Original author: Fu Shaoqing, SatoshiLab, Wanwudao BTC Studio
Some jokes on the Internet are often about discovering some phenomena by accident, but they don’t explain the reasons behind these phenomena. If we analyze them in depth, we will often find good discoveries. From sorting out the knowledge of Bitcoin’s second layer, to sorting out the application architecture of Web3.0, and the disappearance of Satoshi Nakamoto, I have a better understanding of decentralization.
1. Internet jokes: Satoshi Nakamoto disappears, SBF is imprisoned, CZ is restricted
An interesting causal relationship has emerged on the Internet: Bitcoin is strong because Satoshi Nakamoto disappeared, SOL is strong because SBF went in, BNB is strong because CZ is about to go in, so why is ETH weak? In order to promote the rise of Ethereum, many people began to shout to capture Vitalik alive. Many people often laughed when they saw such jokes.
Some jokes on the Internet often discover some phenomena by accident, but they do not explain the reasons behind these phenomena. If we analyze them in depth, we will often find good discoveries.
Why did Satoshi Nakamoto disappear? As the founder of Bitcoin, although the reason for his disappearance is still unclear, there are several possible guesses:
Personal privacy protection: Satoshi Nakamoto chose to disappear in order to protect his privacy and security. Because he was creating a cryptocurrency, and through the research and accumulation of his predecessors, Satoshi Nakamoto felt that his creation was more likely to succeed. In order to avoid causing too much attention and controversy in the real world, he may also want to avoid too much attention and interference. Disappearing is a good way.
Decentralization: Through the study of Satoshi Nakamotos original remarks and emails, he considered a lot about the design of Bitcoin, not only focusing on the realization of technology, but also considering many economic and sociological influences. Another possible explanation for Satoshi Nakamotos disappearance is to ensure the decentralization of Bitcoin. He may believe that a system without a centralized leader can truly achieve freedom and independence. At the same time, this decentralization can also prevent the concentration of power and prevent Bitcoin from being controlled by a few people or institutions, which is more conducive to the development of the community and joint decision-making.
The protection of personal privacy should not have much impact on Bitcoin. Decentralized design may be an important design consideration. Especially compared with Ethereum and Vitalik Buterin, the development path of Ethereum planned by Vitalik Buterin has aroused many peoples doubts. This is a serious centralization. Decentralization is reflected in multiple levels and aspects. We will use some analysis later to look at the role of decentralization from multiple observation angles and theoretical systems.
2. Basic Concepts of Decentralization
2.1. Decentralization, distribution, and centralization
A common classification of system structures in the real world is: Centralised, Decentralised, and Distributed. These are not only three common structures in technical implementation, but also three common structures in other fields such as social organizations.
These three structures have relevant descriptions in the blockchain field. I use this diagram to refer to Vitalik’s article: The Meaning of Decentralization, link URL:
https://medium.com/@VitalikButerin/the-meaning-of-decentralization-a0c92b 76 a 274
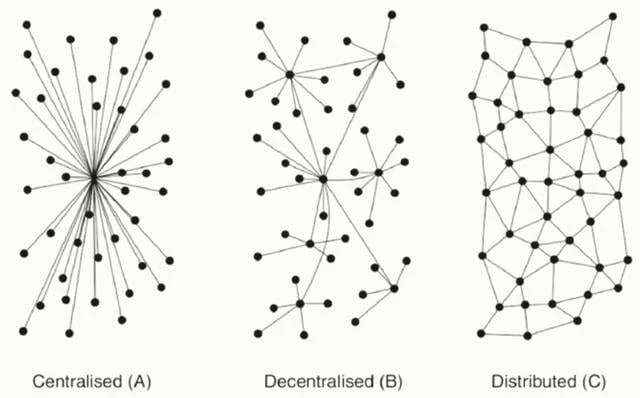
There is often some controversy in China about this diagram, and some people think that the symbols of Decentralised and Distributed are reversed. Explaining from the perspective of control and decision-making should be able to eliminate this controversy and provide a better understanding of Decentralised and Distributed. For Centralised (A) in the diagram, no matter from which perspective you understand it, there should be no controversy, so we only compare decentralization and distribution.
