents in its entirety. The realization of the KZG promise also paves the way for the implementation of Data Availability Sampling (DAS) in Danksharding. With DAS, validators can verify the accuracy and availability of data blobs without downloading the entire blob, improving efficiency and scalability.
Other EIP upgrades:
In addition to EIP-4844, the Dencun upgrade also includes the following four key EIP improvement proposals.
EIP-1153: EIP-1153 introduces a new storage state: transient storage. Previously, all storage on Ethereum was permanent storage. Permanently stored data would not only occupy block space, but also consume Gas fees. However, for some unnecessary data, such as data that is only valid during the course of a transaction, permanent storage is unnecessary and a waste of resources. Therefore, EIP-1153 introduces the transient storage operation code to support smart contracts to read and call temporarily stored data. Once the complete transaction execution cycle is completed, the storage of this part of the data will be cleared to reduce Ethereums storage cost and gas consumption.
EIP-4788: EIP-4788 will introduce the beacon block root into every EVM block. Previously, the two core parts of Ethereum, the EVM and the beacon chain, operated independently and could not communicate directly. That is, the EVM could not directly access the data and status of the beacon chain, and could only capture the beacon chain through an external trusted oracle. state. EIP-4788 is essentially similar to the introduction of a protocol-level oracle that relays the consensus state of Ethereum to the Ethereum mainnet. EIP-4788 will introduce a new field parent_beacon_block_root in the execution block header, from which the EVM can directly export the status of the Ethereum consensus layer to obtain consensus layer data. The parent beacon block root will be stored in a ring buffer and will only be retained by the mainnet for approximately 1 day. Once a new parent beacon block root is added to the buffer and the buffer capacity reaches a critical value, the oldest parent beacon block root will be overwritten, thereby achieving efficient and limited consensus storage. The introduction of EIP-4788 allows the Ethereum mainnet to obtain data from the Ethereum consensus layer in a trust-minimized manner, eliminating dependence on external oracles, thereby reducing potential security risks, oracle failures and malicious manipulation risks.
EIP-5656: EIP-5656 introduces a new EVM opcode called MCOPY. The MCOPY instruction is designed to optimize the process of copying data in memory during smart contract execution. Previously, if developers needed to copy memory data, they needed to reference the two opcodes MSTORE and MLOAD. MCOPY is essentially a combination of these two opcodes, filling the previous operational gap in the field of memory copying in the EVM. The MCOPY opcode can significantly reduce the cost of copying 256 bytes of memory data from the previous 96 Gas to 27 Gas. The introduction of MCOPY will make the operation process of copying memory data faster, lower cost, and more efficient. Based on this, developers can further optimize smart contracts involving memory operations.
EIP-6780: EIP-6780 will restrict SELFDESTRUCT opcode functionality. By limiting self-destruction, Ethereum can better manage its state size, resulting in a more stable and predictable blockchain. This is critical for the long-term scalability and maintenance of the network as it will simplify future Ethereum upgrades.
Cancun upgrade status
12.19 Shadowfork test report
According to the test report of Shadowfork, which was launched on the 19th, the current Ethereum Cancun upgrade test is going well. The Ethereum Foundation will continue to fork Shadowfork in the next two weeks for intensive testing. Goerli, Sepolia, and Holsky nodes will also be tested at three time points: 1.7, 1.30, and 2.7. If the testnet runs well, the Cancun upgrade to the mainnet is expected to be completed within February.
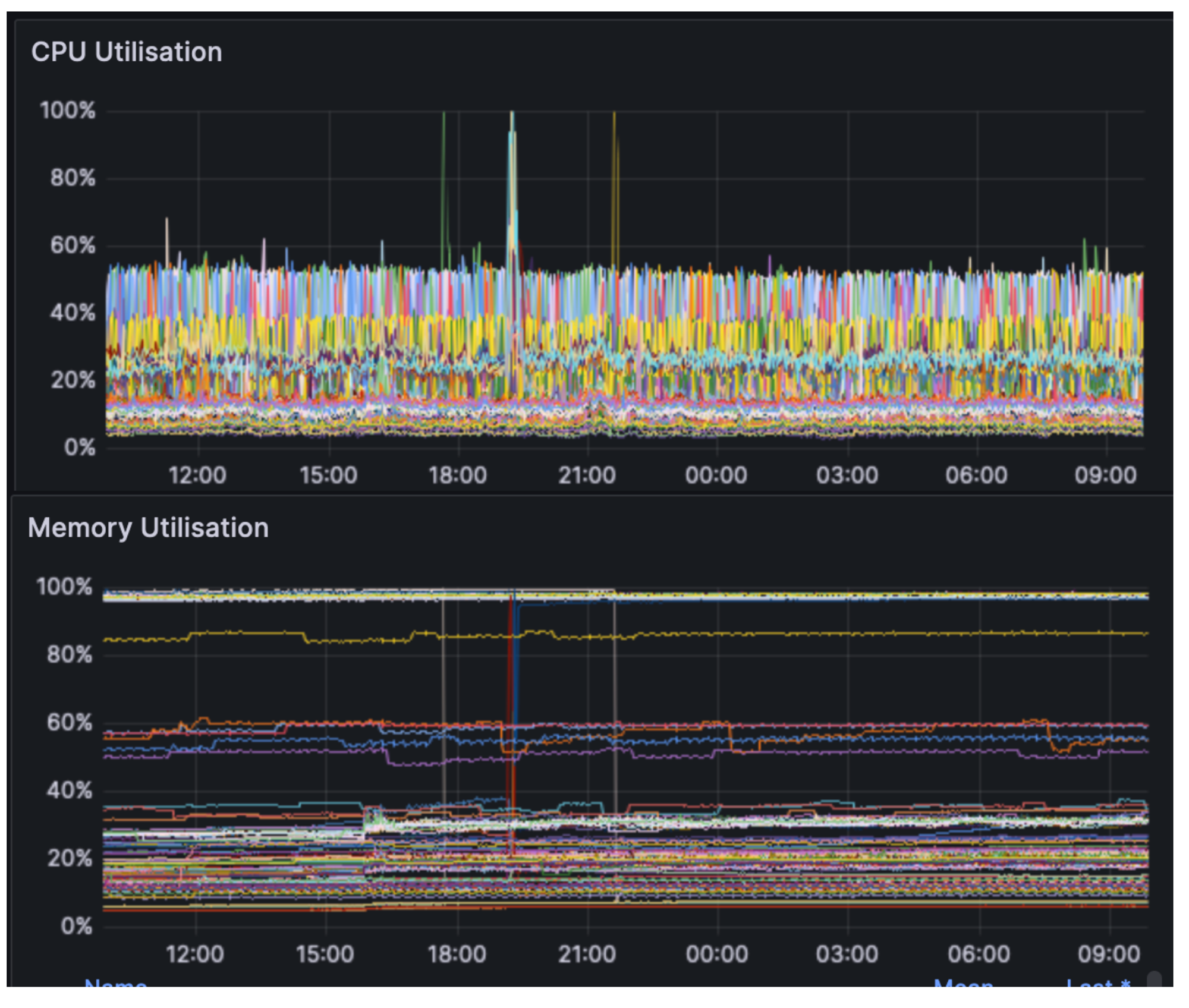
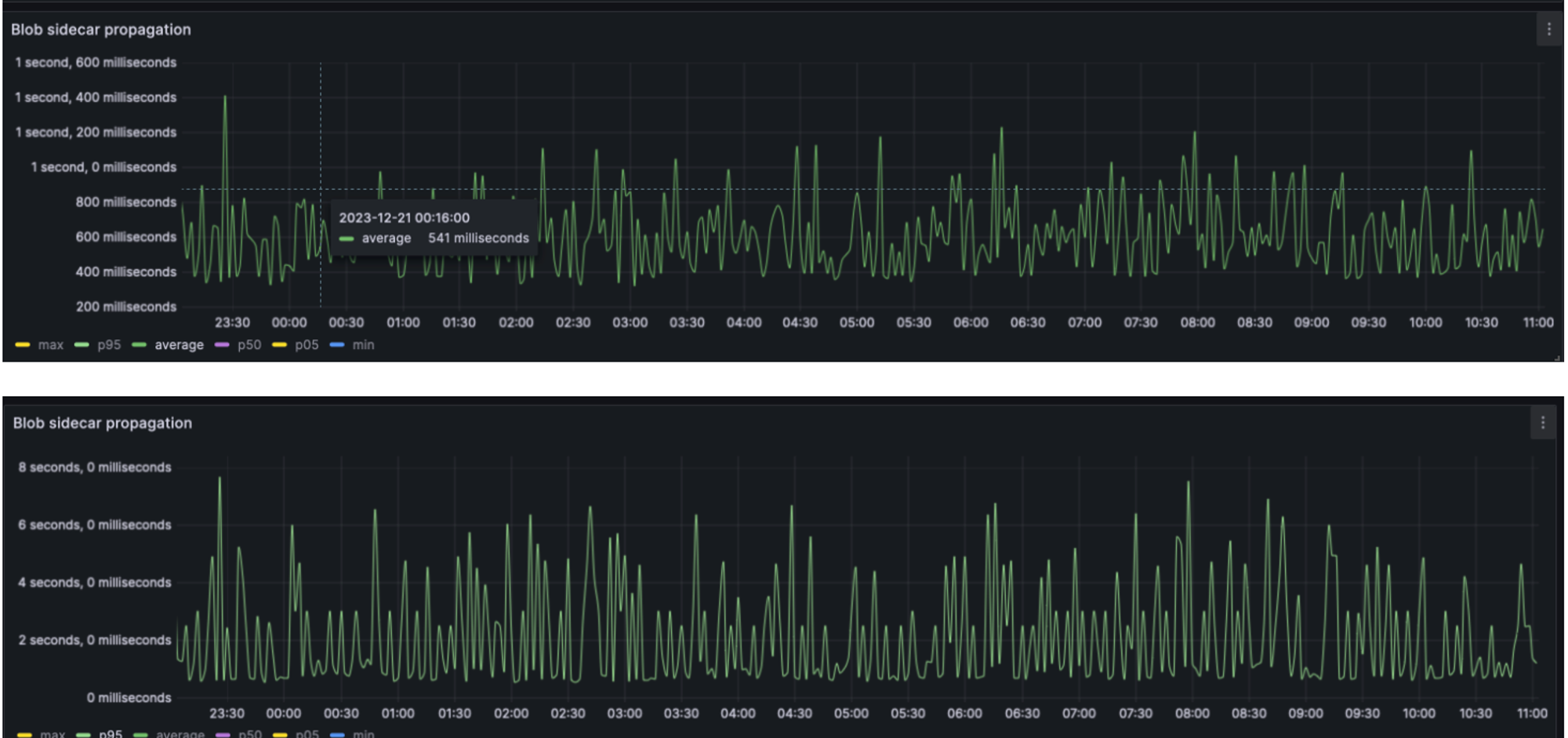
Judging from the Shadowfork test report, the node resource usage, overall network usage, network health, blob distribution and propagation during the test were as expected.
