Fu Shaoqing, SatoshiLab, Wanwudao BTC Studio
1. Preface
It is not just the VC coin and meme coin phenomenon that has aroused more thinking. Many well-known people in the industry have also raised similar questions and are trying to find solutions. For example, in the Twitter space activity where He Yi answered the question about the girlfriend coin, Jason (Chen Jian) asked whether the tokens launched on Binance have a mechanism to solve the problem that the project team sells the tokens as soon as they are listed and then lies flat. There is also the A Crazy Idea for Token Issuance recently published by CZ, which is trying to find a solution to related problems.
I think all teams that are truly working hard on projects hope that the market will reward real contributors, rather than allowing Ponzi schemes, scammers, speculators, etc. to take away the dividends of this industry and disrupt its development.
Because VC coins and meme coins serve as good case studies, this article will analyze these two phenomena.
2. The past and present of VC coins
VC coin did not come out of thin air. There are historical reasons for its emergence. Although VC coin does not seem perfect now, it played a relatively important role in the beginning, and important projects in the industry all involve VC.
2.1. The chaos of ICO in 2017 - a riot of demons
2017 was a key year for the initial coin offering (ICO) in the blockchain field. According to statistics, the amount of financing for ICOs that year exceeded 5 billion US dollars. In addition to the classic ICO projects introduced below, the author also participated in the ICOs of some small projects, and fully felt the madness at that time. It is not an exaggeration to describe it as a swarm of demons. At that time, as long as a projects token was to be ICO, someone would give a platform, and the white paper was well written, and it would be thrown into some groups, and it would be immediately snatched up. People were crazy and irrational at that time. To exaggerate, even if a pile of shit was thrown into the group, it would be snatched up. If you dont believe it, search for the token situation of MLGB (Malego Coin). (This also reflects the powerful power of ICO)
As for the cause of the outbreak , I summarized it as follows through communication with DeepSeek and Chatgpt, as well as my own understanding:
(1) The maturity of coin issuance technology: In particular, the launch of Ethereum has enabled developers to easily create smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps), which has promoted the rise of ICOs.
(2) There are several other reasons: market demand, the concept of decentralization has gained popularity, people have good expectations, and there is a low threshold for investment.
Several classic cases occurred during this period:
(1) Ethereum: Although Ethereum’s ICO was conducted in 2014, in 2017, Ethereum’s smart contract platform was widely used in the ICOs of many new projects. This project was also conducted through ICO. Overall, this project is still very good and has now grown into the second largest project in the Crypto world.
(2) EOS: EOS raised nearly $4.3 billion through a year-long, phased ICO in 2017, becoming one of the largest ICOs of the year. This project has now almost disappeared, partly because it did not take the right technical route and partly because it did not have enough control over market demand.
(3) TRON: TRON also raised a lot of money in its ICO in 2017. During the period, it was accused of exchanging coins with other projects and plagiarizing other projects. However, it developed rapidly afterwards and attracted a lot of attention. From this point of view, compared with those projects that ran away, is Sun Ge doing quite well? He has a very accurate grasp of market demand. For example, the revenue of Tron stablecoin. Trons control of technical implementation and market demand is in sharp contrast with EOS. The development results of Tron are quite good. If HSR (Hshare, nicknamed braised pork), who exchanged coins at the beginning, kept the share of Tron, the income would be higher than his own project.
(4) Filecoin: Filecoin successfully raised more than $250 million in 2017. Its concept of distributed storage has attracted widespread attention. The founding team, including Juan Benite and others, is quite impressive. This project cannot be said to be a success or a failure, but whether it can develop healthily is a question.
The author personally feels that there are more non-classic cases and they have a greater impact, which is also a major historical reason for the emergence of VC coins.
Problems exposed:
(1) Lack of supervision: Due to the rapid development of the ICO market, many projects lack supervision or are not regulated at all, resulting in high risks for investors. There are many scams and Ponzi schemes, and almost 99% of the projects are exaggerated and fraudulent.
(2) Market bubble: A large number of projects raised huge amounts of funds in a short period of time (these funds were not well managed), but many of these projects lacked actual value or described scenarios that were completely unrealistic, which caused even projects that did not intend to commit fraud to cash out or fail.
