Original author: MiX
Shared security means that one or more blockchains can enhance their own security and achieve decentralized startup and operation by sharing the decentralized trust source of another blockchain. This lowers the startup threshold and operating costs of blockchain from scratch, and helps prevent chaebol rule, allowing the team to focus more on value innovation in Web3.

As we all know, blockchain is a trust machine, and the fundamental value of blockchain is decentralized trust. The reason why public chains have always been in the spotlight is that their business model is to provide decentralized trust for smart contracts on their own chains.
In other words, decentralized trust is a service provided by the public chain to smart contracts. The gas we pay when interacting on the chain is to pay for this decentralized trust. It is estimated that most people are not aware of this nature of public chains. It is for this reason that the entire public chain track has a valuation of over one trillion US dollars.
Sharing security services means extending decentralized trust from one blockchain to more blockchains. The decentralized trust that originally had to be built in the PoW/PoS manner has become a third-party service that can be purchased flexibly at any time.
At this point, for the first time, decentralized trust has become as flexible as cloud computing and cloud storage, and has become part of the cost rather than the goal of Web3 project operations. The team can focus more on business innovation itself.
At the same time, decentralized trust is responsible for the security of the chain. As there are more and more blockchains and more and more assets on the chain, the market size of decentralized trust will become extremely large. I think its scale At least it will start with a hundred billion US dollars.
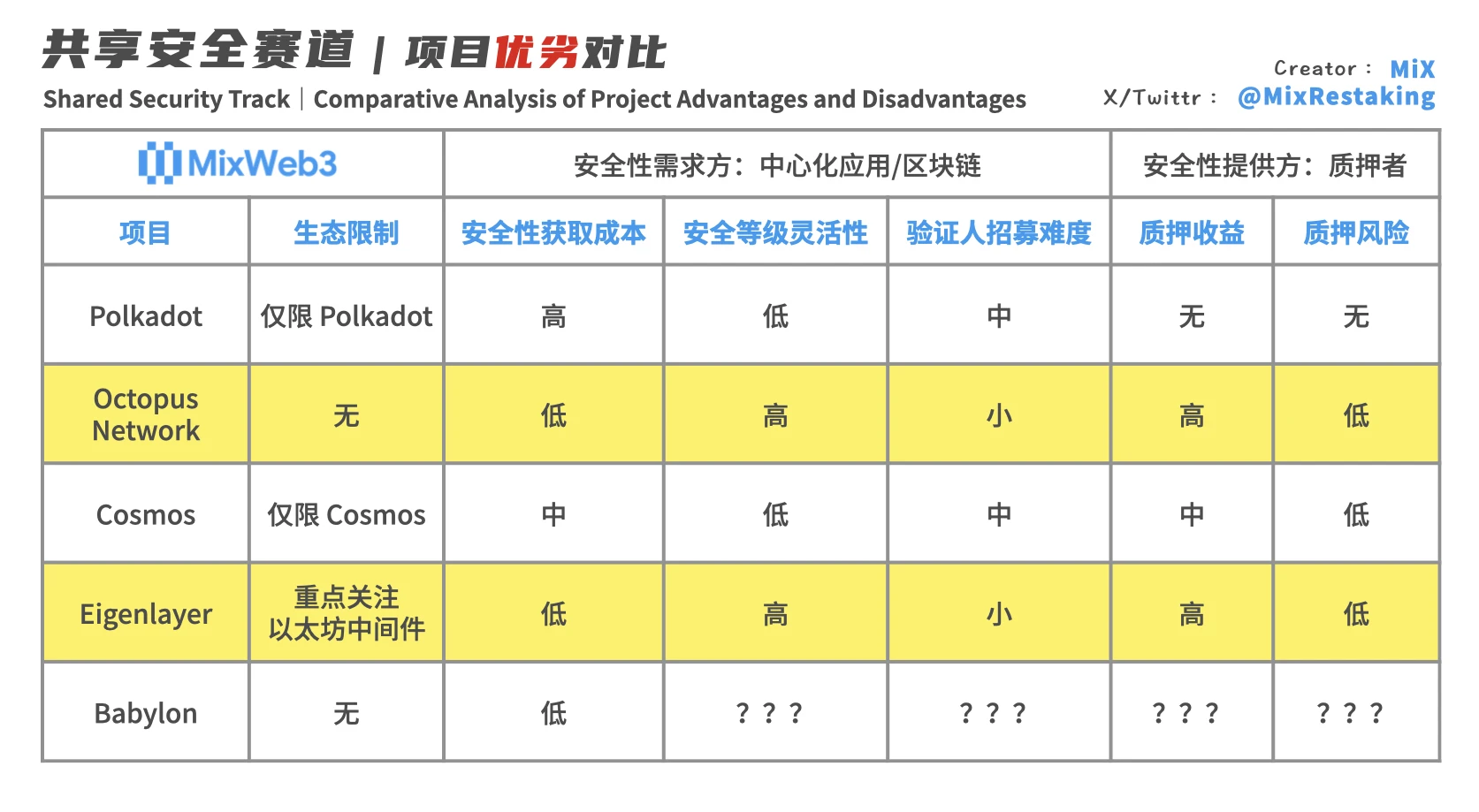
Currently, the most well-known projects on the shared security track are Polkadot, Octopus Network, Cosmos, EigenLayer and Babylon. The solutions of these projects each have their own characteristics, and the advantages and disadvantages cannot be generalized. It should be said that they all have their corresponding era backgrounds and vertical scenarios.