From the perspective of CPU and RAM usage, resource usage did not fluctuate significantly before and after the Cancun test fork, and remained stable overall.
From the perspective of network usage, compared with the Shadowfork baseline, network usage increased significantly after the Cancun test as expected. Under good blob usage conditions, network usage is expected to increase by approximately 200 kbps.
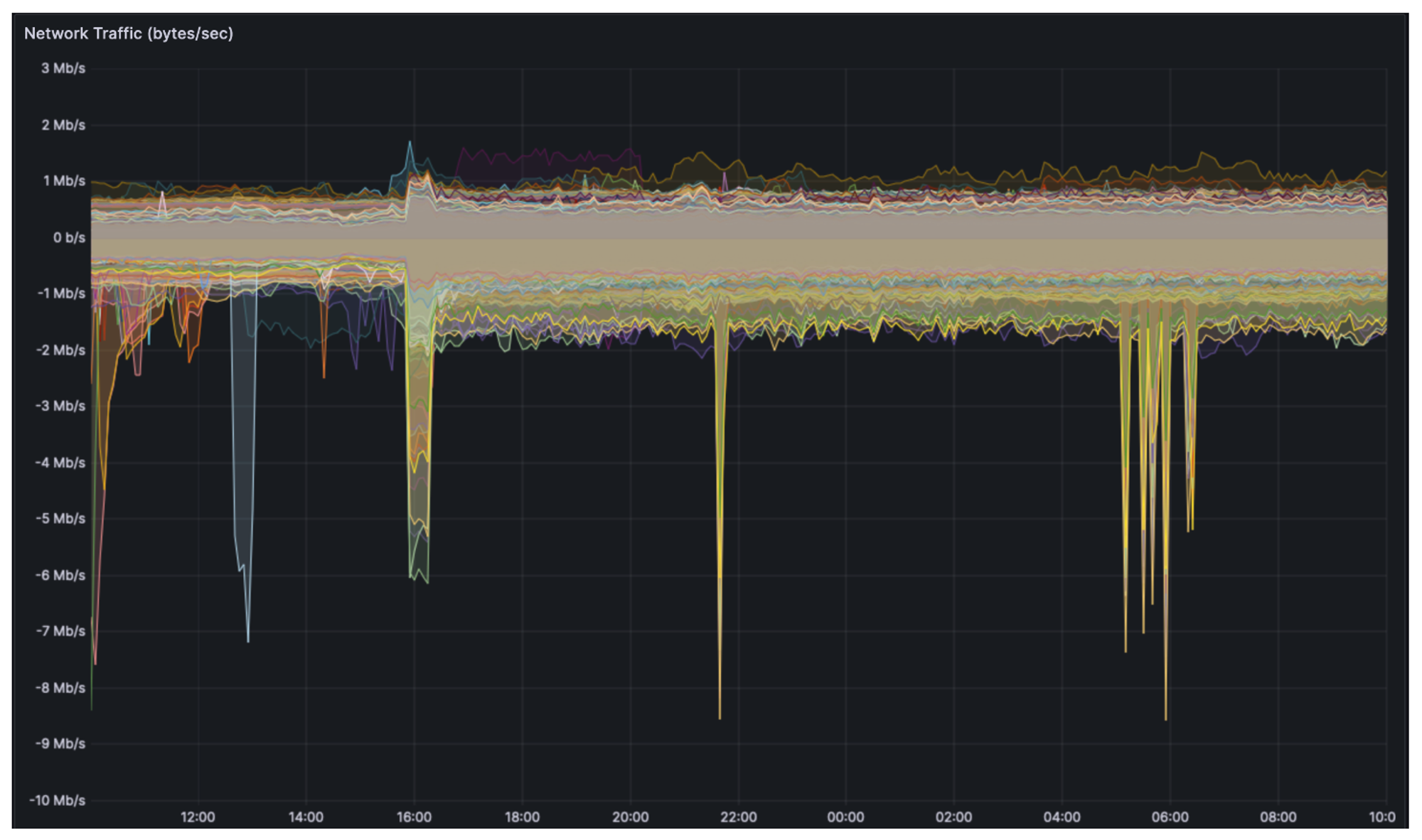
During the test, the overall network remained stable, there was no client downtime, and the clients ran smoothly.
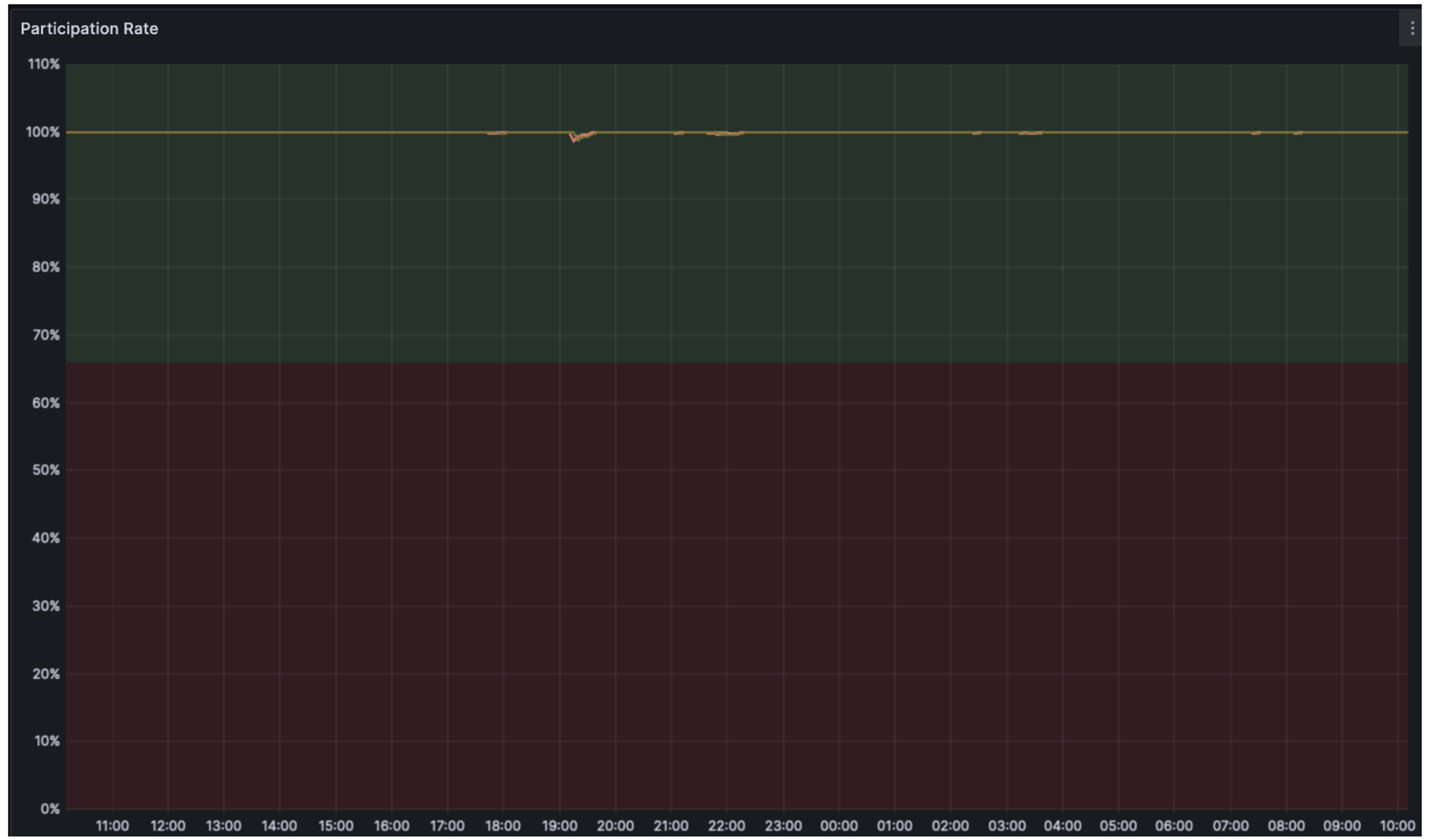
During the test period, most chunks contained 3 blobs, consistent with the target number of blobs.