Professor Hong Shuning once said that the essence of blockchain is decentralization, which is a very accurate description. In this article, we talk about blockchain and decentralization, which usually refer to the same thing. Decentralized is actually a decision-making center composed of multiple nodes, and its control and decision-making also require the participation of certain nodes. At this time, control and decision-making are called consensus. For example, in Bitcoin, only full nodes with mining capabilities have the ability to decide the generation of new blocks and the content written into new blocks. Those nodes without mining capabilities are read-only nodes or verification nodes. In POS and DPOS chains, this situation will be more obvious. Only consensus nodes can decide the data generated and written into new blocks. The difference between synchronous algorithms and asynchronous algorithms in consensus protocols is also more obvious, which will determine the number of nodes that can be accommodated in the blockchain network.
In a distributed system, there is no obvious center, only nodes. Any node can join or leave the network at any time, and its control and decision-making are local, which is one of the reasons why distributed systems can achieve very high performance. Does this eliminate the common controversy between Decentralised and Distributed?
Readers can refer to Hong Shunings Hong Shuning: Blockchain and Cryptocurrency and Vitaliks The Meaning of Decentralization. By comparing the contents of the two articles, many people should find it easier to understand the meaning and the boundaries of some concepts. For the schematic diagram, I used the schematic diagram of Vitaliks article. The Distributed in this diagram is a more general distributed system, such as the Lightning Network, Nostr, eDonkey download and other systems.
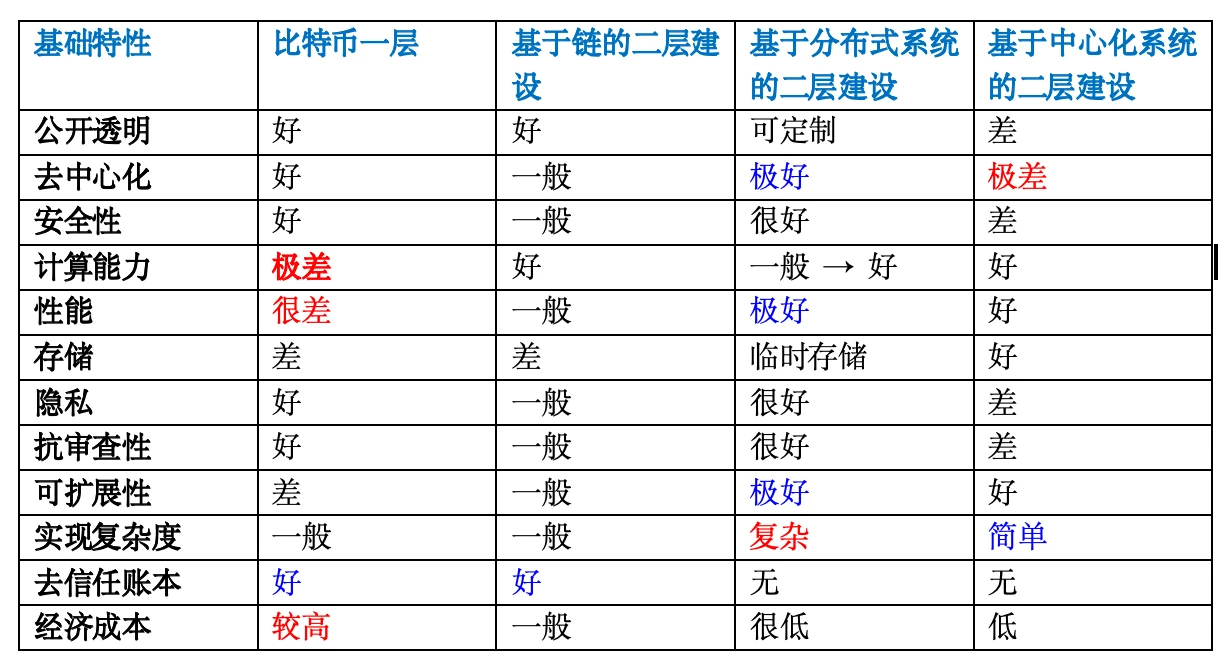
According to my summary of the relevant materials on Bitcoins second-layer construction (see references), lets compare the main features of blockchain systems (decentralized), distributed systems, and centralized systems. These features may be controversial and inaccurately summarized. We only need to focus on the significant differences, such as the ability to trust the ledger.