(3) Insufficient investor education makes it difficult to judge: Many ordinary investors lack knowledge of blockchain and cryptocurrency and are easily misled, leading to wrong investment decisions. In other words, investors have no way to measure projects or monitor the progress of projects afterwards.
2.2.VC Entry and Credibility Endorsement
From the above description, we can see the chaos after ICO. At this time, venture capital (VC) first stepped forward to solve the problem. VC provided more reliable support for the project through its own reputation and resources, helping to reduce the many problems brought by early ICO. At the same time, an additional effect was to help the majority of users to do a layer of screening.
The role of VC
(1) The shortcomings of grassroots financing as an alternative to ICO
Reduce fraud risk: VCs filter out “air projects” through “ rigorous due diligence ” (team background, technical feasibility, economic model) to avoid the rampant white paper fraud in the ICO era.
Standardized fund management: adopt phased capital injection (grants based on milestones) and token lock-up period clauses to prevent the team from cashing out and running away.
Long-term value binding: VCs usually hold project equity or long-term locked tokens, which are deeply bound to project development and reduce short-term speculation.
(2) Empowering the project ecosystem
Resource import: connect projects with key resources such as exchanges, developer communities, and compliance consultants (e.g. Coinbase Ventures helps projects get listed).
Strategic guidance: Assist in designing the token economic model (such as token release mechanism) and governance structure to avoid economic system collapse.
Credibility endorsement: The brand effect of well-known VCs (such as a16z and Paradigm) can enhance the market’s trust in the project.
(3) Promoting industry compliance
VCs push projects to proactively comply with securities laws (such as the U.S. Howey Test) and adopt compliant financing frameworks such as SAFT (Simple Agreement for Future Tokens) to reduce legal risks.
The involvement of VCs is the most direct solution to the problems of the early ICO model. Overall, VCs play a vital role in the success of Web3 projects. Through funding, resources, reputation and strategic guidance, they help projects overcome many challenges faced by early ICOs, and indirectly help the public complete initial screening.
2.3. Issues with VC coins
The emergence of new things is to solve some old problems, but when the new thing develops to a certain stage, it also begins to show a series of problems. VC coin is such a case. In the later period, it showed many limitations.
Mainly reflected in:
(1) Conflict of interest
VCs are investment institutions that make profits through investment. They may push projects to be over-tokenized (such as high unlocking pressure) or prioritize their own investment portfolios (such as exchange VCs supporting own child projects).
(2) Unable to resolve subsequent project development issues.
(3) Conspiring with project owners to deceive retail investors (some project owners and VCs do this, and VCs from big brands are relatively better).
VC institutions only complete the early stage of investment and profit exit. On the one hand, they have no obligation to the later development of the project, and on the other hand, they have no ability or willingness to do so. (Would it be better if the ultra-long unlocking period of VC was restricted?)
The main problem with VC coins is that the project side’s coins lack the motivation to continue to build after listing, and both VC and project side will cash out and run away after listing the coins. This phenomenon makes retail investors hate VC coins, but the fundamental reason is that the projects are not effectively supervised and managed, especially the matching of funds and results.
3. Inscription Fairlanunch and the memecoin phenomenon
Inscription and Fairlanunch, which broke out in 2023, and the pumpfun model of memecoin, which broke out in 2024, both revealed some phenomena and exposed some problems.
3.1. The outbreak of inscriptions and Fairlanunch
In 2023, two significant trends emerged in the blockchain field: the explosion of inscription technology and the popularization of the Fair Launch model. Both phenomena stem from reflections on early financing models (such as ICO and VC monopoly). In the field of inscriptions, most VCs generally reflect that they have no chance to participate in the primary market, and even in the secondary market, they dare not invest too much. This reflects the pursuit of decentralization and fairness by users and the community.
Inscriptions first broke out on the Bitcoin blockchain, represented by BRC 20, and produced important inscriptions such as ORDI and SATS. There are some reasons for the outbreak of inscriptions: the need for innovation in the Bitcoin ecosystem; users need for anti-censorship and decentralization; low threshold and wealth effect; resistance to VC coins; and the attraction of fair launch.
The inscription also raises some questions:
Pseudo-fairness: In fact, many participating addresses may be disguised by a few institutions or large investors;
Liquidity problem: the use of inscriptions on the Bitcoin mainnet has high transaction costs and time costs;
Value is lost. The huge fees generated by creating inscriptions are taken away by miners (anchored assets are lost), and the closed loop of the Token ecosystem is not enabled.