Polkadot
Decentralized trust-based self-selling model serving the Polkadot ecological parallel chain
Polkadot, founded in 2016, was the first project to propose and implement shared security.
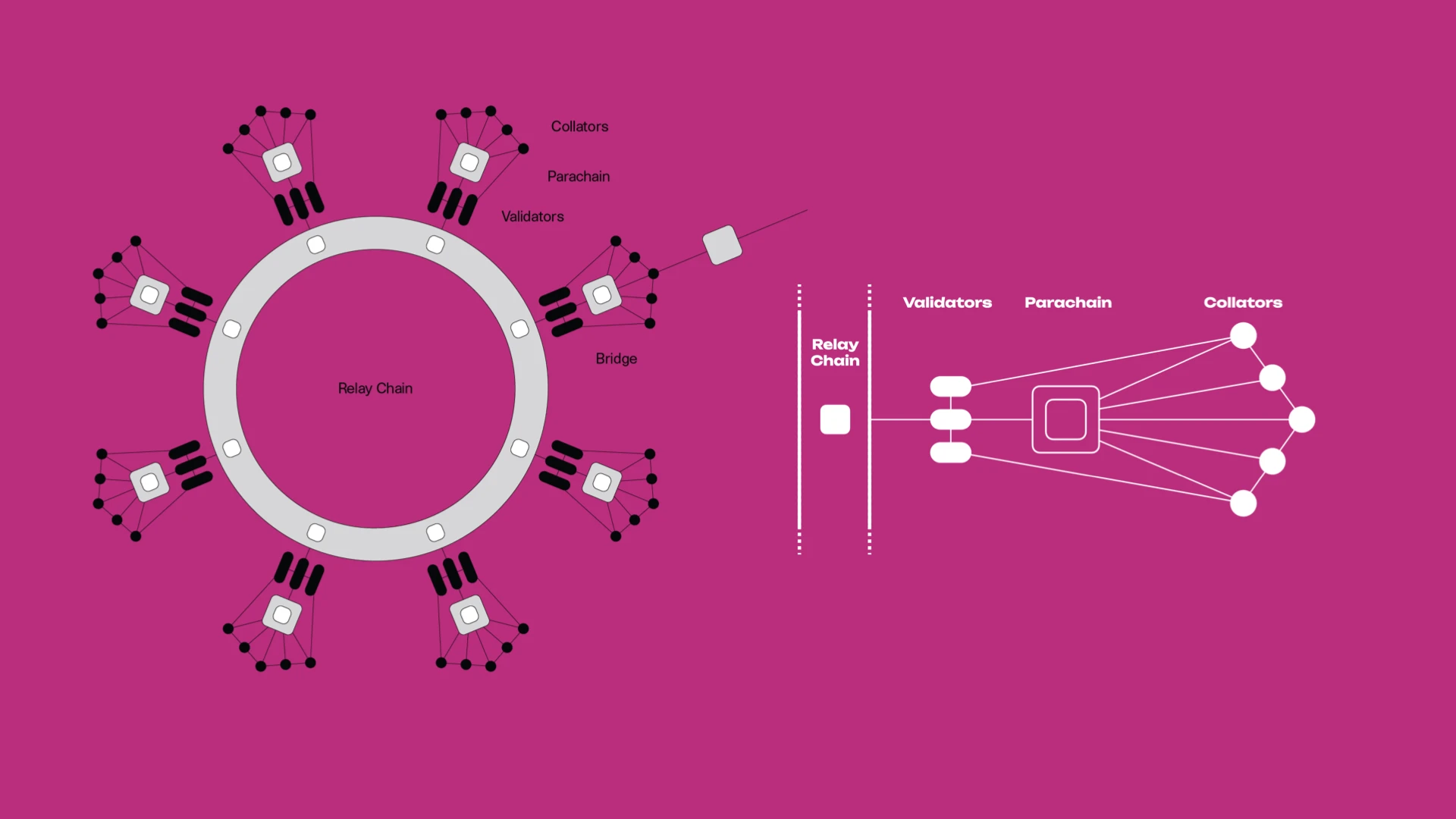
Polkadots shared security mechanism is that the parallel chain auction slot is connected to the relay chain, and the verification nodes of the relay chain provide security, thereby obtaining the same security as the relay chain. This solution allows the Substrate chain to directly obtain the multi-billion-dollar security of Polkadot, which solves the problem of long security bootstrapping time for new blockchains. However, because it can only choose Polkadot’s very high-level security, plus The mechanism of auction sales makes the startup cost of new chains high, which is extremely unfriendly to start-up projects where financial strength and team energy are valuable.
Practice in recent years has proven that most Polkadot parachains do not require such a high level of security. The two-year exclusive slot method also makes the utilization efficiency of the decentralized trust resources of the relay chain very low. Obviously Polkadot Also aware of this problem.
On June 28, 2023, Polkadot 2.0 hopes to build a decentralized trust resource allocation method that is more flexible in terms of time period and security level. Based on the minimum unit resource of block space of the relay chain, the Substrate chain uses DOT to purchase the quantity and usage time of block space on demand, achieving decentralized and secure flexible acquisition.
On October 25, the test network Rococo of the Polkadot relay chain has realized the ability to purchase the relay chain block space on demand and is preparing for testing. The agile core time that replaces the slot is expected to be released in 2024. Achieved in the first or second quarter.
It can be seen that Polkadot treats the decentralized trust of its own relay chain as a commodity and sells it to the Substrate chain that joins the ecosystem, whether it is DOT pledge in the 1.0 era or purchase in the 2.0 era.
In fact, Polkadot is the only project in the shared security field that chooses to sell decentralized trust directly.
Octopus Network
A two-sided market focusing on service application chains (without blockchain ecological restrictions) and decentralized trust
Octopus Network, founded in 2019, focuses on providing shared security services for application chains and pioneered the LPoS lease equity proof mechanism.
Octopus Network has built a secure two-sided market for buying and selling decentralized trust. The application chain is the demander and buyer of security. Use the native token as rent and pay it to the verifier node. The verifier is the decentralized trust. security provider. The underlying logic of Octopus Networks two-sided security market basically establishes the basic paradigm for subsequent shared security services.