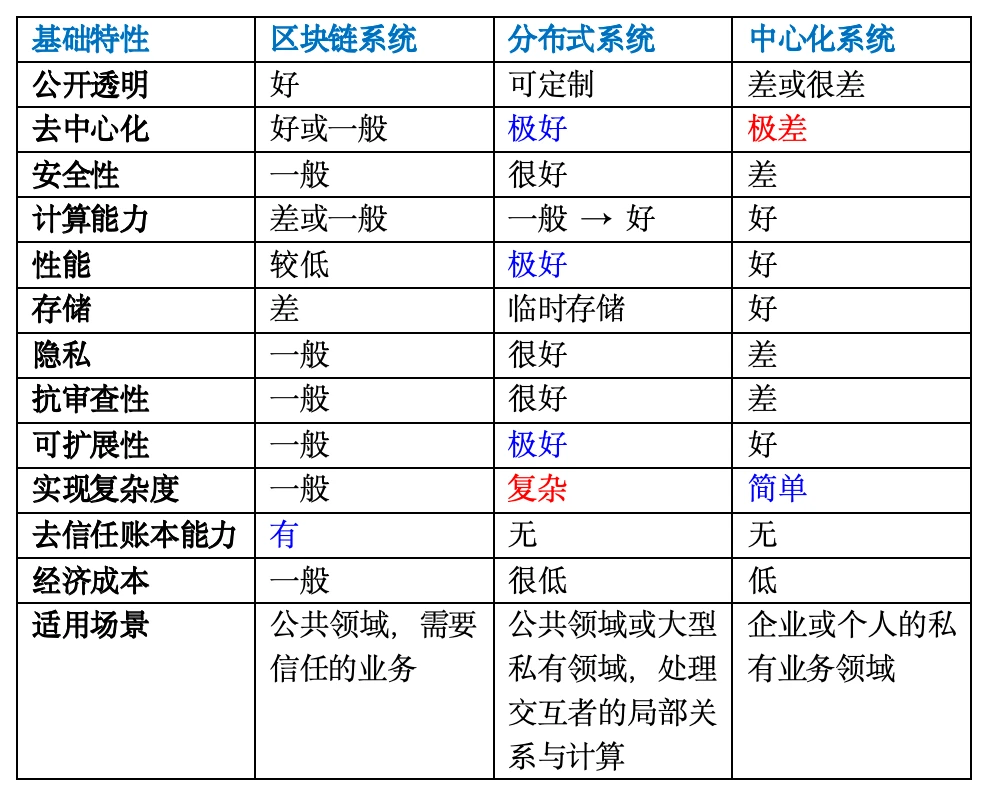
(1) Advantages and disadvantages of decentralization (blockchain system)
The advantages and disadvantages of decentralization (blockchain system) can be found in the table above.
Here is a quote from Professor Hong Shuning: From the perspective of computer systems, blockchain technology is a brand-new distributed system, but the most fundamental difference between blockchain and traditional distributed systems lies in its decentralized nature. Decentralization means that no central controller can control the operation of the blockchain network, and can neither stop it nor manipulate the data in it. The destruction or erroneous behavior of any node will not affect the entire system, and this is the biggest problem of centralized systems. The decentralized nature brings three benefits to blockchain: fault tolerance, anti-attack and anti-collusion , making blockchain an independent, credible, and anti-monopoly technology system, providing technical guarantees for storing and transferring value and trust on it.
If you want to remember it simply, you only need to remember the trustless ledger capability, which is a capability that neither distributed systems nor centralized systems have. This is also the reason why cryptocurrency only came into being after the blockchain system was created.
(2) Advantages and disadvantages of distributed systems
Advantages of distributed systems:
Scalability: Nodes can be added or reduced at any time, and the system has high scalability while improving fault tolerance.
High performance: Tasks can be processed in parallel to improve system performance, and each node can process different tasks at the same time.
Disadvantages of distributed systems include:
Complexity: The design and implementation of distributed systems are relatively complex, and require consideration of issues such as communication, consistency, and data synchronization between nodes, which increases the development and maintenance costs of the system.
Security: The security of distributed systems is an important issue. Communication and data transmission between nodes need to be encrypted and authenticated to prevent data leakage and attacks.
Difficult to debug: Due to the complexity of distributed systems, debugging and troubleshooting may be more difficult when problems occur in the system.
(3) Advantages and disadvantages of centralized structure
Advantages of centralized structure:
Simple control: Having clear controls and decision makers enables better organization and coordination of work.