Regarding application scenarios, inscriptions do not solve the problem of sustainable development of a Token, and these inscriptions have no useful application scenarios.
3.2. The outbreak of Pumpfun and the memecoin phenomenon
Meme originated quite early, and was a cultural phenomenon in the early days. In the real world, the concept of NFT proposed by Hal Finney in 1993 is regarded as the earliest origin. Counterparty, founded in 2014, promoted the emergence of NFT. Based on its creation, Rare Pepes made the popular meme Sad Frog into an NFT application. Meme is translated as meme, which is equivalent to an emoticon package, a sentence, or even a video or animated picture.
Since Meme has emerged in the NFT field, and with the maturity of some technologies, memecoin has begun to take shape. In 2024, the Pump.fun platform based on the Solana chain has risen rapidly and become the core position for the issuance of memecoin. The platform has made memecoin have a greater impact in 2024 through a simple and complete token service process (ICO+LP+DEX) and a speculation mechanism. The author believes that the important contribution of Pumpfun is that the platform combines three separate services into a complete closed loop: Token issuance, liquidity pool construction, and decentralized exchange Dex.
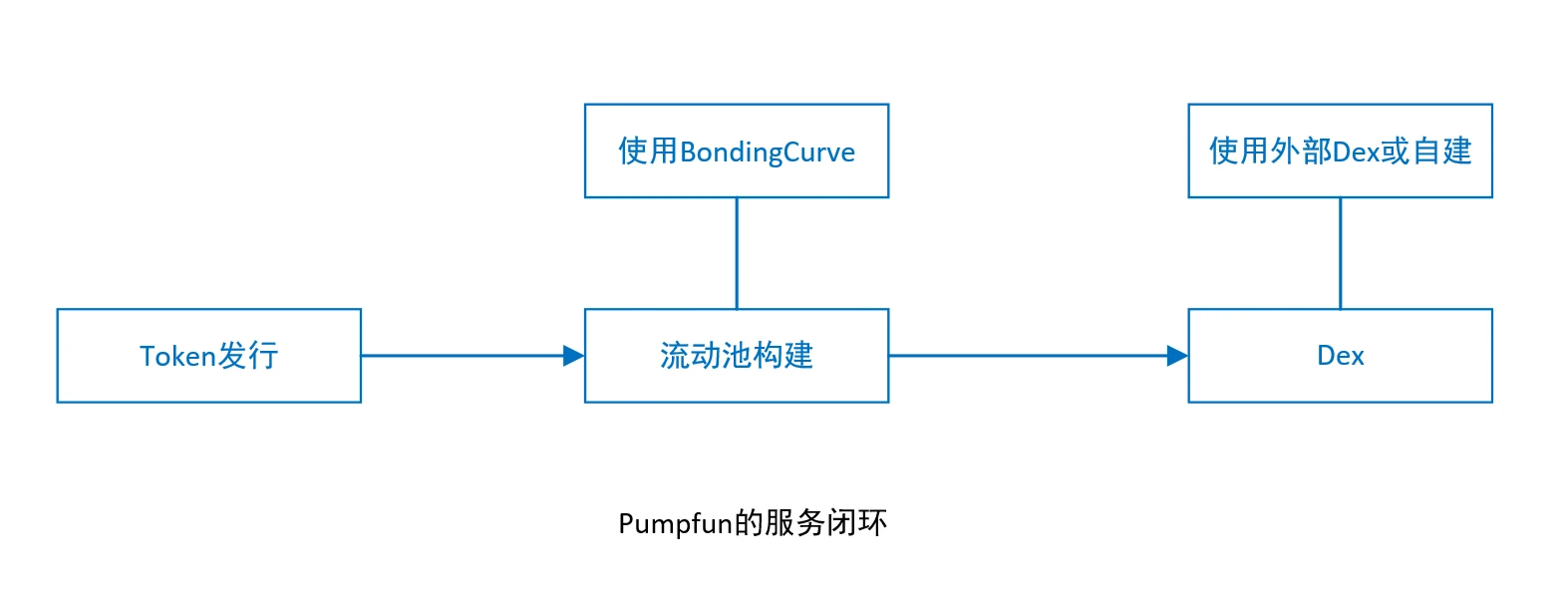
In the early days, the proportion of tokens on pumpfun that were put on dex (known as the graduation rate in the industry) was very small, only 2%-3%, which also shows that the early entertainment function was higher than the transaction function, which is also in line with the characteristics of meme. But later, during the peak period, the token graduation rate often exceeded 20%, turning it into a pure hype machine.