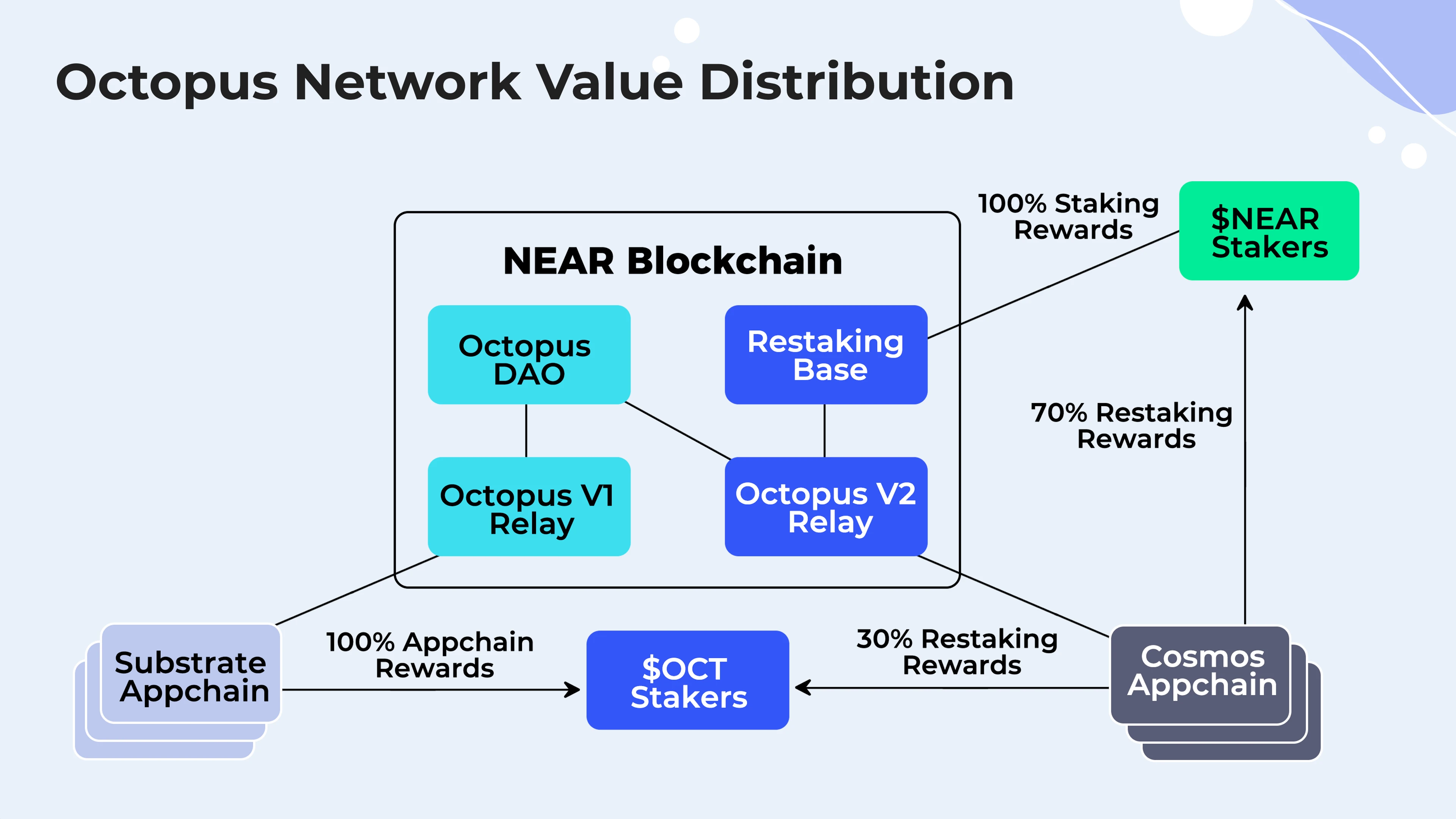
In the V1 stage of Octopus Network, the validators of the Substarte application chain use Octopus Networks $OCT as pledge to ensure the security of the application chain. That is, the application chain rents and shares the security of Octopus Networks $OCT.
In the V2 phase of Octopus Network, on the basis of V1, the $NEAR Restaking mechanism is added, and $NEAR is used to restake application chains based on the Cosmos SDK to provide security. It is planned to go live in the fourth quarter of 2023.
Essentially, Restaking is a shared security mechanism pioneered by Eigenlayer. The same assets can be pledged to multiple decentralized applications/blockchains at the same time to provide security for them. Its breakthrough innovation lies in maximizing the interests of decentralized applications/blockchains, blockchains that provide shared security and pledgers.
The biggest advantage of Octopus Networks shared security solution is focus and flexibility. This solves the problems of high security bootstrapping cost and long cycle of the original PoS mechanism in one fell swoop. The addition of $NEAR Restaking in the V2 era has simultaneously increased the security level it can provide to the billion-dollar level.
Focus lies in focusing on serving an application chain with its own exclusive chain. Flexibility lies in the choice of security levels.
In fact, Octopus Network has built NEAR into a highly competitive fat hub of the blockchain Internet, becoming a potential competitiveness that NEAR cannot ignore.
Cosmos
Decentralized trust distribution mechanism managed and decided by the Cosmos community
Cosmos was founded in 2014 and was the first to propose the concept of multi-chain networks. However, it was not until 2023, that is, March 15 this year, that the Replicated Security replication security mechanism was released to make up for the shortcomings of shared security solutions.