High efficiency: It can realize efficient concentration and management of resources and improve resource utilization efficiency.
Disadvantages of a centralized structure include:
Single point of failure: Failure of the central node may cause the entire system to fail, so the reliability of the system is low.
Privacy risks: Central nodes can access and control all data, which may cause privacy risks.
Concentration of power: A centralized structure may lead to the problem of concentration of power, where the central node has greater control and decision-making power.
2.2. The manifestation of decentralization
When introducing the manifestation of decentralization, we often need to compare it with centralization. At the same time, we also break down the comparison between centralization and decentralization into several levels.
Note: This is best sorted out by someone who has a deep understanding of the classification of philosophical knowledge systems, so that the professional knowledge stratification will be more accurate. I mainly use the two levels of natural science and social science to describe it here.
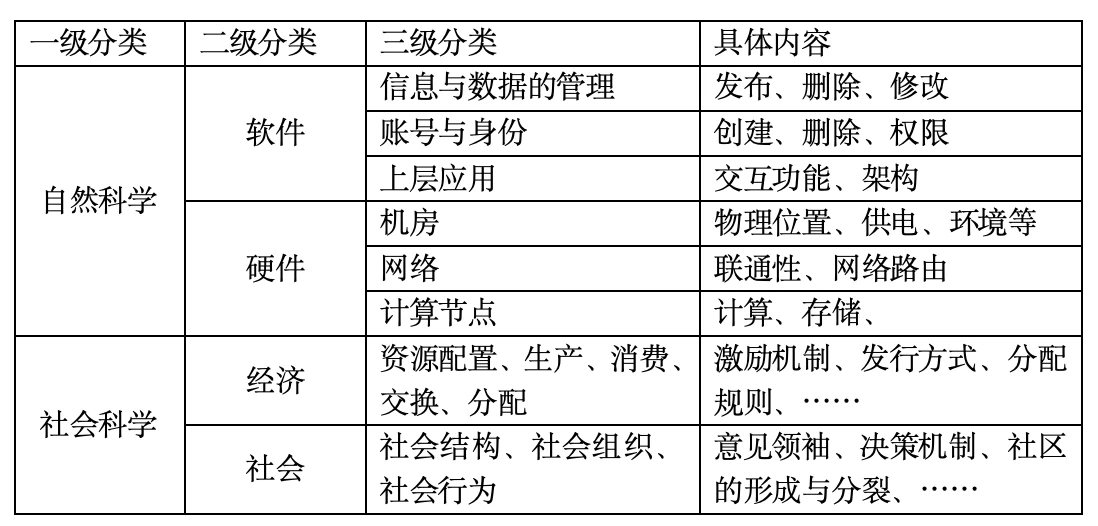
From the table above, we can see that decentralization can be reflected in multiple aspects. We have entered the information age for many years, and our understanding of centralization and decentralization has produced many cases, often comparing and contrasting local concepts. For example, the descriptions of Web1.0, Web2.0, and Web3.0, Read, Write, Owner.
In terms of natural science , on the one hand, it is the centralization and decentralization of the software level. For example, the centralization and decentralization of information (data) release; the centralization and decentralization of information (data) management; the centralization and decentralization of accounts (identities); the centralization and decentralization of software architecture; ...;
On the other hand, there is the centralization and decentralization of hardware. For example, in 2022, AWS and Cloudflare had a crash, which included the centralization of networks and servers. The centralization and decentralization of hardware was not paid attention to at first. After the cloud service provider crashed, many people began to realize that if the hardware is centralized, then even if the software built on the upper layer is decentralized, once someone can control these centralized hardware, the system built on these hardware cannot be considered completely decentralized.
The failures of foreign cloud service providers AWS and CLOUDFLARE on June 21, 2022 caused the interruption of a large number of Web3.0 projects. Some people joked that once these centralized data centers were shut down, Web3.0 would become Web 0.3. This also shows the importance of hardware decentralization. The current cloud infrastructure is basically centralized.
At the social science level, with the development of blockchain technology, DAPP is becoming more and more abundant and manifested more and more. For example, the organizational form of DAO and various confirmation mechanisms for decision-making are already examples of centralization and decentralization in the sociological sense. The significance of Satoshi Nakamotos disappearance is also at this level. This disappearance is a very important decentralization, and no other blockchain system has been able to do this. At this stage, blockchain technology has an increasingly in-depth impact on the real world. This involves more knowledge in economics and sociology, which requires the continuous development of blockchain technology to be more reflected, and also requires experts in the field of sociology to make more analysis and summary.