The blob propagates to 95% of the nodes in less than 2 seconds, and on average, most blobs propagate through the entire network in less than 500 milliseconds. Ideally, block propagation time is expected to increase by about 250 milliseconds.
1.4 Conference call
On the evening of January 4, the 178th Ethereum Core Developer Executive Meeting was held online. This meeting finalized the upgrade schedule of the test network Dencun. The developers unanimously agreed to conduct Goerli, Sepolia and Holesky test network upgrade tests on January 17, January 30 and February 7 respectively.
At the same time, in order to quickly respond and solve possible problems during the test network upgrade process, the developers decided to quickly hold the 179th meeting on January 17, the day after the completion of the Goerli test network test, to discuss the test content, depending on the situation Decide whether the testnet upgrade test schedule needs to be updated.
Although developers have not reached a final consensus on the upgrade time of the main network, judging from the current Shadowfork test data, test network test arrangements and time progress, the Dencun upgrade of the Ethereum main network will most likely be carried out by the end of February.
Potential opportunities and favorable tracks
L2
One of the most direct benefits of Dencuns upgrade is the L2 track. The introduction of blobs has significantly reduced L2 transaction fees and improved throughput to a certain extent. Dencuns excitement for L2 is that it can further compete with other Alt L1s and attract high-quality projects and users from other L1 ecosystems with lower expenses and better performance.
The Dencun upgrade is a good thing for all L2 based on Ethereum, but under the universal benefit, we will focus on observing which L2 projects have more unique competitive advantages and can reap more dividends brought by the Dencun upgrade. .
L2 Ecology
Arbitrum
The current leaders of Ethereum L2 are still Arbitrum and Optimism, but their competitive advantages and segmented competition directions are slightly different. Arbitrum is even more advanced in the diversity of protocols based on Arbitrum One, and Optimism is even more advanced in the inter-chain ecological diversity based on OP Stack.
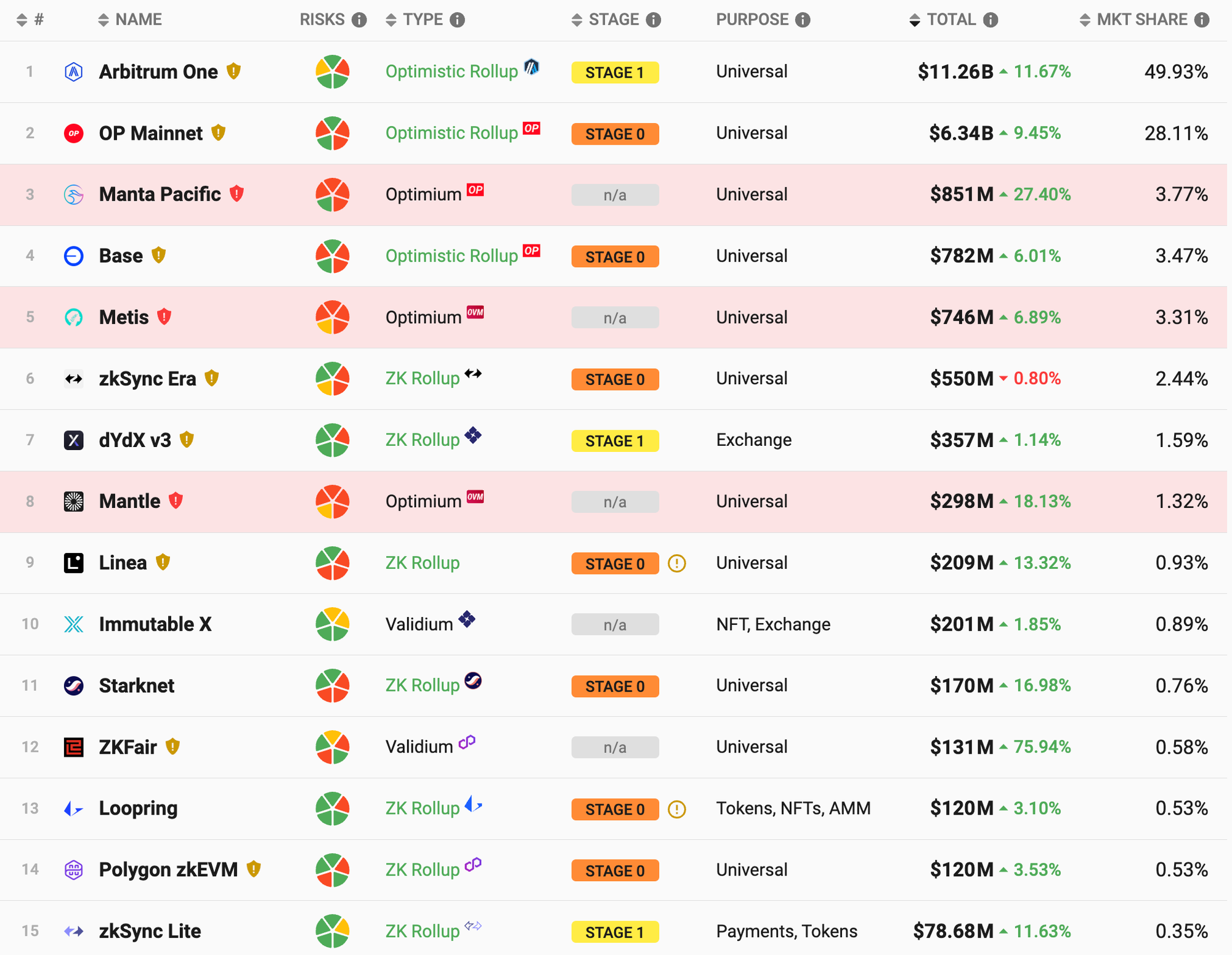
Arbitrum is still the L2 with the richest variety of all protocols. According to incomplete statistics from DeFiLlama, the number of protocols on Arbitrum is approximately 520, far exceeding the second-ranked Optimism’s 216. According to L2b eat data, Arbitrums current TVL is about 11.26 B, accounting for nearly half of the TVL of Ethereum Rollup.
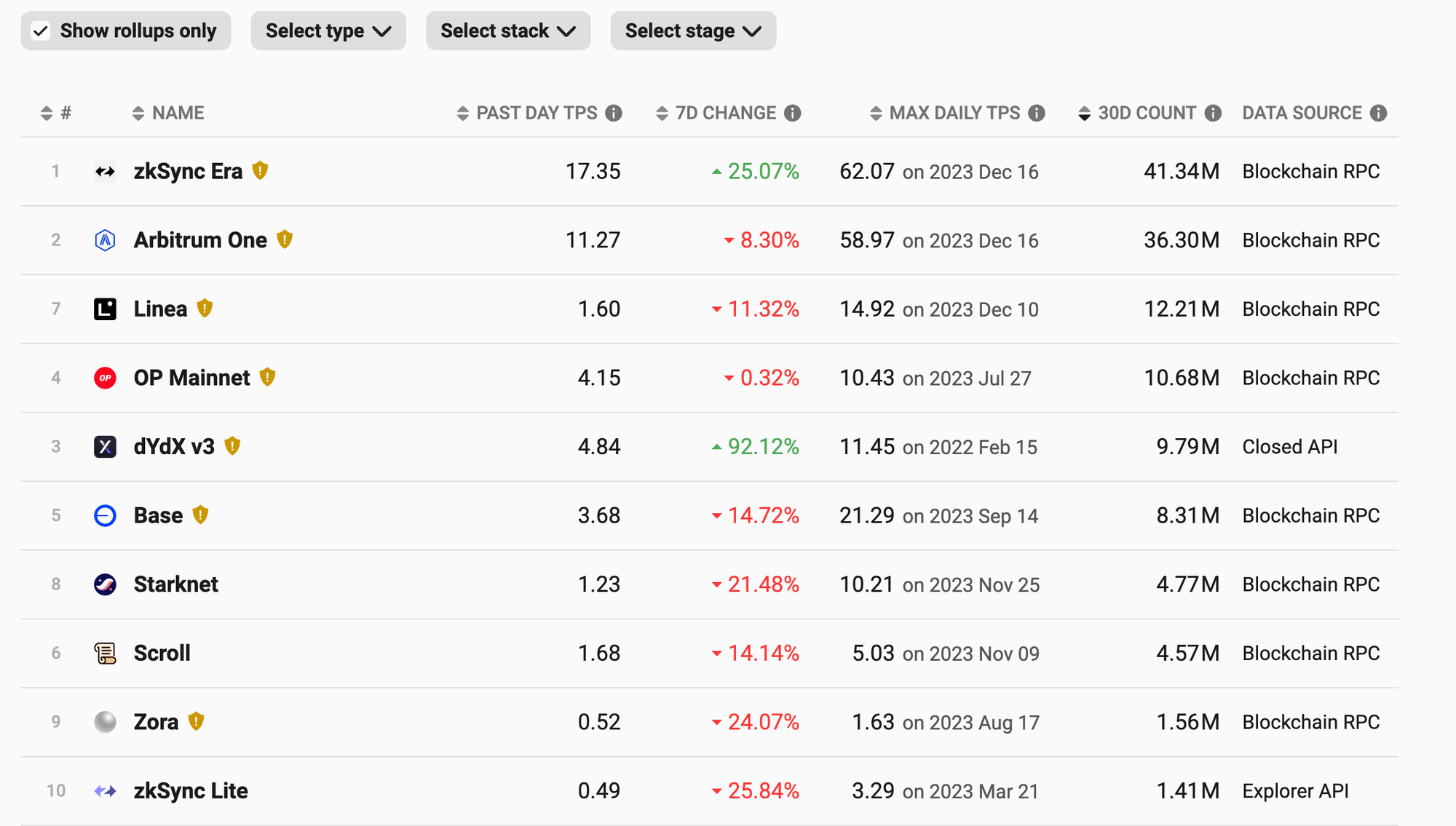
Additionally, online trading activity is booming on Arbitrum. Judging from the ranking of network transaction volume in the past 30 days, Arbitrum has a transaction volume of approximately 36 M, ranking second only to zkSync, which has not yet issued coins but still has a lot of hair-raising activities. If we exclude L2, which has airdrop interactions, and only compare Arbitrum and Optimism, which have issued coins, Arbitrum is also far ahead with a network transaction volume that is 3 times that of Optimism.