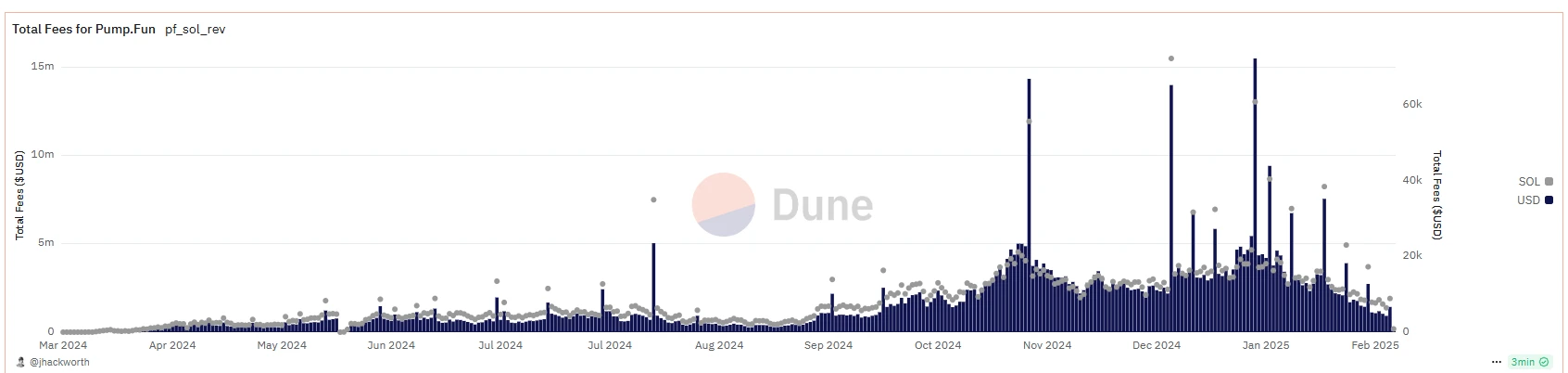
An analysis of data on Twitter also illustrates the problem of the memecoin model. (The reliability of this data has not been confirmed by the author)

Pumpfun’s total revenue is close to $600 million, so much so that US President Trump and his family have also issued their own tokens, which shows the outbreak and climax of memecoin. From Dune’s analysis above, memecoin is also going through a cycle from generation to growth to outbreak.
The main problem with memecoin
(1) Systemic fraud and collapse of trust: According to Dune data, about 85% of the tokens on Pump.fun are scams, and the average cash-out time for founders is only 2 hours.
(2) False propaganda is rampant: Project owners forge KOL platforms and forge transaction volumes (through order-brushing robots). For example, the token MOON claims to be endorsed by Musk, but it is actually a fake PS.
(3) Distortion of the market ecology: Liquidity siphoning effect, memecoin occupies a large amount of on-chain resources, squeezing the development space of normal projects (such as the TVL of Solana on-chain DeFi protocol dropped by 30%). These led to the expulsion of real users, and ordinary investors gradually withdrew from the market because they could not fight against Bot and insider trading. Some project teams even had the idea of using the investment funds they obtained to operate a memecoin and run away with arbitrage.
Memecoin has evolved from an early entertainment function to PVP (Player versus Player) in the middle and late stages, and later to PVB (Player versus Bot), becoming a tool for a few experts to harvest retail investors. It is a serious problem that memecoin has not had effective value injection. If this problem is not solved, memecoin will eventually decline.
4. What kind of projects do users or the market want?
By reviewing the development history of Web3 projects, we understand the historical reasons and advantages and disadvantages of VC coins, and also briefly analyze inscriptions and the memecoin phenomenon promoted by pumpfun. They are all products of the development of this industry. Through these analyses, we can see that there are still some key issues in the development of web3 projects.