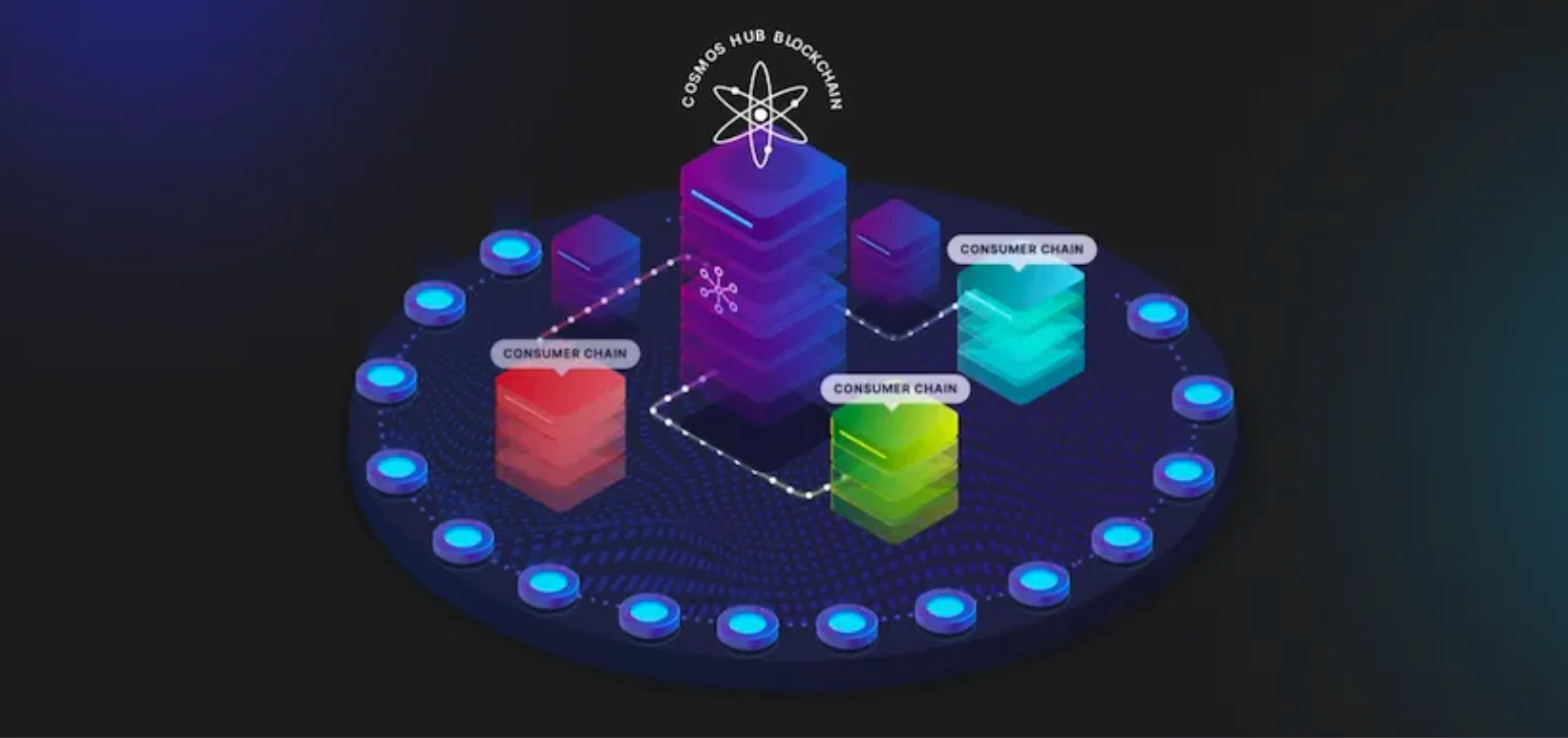
The core logic of Cosmos replication security is to treat all Cosmos validators as a whole. After the community votes to provide security for the consumer chain, the validators can use the $ATOM that has been pledged in Cosmos to provide security for the Cosmos ecological consumer chain. Run verification nodes separately to achieve decentralized security.
This plan refers to the construction logic of Octopus Network’s two-sided market, and also integrates the Restaking ideas proposed by Eigenlayer, but it is very different in terms of flexibility, which brings two problems:
1. The value of the consumer chain needs to empower the Cosmos hub in order to gain enough votes to gain community approval. For example, Neutron, which is the DeFi center of the Cosmos ecosystem.