Taken together, Arbitrum, which has the highest network transaction volume, can obviously reap more dividends from reduced transaction fees. The optimization of TPS is also conducive to the prosperity of protocol ecology with higher performance requirements such as GMX and GNS on Arbitrum. From the perspective of network fundamentals, Arbitrum is undoubtedly one of the biggest beneficiaries of the Dencun upgrade. In addition, Arbitrum is also actively promoting the Arbitrum Orbit and Stylus languages, supporting developers to use Orbit to build Rollup based on EVM and WASM VM at the same time, creating a network effect based on Arbitrum.
Optimism
Different from Arbitrum, Optimisms competition focuses more on the Optimism SuperChain network based on OP Stack, and the value of Optimism depends more on the network value of Optimism SuperChain.
Since the release of OP Stack, a large number of projects such as Base, Lyra, opBNB, Redstone, Zora, Mode, Debank, etc. have built their own L2 based on OP Stack. The upgrade of the OP Stack Bedrock version also further optimizes transaction costs, transaction processing within blocks, node performance, etc., making it more attractive to build L2 based on OP Stack. According to the plan of Optimism SuperChain, all Rollups using OP Stack will be integrated into a standardized OP chain. These chains can communicate directly via the cross-chain messaging protocol, sharing a common Ethereum cross-chain bridge and sequencer network.
If the Dencun upgrade can benefit all L2s at the same time, then the upgrade premium enjoyed by Optimism is the combination of network value brought by all Optimism ecological chains. If the Dencun upgrade can spawn more new L2s, then the upgrade premium enjoyed by Optimism is that more L2 chains may be built using OP Stack, and Optimism will get closer and closer to the ultimate vision of the Optimism SuperChain super ecology. .
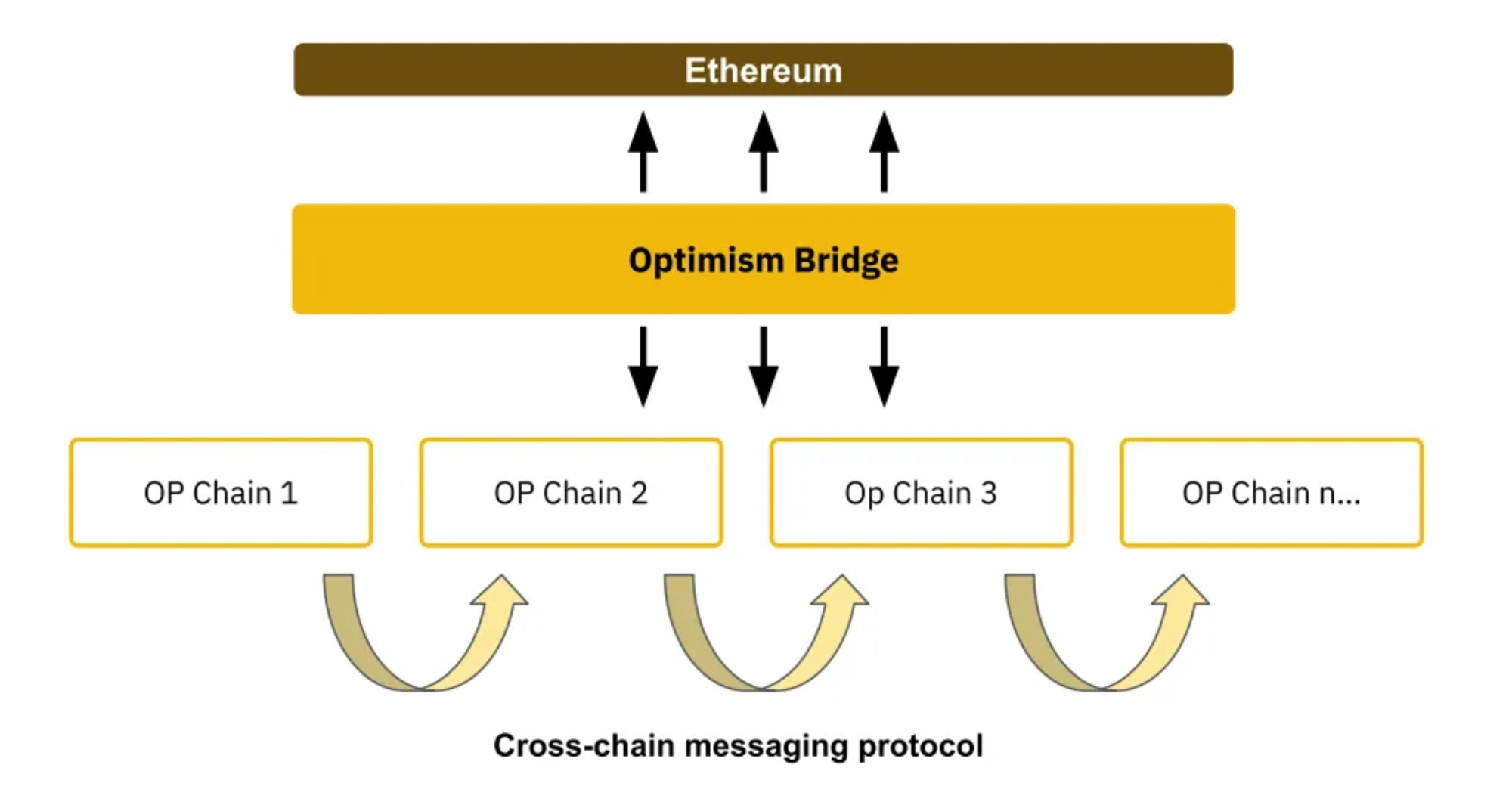
Sequencer decentralization
Metis
The competition between Arbitrum and Optimism is more about protocols, network activity, ecological value and other aspects. However, another major problem that needs to be solved is the decentralization of L2 Sequencer, which has become the elephant in the room. As the Dencun upgrade brings more L2 explosions, problems such as single points of failure, malicious arbitrage, grabbing MEV value, and censorship of user transaction space caused by centralized sorters may become increasingly serious.
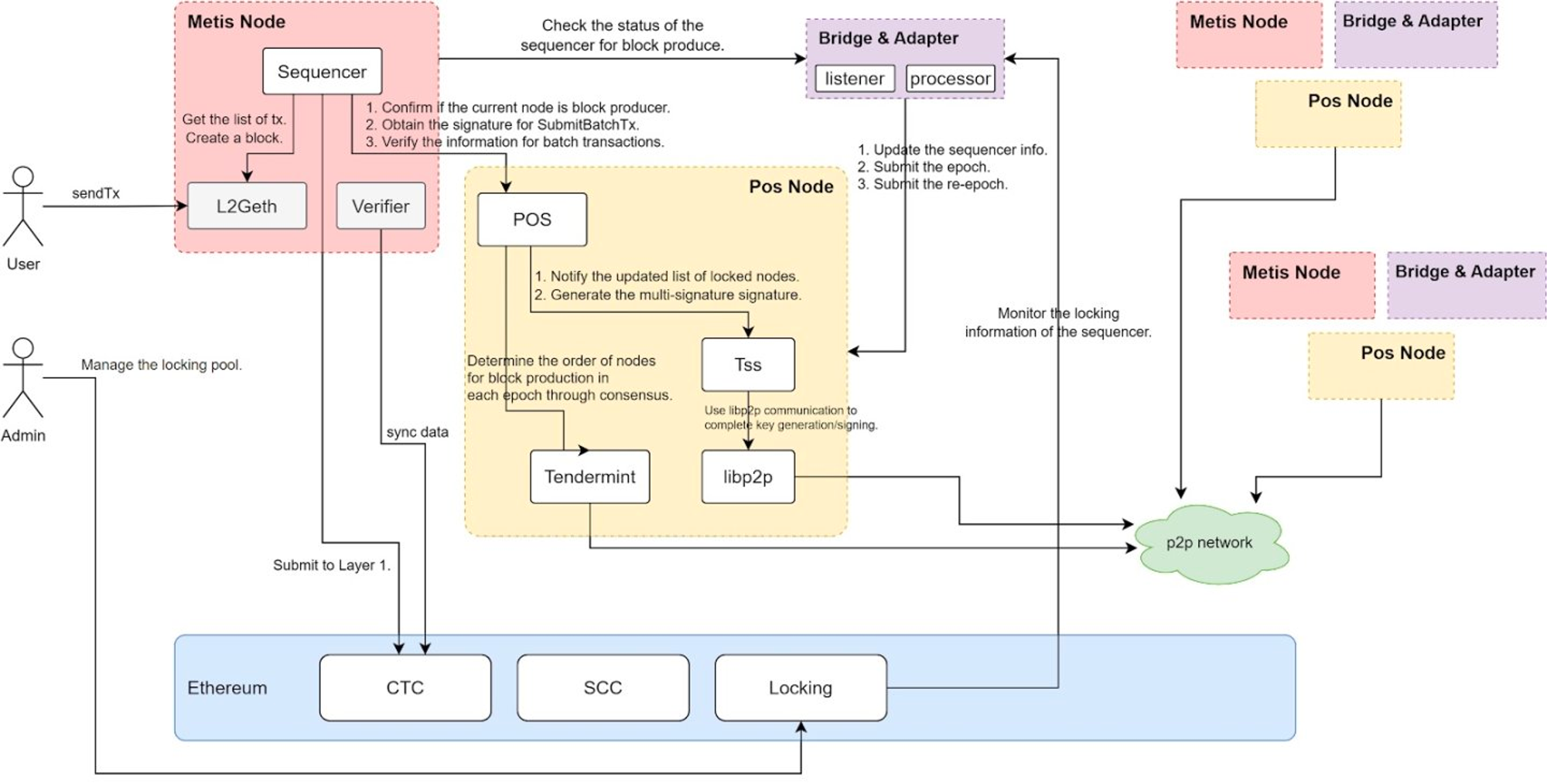
Metis has taken the lead in making changes in this regard and may become the first Ethereum L2 to run a decentralized PoS sequencer.