Comment: Do VC coins and meme coins reveal all the problems? Or do they reveal the main problems at hand?
4.1. Summary of existing problems
From the previous content, we summarize the problems of current Web3 projects:
1. The project must have a continuous driving force for construction. No one can get too much money too early. Token holders and subsequent construction must receive continuous rewards, rather than being suppressed or deceived.
2. Eliminating or reducing PVP is largely fairer and reduces the manipulation of the dealer, so a truly fair launch is more important. However, after going on dex, the game will still run fast, because the value of the pool is fixed, and those who get it early will get more.
How to solve the above problem:
1. Project management issues: Do not allow project parties or VCs to obtain large amounts of funds too early, or use funds under supervision, or allocate funds to teams that make contributions and construction.
2. Sustainable external value injection: This can solve the PVP problem and reward medium- and long-term token holders and builders. Continuous external value injection can provide financial support to real project builders, and can also allow token holders to have medium- and long-term growth expectations, and can also reduce the problem of premature cashing out.
This simple conclusion is not easy to describe the problem clearly. For project management issues, it is necessary to analyze the stakeholders in a project ecosystem and dynamically analyze possible problems from different stages of the project (issuance, circulation, governance).
4.2. Different stakeholders of the project and management issues at different stages
1. Different stakeholders
The most relevant part of the Web3 project is its economic model design. The stakeholders in the project generally include the project team, investors, foundations, users and communities, miners, exchanges, market makers or other participants in the project ecosystem . An economic model is needed to plan the token allocation and contribution incentives for different stakeholders at various stages. The economic model generally includes the token ratio allocated to stakeholders, the token release rules, the incentive method, etc. The specific ratio and release rules will be determined according to the actual situation of each project and the contribution of each stakeholder, and there is no fixed value. There is also a group of bystanders outside the project (speculators, hair-pulling studios, scammers, etc.).
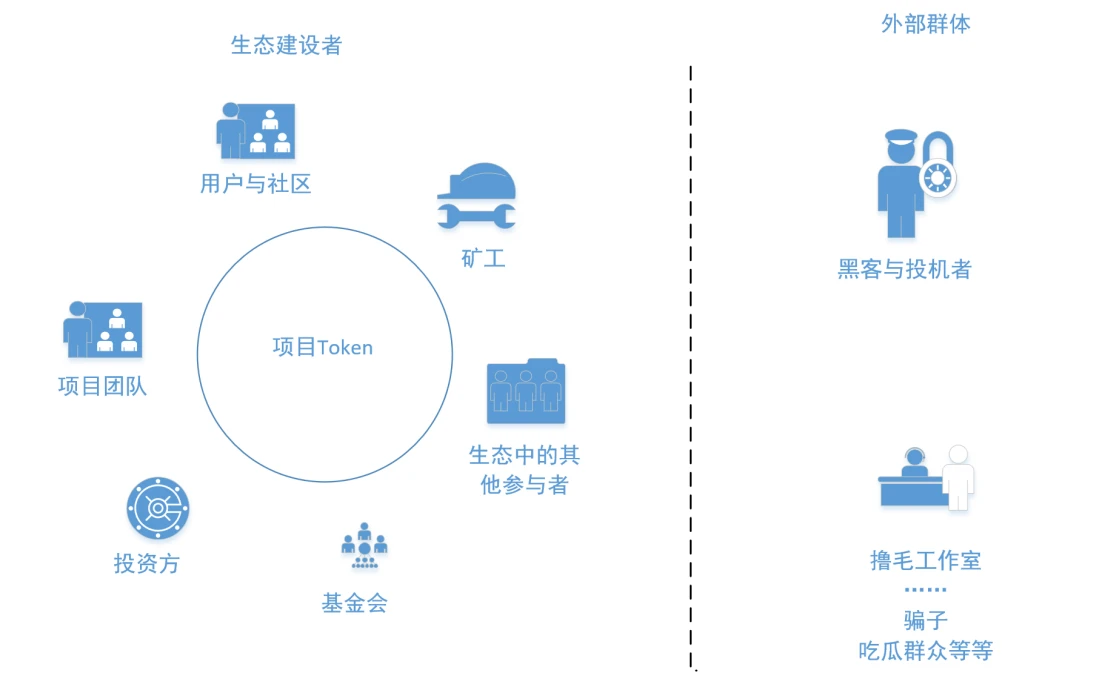
Among different interest groups, we must prevent a certain interest group within the ecosystem from taking away too much benefit, such as in VC coin projects, the project team and investors took away most of the value of the token, resulting in a lack of sustained construction motivation in the later stages; we must also prevent improper benefits from being taken away by external groups, such as speculators in memecoin.