2. The consumer chain needs to provide rent for the $2 billion-level security of the Cosmos hub, which will inevitably bring huge economic pressure. Some time ago, the Cosmos community had a very interesting proposal: Stride, a liquidity staking project based on replication security startup and operation, proposed to be merged into the Cosmos Hub and all $STRD converted to $ATOM to become a satellite chain of the Cosmos Hub. Although nothing happened in the follow-up, it also cast a shadow over the copy security solution.
EigenLayer
A decentralized trust-based two-sided market serving Ethereum middleware
EigenLayer, founded in 2021, introduces Ethereum-level trust into middleware: allowing ETH that has been pledged on Ethereum to be pledged on Ethereum middleware again, allowing it to share the almost unshakable economic security of Ethereum. EigenLayer proposed the Restaking mechanism for the first time, which is also the creative source of the $NEAR Restaking mechanism mentioned above in Octopus Network 2.0 version.
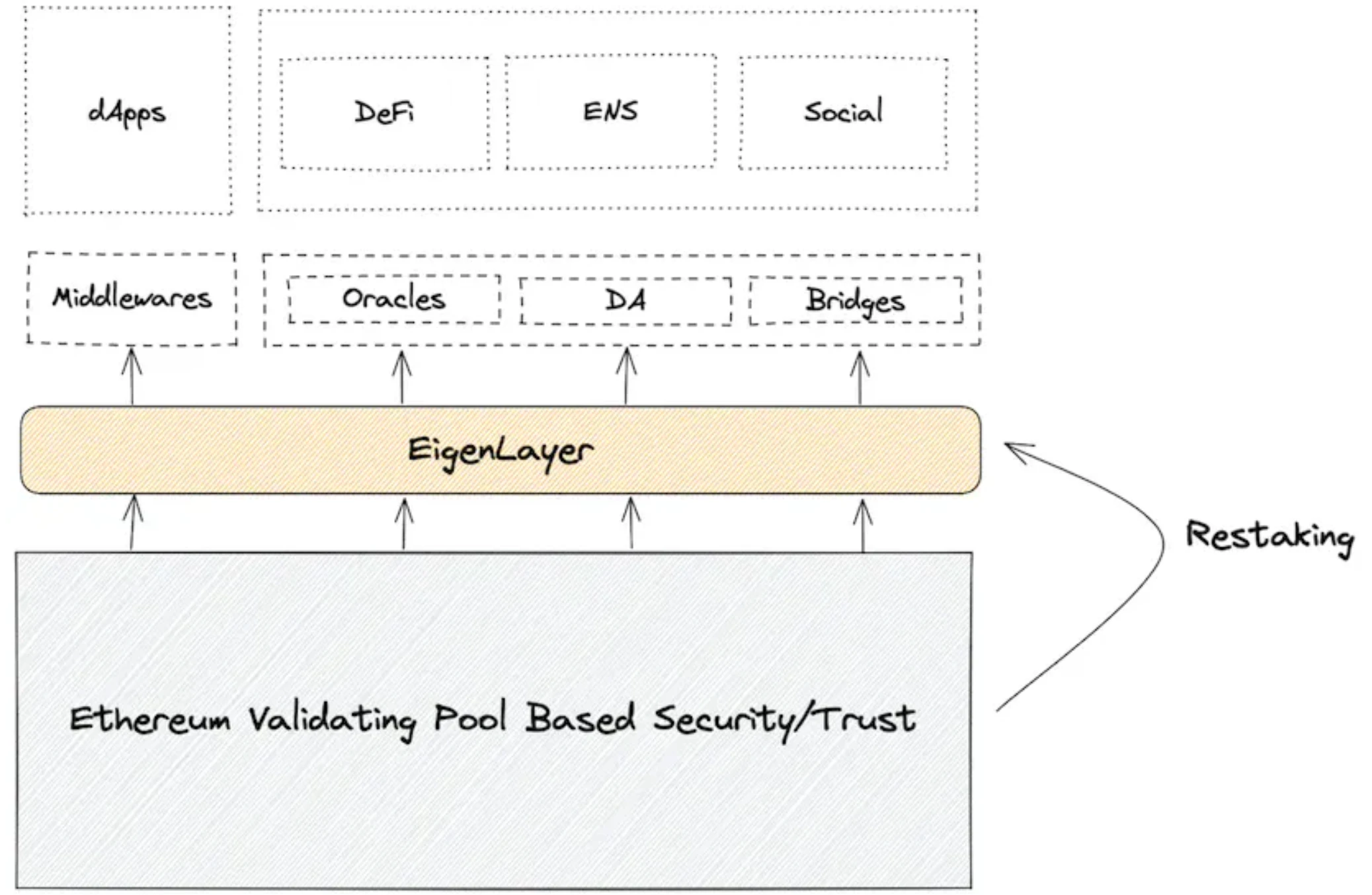
Its advantages mainly lie in two aspects:
1. Focus on shared security solutions for Ethereum middleware to make up for the shortcomings of the entire Ethereum ecological and economic security.