Metis breaks the pattern of sorter centralization and supports nodes that pledge at least 20,000 METIS tokens to enter the sorter pool and become sorter operators. The sequencers entering the sequencer pool will be responsible for determining the packaging order of transactions, and at least 2/3 of the sequencer signatures are required to package and upload the data to the L1 main network. In addition, in order to further prevent the sequencer from doing evil, Metis has also introduced the role of a validator to conduct sample surveys on blocks to ensure that the sequencer sorts the transaction order correctly.
Metis chose to actively give up profits and actively gave away the most profitable sorter income to the pledge nodes. With the emergence of more pledge protocols for sorters in the future, we can also foresee that a wider range of users will be able to participate in sorter pledges and share the sorter profits. Metis innovation in sorter decentralization and empowerment of METIS tokens have increased the price of METIS tokens, the pledge rate of METIS tokens, and the inflow of funds into the Metis network. With the prosperity of the METIS network ecology and the growth of sorter income, more and more METIS will be pledged to the sorter nodes, and there will be less and less METIS in circulation. The demand for METIS in the market will instead increase. The more, it will promote Metis and METIS tokens to move towards a positive cycle of rising TVL, ecology and currency prices.
The competition for decentralized sequencers may become the core theme of Dencun’s L2 competition after its upgrade.
Token empowerment
Another core factor that determines the price of L2 tokens is L2’s token empowerment. Currently, almost all Ethereum L2 uses ETH as the Gas token, and its own L2 token has no other use except governance. Without a stable value consumption scenario, the tokens in the hands of users will become discardable pieces at any time. Tokens with actual empowerment, such as METIS, are more likely to move towards a positive spiral in which L2 fundamentals and currency prices rise simultaneously.
In addition to the previously mentioned METIS tokens that can be used as pledge tokens for decentralized sorters and share sorter income, another case worth learning from is ZKF. ZkFairs token ZKF can not only be used as a Gas token, but can also be pledged to share the Gas income of the ZkFair network. Similar to METIS, token empowerment with pledged dividends is also more likely to promote a spiral increase in the ZKF market price. In addition, Arbitrum Orbit has also added the function of supporting custom Gas tokens.
As mentioned earlier, all Rollups sharing the OP Stack will share a common sequencer network. Imagine how much market demand and buying power this will bring to OP if Optimism also learns from Metis and introduces a module that pledges OP to become the OP Stack decentralized sorter. The rise in currency prices will in turn attract more funds and users for applications within the ecosystem, feeding back the prosperity of the ecosystem. Ethereum L2’s measures in terms of token empowerment after the bumpy upgrade are also one of the core issues that need to be focused on.
other
As mentioned above, the reduction in transaction fees and the increase in L2 TPS brought about by the Dencun upgrade will benefit every Ethereum L2. In addition to the projects we discussed in the previous article, there are some other projects whose performance is also worth looking forward to.
Base can be regarded as one of the best-performing L2s in 2023. The strong binding relationship with Coinbase allows Base to accept a large number of users and funds from Coinbase, and it has become the Ethereum L2 that ranks third in TVL today. The rise of Base is inseparable from the hype of popular projects such as Friend.tech and FrenPet on Base. One of the major characteristics of the above-mentioned projects is that the frequency of interaction is high and the income from a single interaction is low. Moreover, the number of users undertaken is relatively large, and the application has higher performance requirements. The benefits brought by the Dencun upgrade coincide with the needs and characteristics of this type of project. We may see more pan-social and gaming light applications appear on Base, bringing more users and funds into the Base ecosystem and stimulating the ecological vitality of Base.
In addition, there are more L2s such as Mantle and Blast that have not yet been issued coins and are still accumulating power. This type of L2 attracts users to participate in ecological interactions through currency issuance expectations and superimposed revenue marketing. Dencun upgrade can greatly reduce the cost of user interaction and further promote the prosperity of such L2 chain activities. However, it is worth noting that we still don’t know where this type of L2 will go after the airdrop. At this stage, we can only remain cautiously optimistic about this type of project.
data availability layer
One of the core modules of Dencun upgrade is the introduction of blob storage data submitted by L2 to L1. However, blob data storage is not permanent, and the stored data will be discarded after about a month or so. However, this part of the data still has the potential value of being called and analyzed. Therefore, the storage of this part of data will also drive the demand for decentralized storage business.
ETHStorage
EthStorage is the first layer-2 solution to provide programmable dynamic storage based on the availability of Ethereum data. It can expand programmable storage to hundreds of TB or even at a cost of 1/100 times to 1/1000 times. Petabyte level.
ETHStorage is highly integrated with ETH. The client of EthStorage is a superset of the Ethereum client Geth. This means that when running an EthStorage node, you can still participate in any process of Ethereum normally. A node can be an Ethereum validator node. It is also the data node of EthStorage.
Moreover, ETHStorage has stronger interoperability with EVM and can achieve perfect compatibility with EVM. Taking the Mint NFT image as an example, converting the Mint image stored on Arweave into an NFT image on Ethereum requires three smart contract operations, while ETHStorage only needs one to complete it.
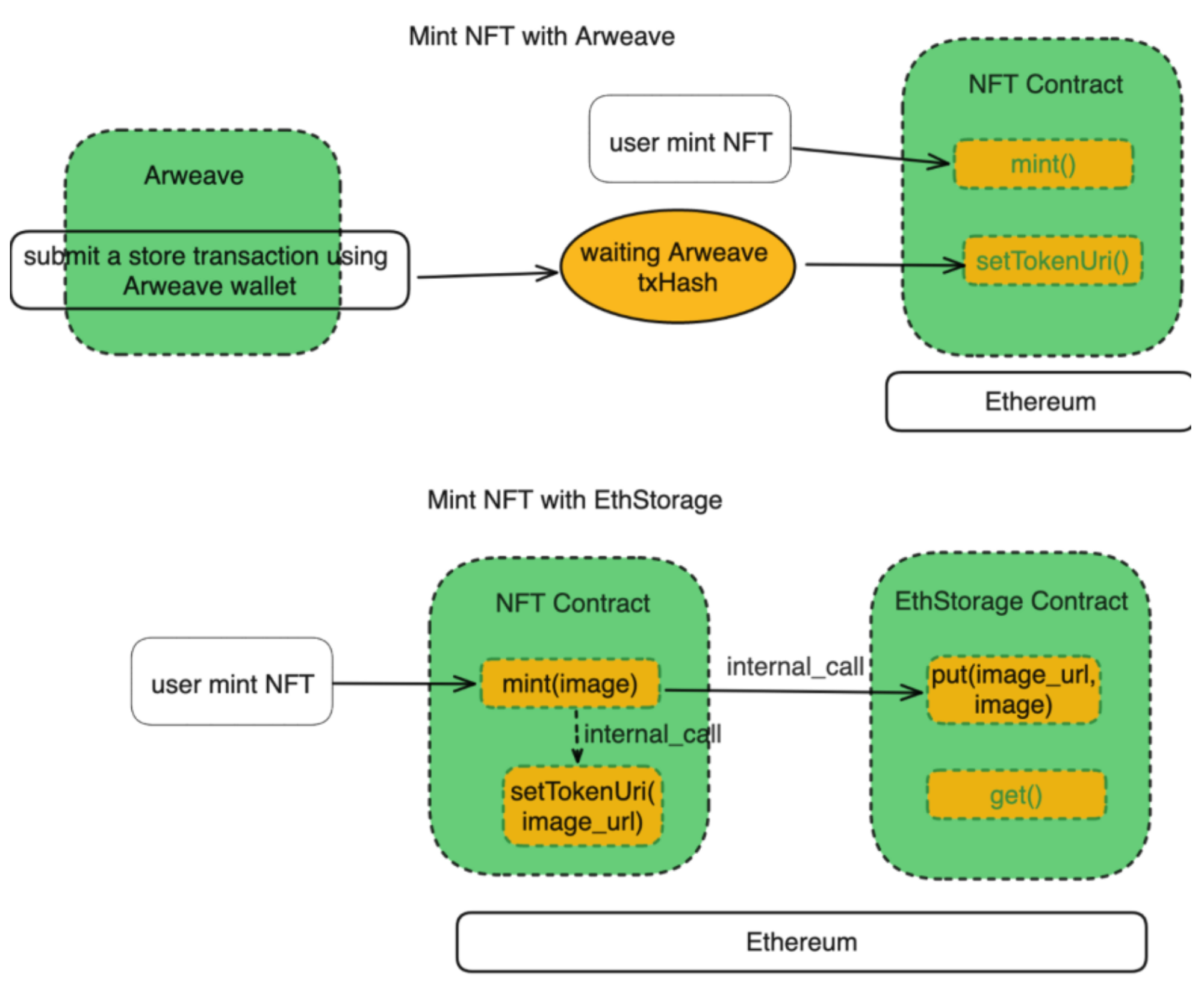
ETHStorage adopts the key-value storage paradigm and supports complete CRUD operations (create, read, update, delete stored data). from
ETHStorage is positioned as the first storage L2 of the Ethereum ecosystem. Thanks to its seamless interoperability with EVM and low storage costs, ETHStorage is expected to inherit L2 state data discarded by blobs.