2. Analyze issues from multiple aspects such as issuance, circulation, and governance
(1) Issuance of Tokens
There are many ways to issue digital currency. In addition to the mining issuance based on Pow, there are also ICO, STO, IBO and other methods, as well as various airdrops like Ripple. Regardless of the method used, the main purpose of issuing digital currency is twofold: one is to raise funds ; the other is to send digital currency to users so that more people can use it.
(2) Token circulation and management
Compared with the early days of Web3 projects, there are already many ways to issue tokens, allowing a large amount of digital currency to enter the circulation field. In the circulation of tokens, due to insufficient demand and limited means of managing token liquidity, many problems have arisen in the circulation of tokens. Many token management purposes are achieved by providing various applications. For example, the transaction function of tokens, token staking, the entry threshold of members (the number of tokens or NFTs held), and consumption in applications (Gas fees of public chains, registration fees and renewal fees for ENS, etc.)
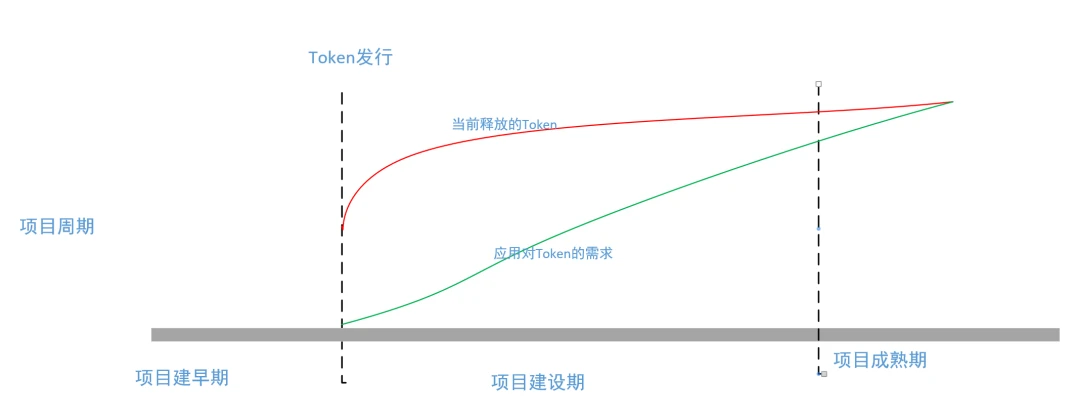
The tokens released prematurely by the project, that is, the part between the red line and the green line, need to use the liquidity lock function to prevent any interested party from taking them away in advance. These locked tokens and the project progress during the construction period involve management issues.
3. Project governance issues
In Web3 projects, the most direct control is achieved through the design of consensus mechanisms and economic models. Tokens in the economic model are used to control the supply and consumption of resources. The design of the economic model plays a very important role in Web3 projects, but the scope of this role is limited. When the economic model cannot complete this part of the function, other methods are needed to supplement the areas that the economic model cannot reach. The community governance mechanism is a functional supplement to the areas where the economic model is not good at.
Due to the decentralized nature of the blockchain world and its network foundation that relies on programmed rules, community organizations such as DAO and DAC have emerged, which can be compared to traditional companies and corporate governance with centralized structures in the real world.
The management of this part, combined with the DAO and foundation models, can better complete the management of funds and ecology, while also providing sufficient flexibility and open transparency. The management members of the DAO must meet certain conditions and must include major stakeholders and third-party institutions as soon as possible. If the exchange that lists the currency is regarded as a third party, can Jasons suggestion be adopted in this case, and the exchange has certain rights and functions of supervision and notarization? In fact, Binance played this role in the GoPlus and Myshell market maker crash.