Professor Hong Shuning once said: Blockchain technology cannot change the world. What can change the world is the decentralization trend achieved based on blockchain technology. Decentralization has changed the economic and political mechanisms that have lasted for thousands of years. The impact on mankind is extremely profound. The Enlightenment Movement of the 17th century can be compared with it. This perspective of understanding is the understanding at the level of economics and sociology.
Some time ago, the famous entrepreneur Zhang Ruimin was a guest at Yuhuixingxing and mentioned a point of knowledge. In the I Ching Bagua, the highest realm is a group of dragons without a leader. Compared with Qianlong Wuyong, Jianlong Zaitian, Feilong Zaitian, and Kanglong Youhui, is a group of dragons without a leader a philosophical interpretation of decentralization?
For decentralization, you can also refer to the article The meaning of decentralization published by Ethereum founder Vitalik Buterin in February 2017, which elaborates on the meaning of decentralization. Vitalik Buterin believes that the centralization and decentralization of computer software should be distinguished from three perspectives, namely architecture, governance, and logic . Architecture centralization refers to how many nodes the system can tolerate and continue to operate; governance centralization refers to how many individuals or organizations are needed to ultimately control the system; logic centralization refers to whether the interfaces and data presented by the system are like a single whole. Are architecture and logic centralization and decentralization analysis at the level of natural science? Is governance an analysis at the sociological level?
2.3. Efficiency and fairness in economics
In order to better understand centralization and decentralization at the sociological level, we can understand it from some related things and service objects. For example, the efficiency and fairness issues in economics are very similar to the role of the incentive mechanism and governance mechanism of the economic model in the blockchain. If you are simply pursuing efficiency, full centralization or very centralized like DPOS is a better choice. In order to maintain other characteristics, decentralization is a better choice.
In order to better understand the combined effect of the incentive mechanism and governance mechanism of the economic model, we first need to understand the two goals of maximizing economic benefits and maximizing social benefits in real society. The balance between the two is usually achieved by combining the first distribution and redistribution systems.
An important principle that the distribution system should reflect is to balance efficiency and fairness , to oppose egalitarianism and to prevent income disparity. National income distribution is divided into two processes: primary distribution and redistribution. The primary distribution of national income based on efficiency standards may lead to a large gap between the rich and the poor, while the government can control the income gap within a reasonable range and maintain social fairness through national income redistribution aimed at achieving the overall and long-term interests of society.
The same problem exists in the blockchain world. If we simply rely on the incentive mechanism of the economic model, just like the functions completed by the market mechanism, it may be easier to solve the problem of maximizing economic benefits. However, the simple incentive mechanism has its flaws. For example, in Bitcoin mining, if the computing power of a single mining pool is too large, a 51% attack will occur. If it is not intervened, it will disrupt the normal operation of the Bitcoin network. In addition, such as the Ethereum DAO incident, due to system vulnerabilities, more than 3 million ether assets were transferred out of the DAO asset pool. If no notice is issued in the community and relevant governance measures are adopted, these problems cannot be well solved.
Through the incentive mechanism of the economic model and the related governance mechanism, the interests of all participants in the blockchain project and the blockchain ecosystem are guaranteed. The incentive mechanism of the economic model ensures maximum efficiency, and community governance, including on-chain governance and off-chain governance, is more about solving the problem of maximizing social benefits. Make trade-offs between efficiency and fairness.
3. Decentralization from the perspective of Bitcoin’s second-layer construction and Web3.0’s application architecture
3.1. Bitcoin’s Second Layer Construction and Decentralization
Here we need to quote the table in A Basic Knowledge System for Bitcoin Layer 2 Construction. In this table, we can see three different structures of Bitcoin Layer 2 construction, which make various trade-offs for decentralization.
The second-layer construction based on the chain abandons a certain degree of decentralization of Bitcoin, thereby achieving the improvement of other performance indicators. Based on the distributed system, by increasing the complexity of implementation, it ensures the decentralization of Bitcoin on the second layer while completing the expansion of performance and functions. The centralized system does not change the decentralization of assets on Bitcoin, and only uses the statistics or auxiliary functions of the second layer to complete the auxiliary management of the first layer of Bitcoin.