2. The security level can be flexibly adjusted. Middleware protocols can flexibly obtain and adjust the pledge amount and security level according to their own security needs at different stages of development.
Babylon
A two-sided market based on BTC with the largest decentralized trust pool and decentralized trust.
Babylon, founded in 2022, has set its sights on Bitcoin. Babylon is an independent PoS blockchain. On the one hand, Bitcoin holders use Babylon to transfer their Bitcoin Staking and Restaking to blockchains that require security to obtain security rewards; on the other hand, they obtain security guarantees. The blockchain also manages and controls security on Babylon.

BTC is an asset worth more than 500 billion U.S. dollars even if it is currently in deep trouble. Coupled with the natural security advantages of PoW proof-of-work and the large amount of idle liquidity of BTC, this has become the core value of Babylon, which is to own the blockchain. The worlds undisputed largest decentralized trust pool.
Sort out the advantages and disadvantages:
Based on the core advantages of shared security
For new decentralized applications/blockchains (security demand side)
1. The cost of security acquisition is low, and excessive issuance of application chain tokens can be avoided to dilute the value. As we all know, independent PoS usually requires an additional issuance of about 10% of tokens every year to reward the verifier group. High additional issuance dilutes the value of tokens and creates continuous selling pressure in the secondary market.
2. The security level can be flexibly adjusted. Blockchains can flexibly set the security level of the application chain according to business scenarios and development stage needs. Generally speaking, the security level can be lower in the early stage. When the economic scale and asset scale of the application chain expand, a decision is made to increase the security rent through on-chain governance, and then the technical team adjusts the block reward of the application chain, and a higher level can be obtained quickly. level of security.
3. It is easy to recruit validators and can start the blockchain more quickly. In the startup phase, there is no need to let the native token have a value consensus before becoming a verification node. This allows the team to save at least several years of time and millions of dollars in funds, and skip the verification group recruitment stage, saving time and effort. , to achieve fast and safe startup of the application chain.
For stakers (security providers)
1. The risk of staking is lower. Use $DOT, $OCT, $NEAR, $ATOM and even more robust $ETH and $BTC with value consensus for staking. Compared with staking the native Token of the application chain, the risk of asset depreciation is lower. .
2. Higher staking returns. Restaking and copy security mechanisms allow pledgers to obtain multiple benefits.
In addition, there is actually another extremely important but difficult-to-find deep advantage, which is to prevent the blockchain from being dominated by plutocrats.
As the validator group of traditional PoS continues to obtain additional tokens, it gradually controls most of the governance rights and becomes a chaebol. Even proposal voting increases the block reward, increasing its own income and the security cost of the chain. For blockchains that use a shared security mechanism, verification nodes do not pledge native tokens with governance effects, which fundamentally solves the problem of verifiers controlling the blockchain. In a blockchain that adopts a shared security mechanism, its validators are purely there to earn rewards and will not affect the governance and decision-making of the new blockchain, thus avoiding the embarrassing situation of the blockchain being dominated by verification nodes.
Innovation requires continuous iteration, lower startup threshold and trial and error costs.
With the launch of new decentralized protocols and blockchains, the adoption of shared security solutions will be the general trend. After all, only by exponentially reducing the startup risks and operating costs of blockchains can we have the opportunity to accelerate Web3 innovation again.
It can be seen that shared security will surely become one of the most important infrastructure services in the encryption field.

Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and may not be relied upon as legal, tax, investment, financial, or any other advice.