Covalent
Another decentralized storage project worth watching is Covalent. Covalent was the first to smell the business opportunities in data availability after the Cancun upgrade, and launched the Ethereum Wayback Machine (EWM) in November 2023 for long-term storage of L2 state data discarded by blobs.
Of course, just storing data is of limited value to Covalent, so Covalent goes beyond simple storage and will also integrate L2 data into its existing decentralized data analysis infrastructure services. Covalent supports users to seamlessly access blockchain data and provides data service support for specific user groups such as arbitrage traders, MEV researchers, AI researchers, blockchain data websites, etc.
No matter how the execution layer, settlement layer, consensus layer and short-term data availability layer evolve in the future of modular blockchain, Covalent hopes to become the long-term data availability layer for all project parties, providing permanent data storage and availability services.
With the implementation of the Cancun upgrade, it is expected that the data storage and availability tracks will usher in a new round of hype. Covalent, which is endorsed by well-known exchanges such as Binance, Coinbase, 1kx, Delphi Digital, and first-tier investment institutions, and has a solid business, will not be at a disadvantage in the competition.
Filecoin, Arweave, Storj and other established decentralized storage projects
The Cancun upgrade will also bring more practical decentralized storage business needs to established decentralized storage projects such as Filecoin, Arweave, and Storj. It is expected that the above projects will also take over some of the L2 status data discarded by blobs. Since this part of the data is only valuable to some special groups of people who are oriented to data analysis and research, frequent status changes are not required. Therefore, in comparison, Arweave, which focuses on one-time payment and permanent storage, may be able to win more growth in the L2 state data storage business.
If we take the long view, L2 also needs to have a dedicated data availability layer. In the long run, what is stored in the blob may not be the data and status submitted by L2, but the Merkel root of this part of the calculation. Let Ethereum no longer bear any additional data storage and return to the most fundamental consensus.
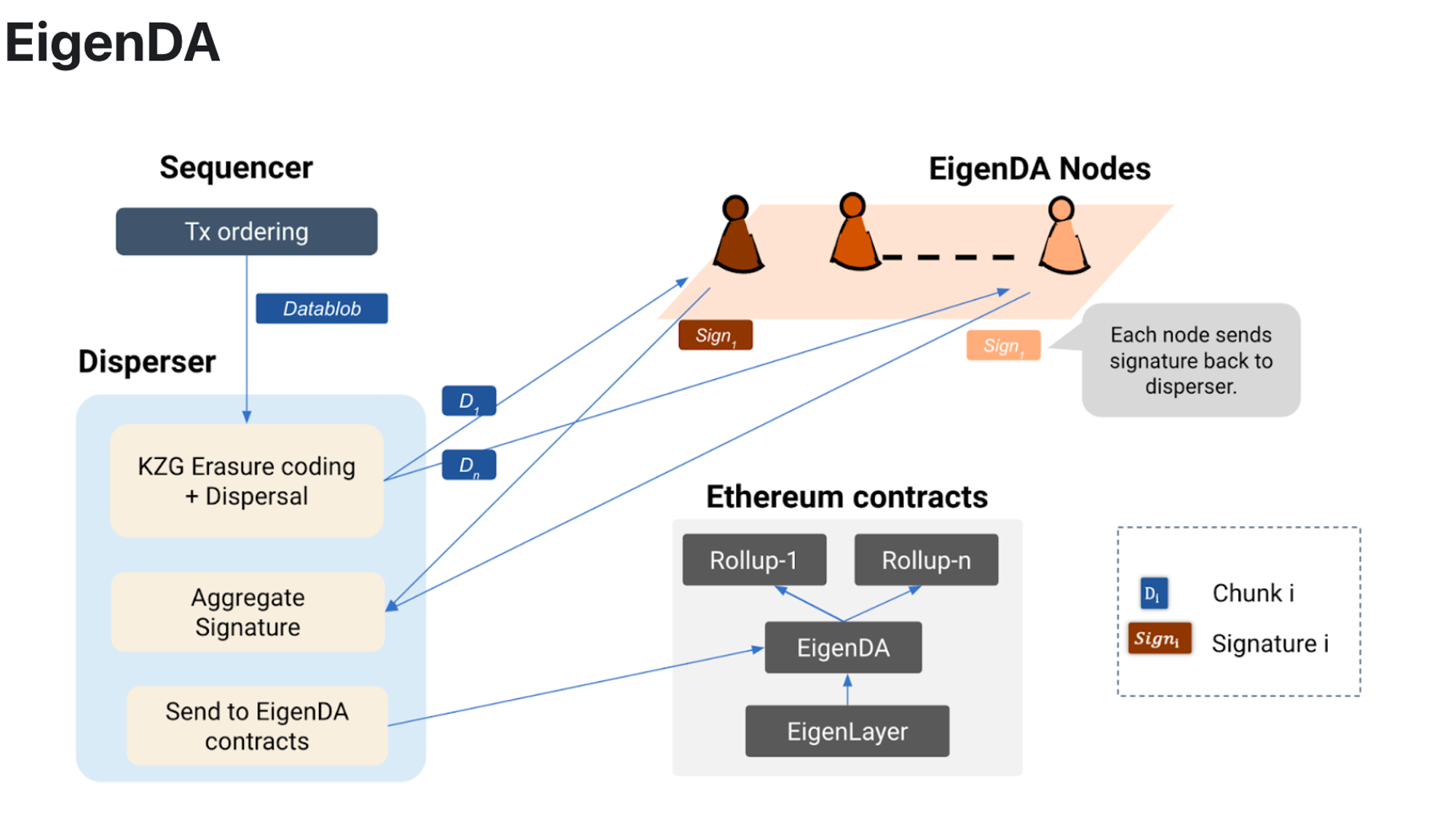
EigenDA
EigenDA is a promising DA solution. EigenDA realizes the decoupling of data availability and consensus. First, Rollup needs to encode the Data blob using erasure coding and KZG commitments and publish the KZG commitments. Subsequently, the EigenDA nodes composed of re-pledges need to proofread and verify the KZG commitment and final consensus confirmation. Finally, the data confirmed by consensus will be submitted to the Ethereum main network. The core of EigenDA is to reuse the consensus of Ethereum, abstract the verification and final consensus confirmation links in DA, and complete this part of the work through the reused consensus.
Polygon Avail
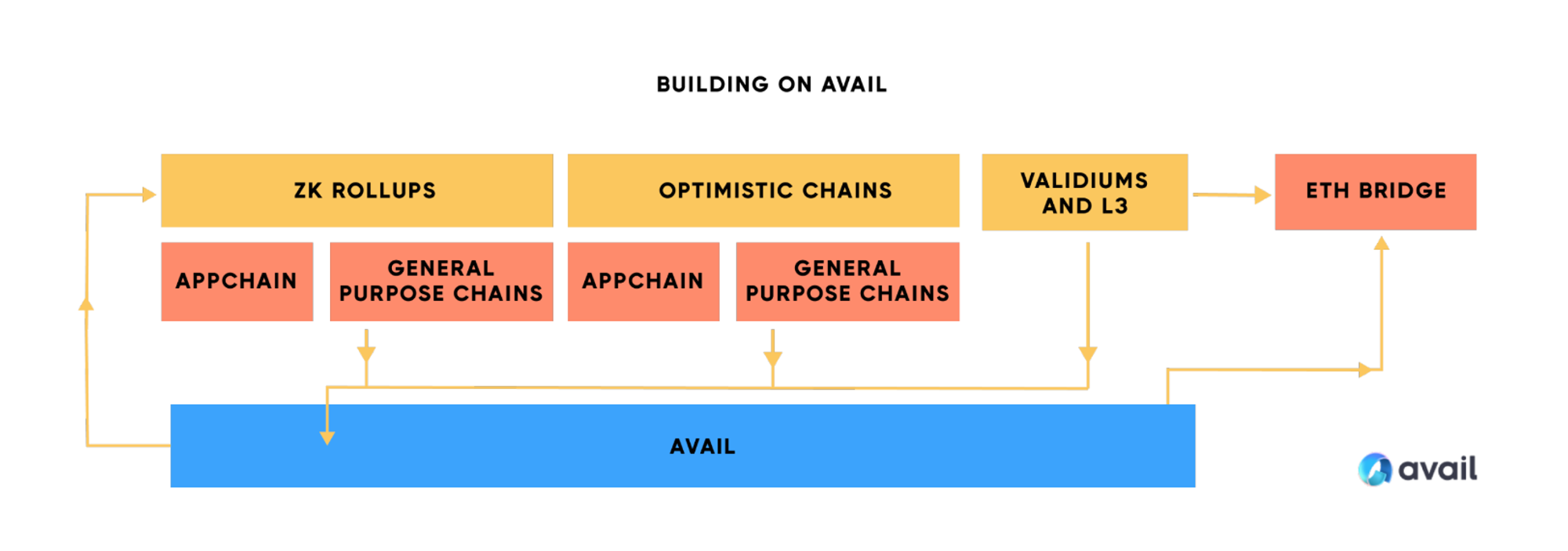
Polygon Avail is a project proposed by Polygon that focuses on solving data availability in the Ethereum expansion route. Avail aims to provide data availability services for different expansion solutions such as L2 and side chains. Avail supports EVM-compatible Rollup to publish data to Avail. Avail efficiently sorts and records transactions, and provides data storage and validity verification. In terms of validity proof, Avail uses KZG polynomial commitment, which can provide a more concise proof than Celestia and reduce the memory, bandwidth and storage requirements of nodes. Avail has been consistent with the Ethereum upgrade and expansion route since the beginning of its design, allowing developers to store data in Avail and choose to settle on the Ethereum mainnet. In the trend of modular blockchain, Avail is expected to become the underlying data availability service provider for more EVM Rollups.