3.2. Application Architecture and Decentralization of Web3.0
Here we need to quote the Web3.0 application architecture diagram in Observing Bitcoins second layer from the perspective of the state machine, we can see the architecture and construction path of future Web3.0 applications.
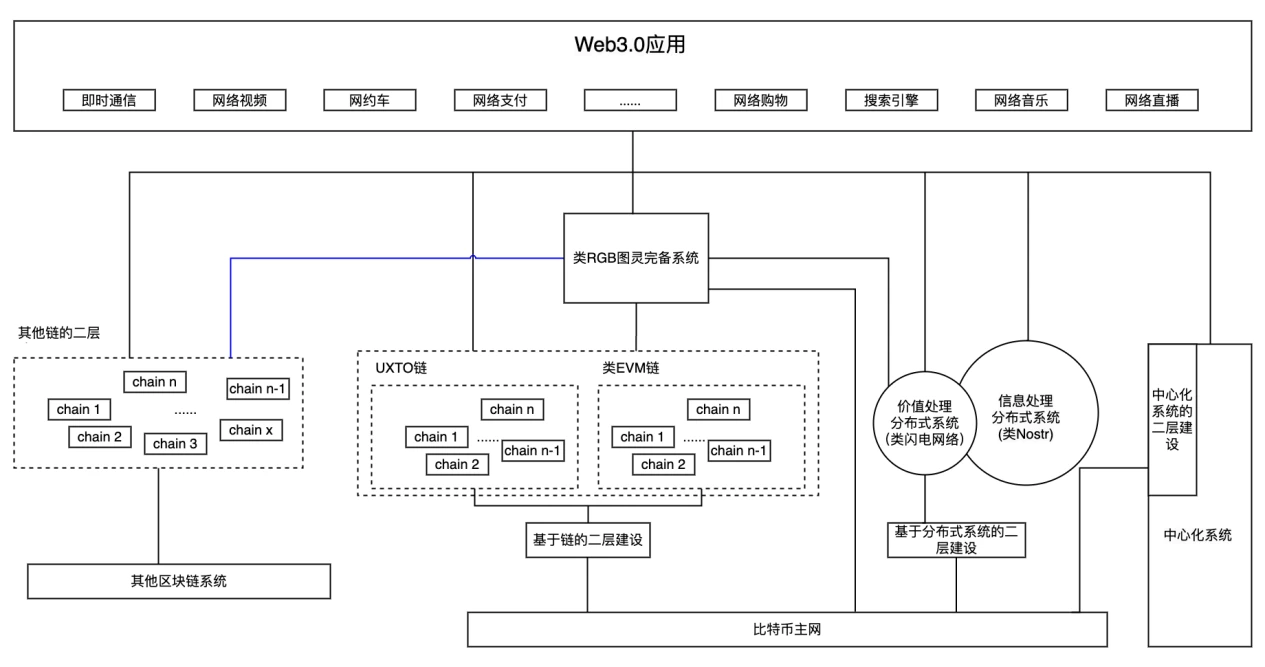
We will see that the future Web3.0 application is a complex architecture built on the blockchain system (decentralized), distributed system, and centralized system . The blockchain system and its second-layer extension complete the transmission and processing of value, and the distributed system and centralized system complete the transmission and processing of information. Without the decentralized blockchain system, we can only stay in the Web2.0 era. With the blockchain system, we can build more and richer applications. It’s just that the current development of blockchain is not mature enough, and this situation is not obvious enough. The application of Web3.0, especially with the decentralized blockchain system, will greatly change our current technological and social status. The Web3.0 era will be a glorious era that will exceed our current imagination.
references
(1) The Meaning of Decentralization, Vitalik
(2) Hong Shuning: Blockchain and Cryptocurrency
(3) “Decentralization is the most fundamental feature of blockchain, but do you have some misunderstandings about decentralization?” by Hong Shuning
(4) “A Basic Knowledge System for Bitcoin Layer 2 Construction” Version 1.5.
(5) Observing Bitcoins second layer from the perspective of the state machine can reveal the architecture and construction path of future Web3.0 applications
(6) Blockchain Basics | Most of us have misunderstandings about the decentralization of blockchain