RaaS
RaaS providers can abstract the complex technology of building blockchain and help users quickly deploy L2 with one click through simple and easy-to-use tools or even code-free forms. As mentioned above, the Cancun upgrade will bring an explosion of L2. The improvement in L2s ease of use and performance will also promote the emergence of more L2, thereby benefiting the underlying Rollup as a Service infrastructure.
Among the current RaaS solutions, there is also discussion on whether to choose the OP or ZK solution. Solutions based on OP have better compatibility, richer ecology and lower threshold. ZK-based solutions have a higher degree of customization and higher security. Although in the long run, ZK-based solutions are more customizable, have stronger dislocation competitiveness, and can bring unique functional and performance empowerment to the project. But in the short term, the OP-based solution can amplify the cost and performance advantages brought by Dencun upgrade to L2 with its advantages of low threshold and high compatibility, reuse the existing complete EVM infrastructure more quickly, and realize early With the rapid expansion of users and funds, the short-term leverage effect is more obvious.
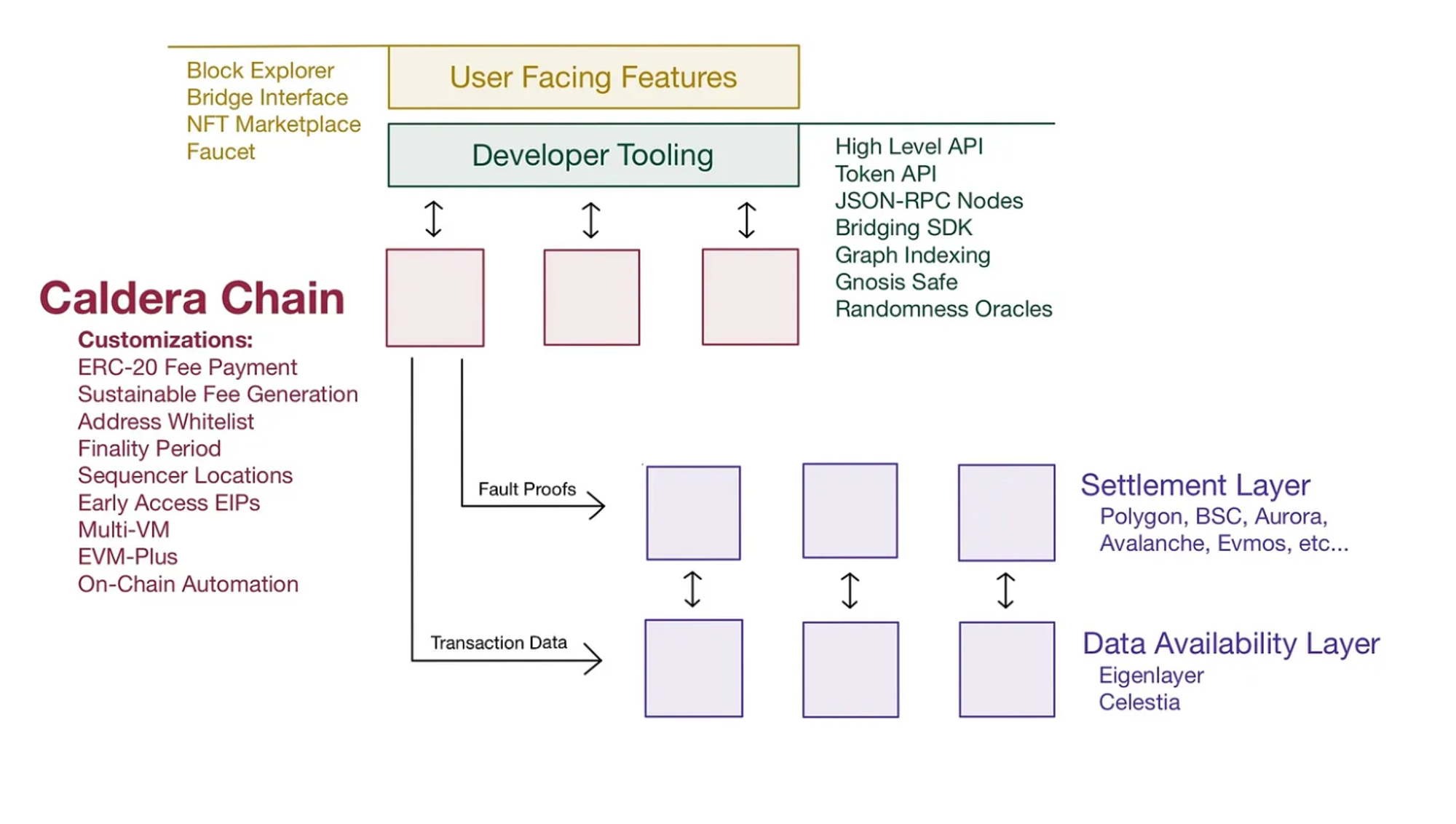
Caldera
Caldera is a RaaS service provider built on OP Stack, which supports users to quickly build an Optimism L2 in a codeless manner. Using L2 released by Caldera can achieve complete EVM compatibility, which can greatly reduce the development threshold for developers and facilitate the direct reuse of existing EVM ecological projects, thus providing a more complete infrastructure for L2. In addition to L2 itself, Caldera also configures a series of blockchain infrastructure for users, such as blockchain browsers, test network faucets, etc., thereby further reducing the cost of chain issuance and usage threshold, plug and play.
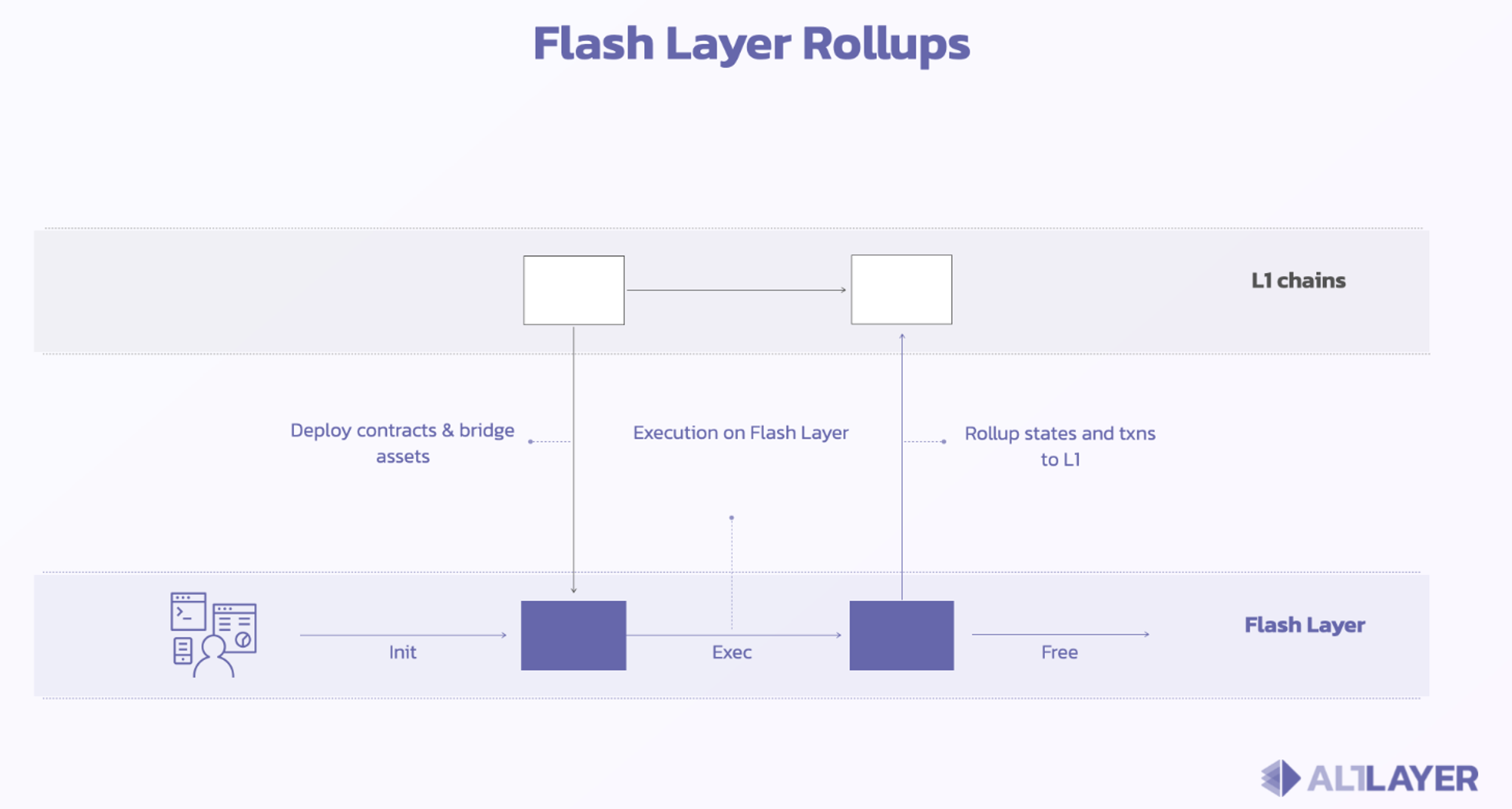
Altlayer
Altlayer is another noteworthy RaaS solution under the Optimism family. Altlayer supports codeless deployment of L2. Developers only need to perform simple graphical interface operations to quickly create a Rollup chain. In addition, AltLayer also supports flexible Rollup - Flash Layer. When the demand for mainnet applications surges, such as when popular NFT projects start minting or popular DeFi projects issue airdrops, developers can quickly deploy a Rollup chain through Altlayer to respond to the short-term surge in performance demand. When the event ends and the state and assets are transferred back to the base chain, the Flash Layer can be deleted directly. Altlayer provides an instant expansion solution that avoids resource waste and can meet more complex business needs.
Lumoz
Lumoz (formerly Opside) is a RaaS solution based on ZK, allowing developers to deploy their own ZK-Rollup with one click and generate customized zkEVM application chains. At the same time, the emergence of a large number of ZK-Rollups will also create huge computing power requirements for ZKP calculations. Lumoz has also built a decentralized ZKP market to support ZK mining and generate zero-knowledge proofs for ZK-Rollup. In terms of actual use, developers do not need to know anything about ZK and can quickly deploy a ZK-Rollup through simple front-end operations. The computing power requirements involved in the operation of ZK-Rollup can also be solved through the ZK-PoW service provided by Lumoz, which can greatly reduce the operational threshold and operating costs of the project party. In particular, Lumoz also supports 0 Gas Fee contracts, which can provide users with a smooth Dapp experience without interaction costs. The recently popular ZKFair is one of the L2s built on Lumoz.
Application layer
Previously, we discussed in detail the benefits of Dencun upgrade for Infra track levels such as L2, DA and RaaS. Dencun upgrades improvement in L2 cost and performance will also promote the development and innovation of the application layer. Next, we will briefly analyze the application layer tracks that can significantly benefit from Dencun upgrades.
Perps
Overall, interactions in the DeFi track are characterized by low interaction frequency but high single-point interaction returns. Therefore, in a sense, DeFi does not particularly rely on high performance, and the benefits brought by a single DeFi operation can also well cover the cost of interaction. However, decentralized derivatives are relatively exceptions. The limitations of performance bottlenecks and the shortcomings of excessive network transaction fees will be infinitely amplified during the operation of decentralized derivatives protocols.
Due to the performance limitations of the L2 network, Perps projects are almost unable to run on-chain order books and cannot efficiently respond to real-time order matching needs. Moreover, excessive network fees will greatly limit the high-frequency trading of market makers and high-frequency trading users. The existence of the above problems has resulted in Perps low trading efficiency and relatively high transaction slippage. It is unable to attract deep liquidity and professional trading users, and it cannot provide users with a trading experience comparable to CEX.
We believe that the Dencun upgrade can solve the above problems to a certain extent, especially the improvement in performance is particularly critical for derivatives trading. Compared with point-to-pool and AMM model Perps, the Dencun upgrade is more beneficial to L2 Perps decentralized derivatives exchanges with order book models such as ApeX Protocol, Aevo, and Vertex Protocol. Similarly, the reduction in network transaction fees will further stimulate the transactions of more mature point-to-pool model Perps such as GMX, Synthetix, and GNS.
LSD
In addition to EIP-4844, the Dencun upgrade also includes the introduction of EIP-4788. EIP-4788 will introduce the beacon block root into every EVM block. This allows the Ethereum mainnet to obtain data from the Ethereum consensus layer in a trust-minimized manner, eliminating dependence on external oracles, thereby reducing potential security risks, oracle failure and malicious manipulation risks. The introduction of EIP-4788 can further improve the security of the staking protocol. Although this improvement is not direct for users, it is a potentially significant benefit to LSD and the ReStaking track. EIP-4788 enables liquidity staking protocols such as Lido, Rocketpool, Swell, and re-staking protocols such as Eigenlayer to directly access key data such as validator balances and status from the consensus layer, thereby significantly improving their security and operational efficiency. We still have high expectations for Dencun’s upgraded LSD, especially for the development of the ReStaking track represented by Eigenlayer. Eigenlayer has also been active recently and has successively supported a variety of LSTs. It has cooperated with Altlayer to launch Restaked Rollups, the ecological re-pledge protocol Renzo has been launched, and EigenDA has also opened the second phase of the test network. Eigenlayers TVL has also reached 1.7 B and continues to rise. The narrative of re-staking has just emerged, and EIP-4788 will provide a solid underlying security guarantee for re-staking.
FOCG
Full-chain games are one of the great beneficiaries of Dencun’s upgrade. Unlike Web2.5 games where only the assets are on the chain and the game body is still off-chain, the game content, logic, rules, and assets of the full-chain game are all on the chain. The Gas fee on the chain determines the interaction cost of each game operation, and the performance on the chain determines the players user experience. Obviously, due to performance limitations, previous full-chain games were limited to simpler turn-based strategy games. The high cost of interaction and the game’s need for high-frequency interaction also discourage many players.
Dencun upgrade can intuitively improve the development dilemma of existing full-chain games, and even spawn more full-chain game types. We are optimistic that more full-chain games will be built based on full-chain game engines such as Mud and Dojo, and run on L2 Redstone and StarkNet. Existing full-chain games such as Sky Strife, Loot Survivor, Isaac, and Influence may also capture more real players due to the improvement in user experience brought about by the Dencun upgrade.
The implementation of the Dencun upgrade will once again inject new vitality into the Ethereum ecosystem. Of course, in addition to benefiting the tracks mentioned above, the Dencun upgrade will also reduce the attractiveness and core competitiveness of some tracks such as side chains and non-EVM expansion solutions. The substantial cost reduction and performance improvement of EVM ecological L2 and L3 will further eclipse side chain solutions such as Polygon, and non-EVM expansion solutions such as BSC will also reduce the attractiveness brought by cost and performance advantages. The Dencun upgrade will refocus the market on the Ethereum ecosystem with L2 and L3 as the core.
Summarize
As part of The Surge in the Ethereum upgrade roadmap, the Dencun upgrade aims to further reduce the cost of using the Ethereum ecosystem and improve the scalability of the Ethereum ecosystem. The Dencun upgrade will introduce instant storage operation codes through EIP-1153, reducing the storage cost and Gas consumption of the Ethereum main network, and improving the scalability of the main network. The Dencun upgrade will also introduce EIP-4844, which will significantly reduce the transaction cost of Ethereum L2 and improve the transaction throughput of L2 by introducing a new data structure blob.
Judging from the current Shadowfork test report and the recently held 178th Ethereum core developer executive meeting, the current testing situation of the Ethereum Dencun upgrade is good, and the three major testnets will be tested separately from January to early February as expected. Dencun upgrade test. If the testnet test goes smoothly, the Dencun upgrade of the mainnet is expected to be completed within February.
The Dencun upgrade will further promote the prosperity of the L2 ecosystem. Optimism, Arbitrum and Metis are particularly worthy of attention. The Dencun upgrade will also drive demand for Infra tracks such as decentralized storage, DA and RaaS. The development of ecological projects such as EthStorage, Covalent, EigenDA, Polygon Avail, Caldera, Altlayer, and Lumoz deserves attention.
The Dencun upgrade will also promote the development and innovation of the application layer, and the order book model Perps represented by ApeX Protocol, Aevo, and Vertex Protocol will benefit significantly. EIP-4788 will improve the underlying security of the LSD and ReStaking protocols, and will especially drive the development of the re-staking track represented by EigenLayer. The entire chain of games will also bring a better interactive experience to users due to the Dencun upgrade.
Finally: MT Capital is very optimistic about the EVM ecological innovation brought about by the Dencun upgrade. We welcome early projects and entrepreneurs in ReStaking, DA, L2, Perps, FOCG and other tracks to contact us at any time. (Twitter: @0X_IanWu, @Severin 0624, MT Capital Email: deck@mt.capital)
Reference:
https://www.datawallet.com/crypto/ethereum-cancun-upgrade-explained#:~:text=Ethereum Cancun EIPs,-The imminent Ethereum&text=The Cancun component of the, costs%2C efficiently using block space.
https://ethereum-magicians.org/t/a-rollup-centric-ethereum-roadmap/4698
EIP-4844 Unveiled: Paving the Way for Proto-Danksharding in Ethereum
Ethereum’s Cancun-Deneb (Dencun) Upgrade: another milestone after the Shanghai Upgrade
https://hackmd.io/@vbuterin/sharding_proposal#ELI5-data-availability-sampling
https://docs.altlayer.io/altlayer-documentation/rollup-types/flash-layer-rollups
MT Capital
MT Capital, headquartered in Silicon Valley, is a crypto-native fund focusing on Web3 and related technologies. We have a global team, and our diverse cultural backgrounds and perspectives allow us to have an in-depth understanding of the global market and to seize investment opportunities in different regions. MT Capitals vision is to become the worlds leading blockchain investment firm, focused on supporting early-stage technology companies that can generate significant value. Since 2016, our investment portfolio covers Infra, L1/L2, DeFi, NFT, GameFi and other fields. We are not just investors, we are the driving force behind the founding team.
Official website:https://mt.capital/
Twitter:https://twitter.com/MTCapital_US