Can this management structure also better implement the model proposed by CZ in A Crazy Idea for Token Issuance? Lets take this management concept in CZs article as an example for analysis, as shown in the following figure:

(1) Initially, 10% of the tokens are unlocked and sold on the market. The proceeds will be used for product/platform development, marketing, compensation, etc. by the project team. (This is a good design, but who will manage and supervise it? This part of the work is handed over to the projects DAO organization. Wouldnt it be better to use a treasury and third-party supervision?)
(2) Determine the conditions that must be met for each future unlocking ( this design is for the subsequent continuous work and management of token liquidity after the initial period. If it is handed over to DAO management, the effect will be better.)

(3) The project team has the right to postpone or reduce the size of each unlock. If they don’t want to sell more, they don’t have to. But they can sell (unlock) up to 5% each time, and then they have to wait at least 6 months for the price to double again. (This design must be done by a third-party organization such as DAO, changing the team’s right to do it to the DAO’s right to decide. Because the project team is also an important member of the DAO, it should not have too many side effects)
(4) The project team has no right to shorten or increase the size of the next unlock. The tokens should be locked by a smart contract whose keys are controlled by a third party. This prevents new tokens from flooding the market when prices are low. This also motivates the project team to build for the long term. (This design further illustrates the need for a third-party organization, which will be more controllable and manageable than smart contracts. In fact, CZ has already subconsciously proposed the idea of DAO)
Of course, this is just a case study. Real project governance includes many aspects. I believe that as web3 develops to this day, it will gradually improve and expand the implementation of this solution, and will continue to correct problems and find better specific methods in practice.
4.3. How to build long-term projects (value capture and value injection)
If there is no cooperation with technology and application innovation, the current projects in the industry will not last long if they rely on the shouting model. In the end, the problems of VC coins and meme coins will reappear. In fact, pumpfun provides a framework for reference. Its outbreak and subsequent demise are due to the lack of an important link: Token empowerment (also known as value capture and value injection). As shown in the figure below
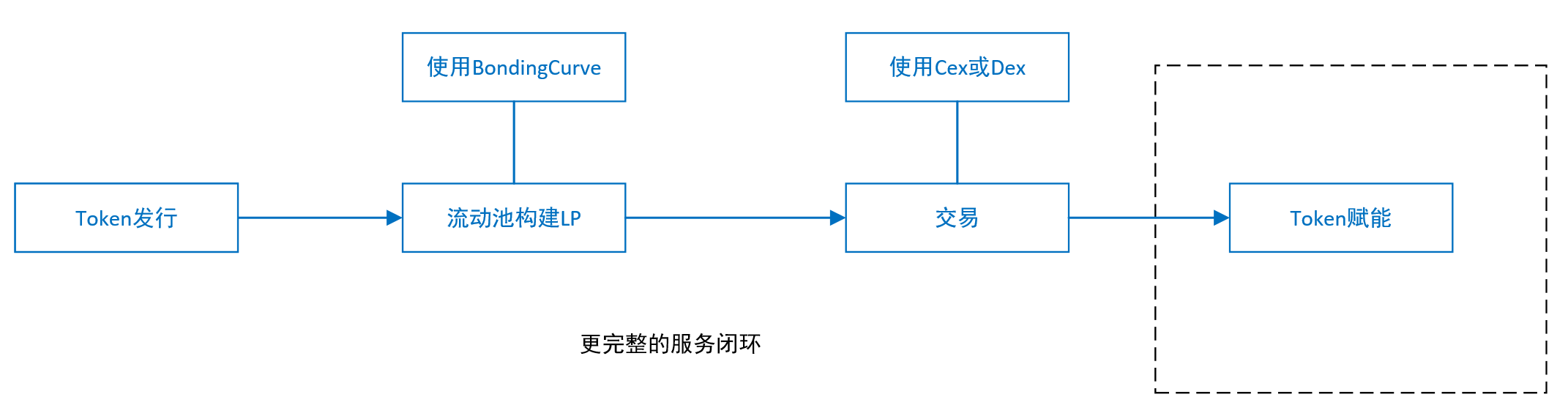
According to the above figure, we can see that after the VC coin is listed on the exchange, the project party will obtain relatively rich returns, and there will be no motivation for later construction. Because the later construction not only has greater risks, but also does not have enough returns, lying flat is the best choice. However, there are some teams with ideals and capabilities that will continue to build, and the number of such teams is relatively small. Pumpfuns memecoin model itself does not have the subsequent Token empowerment, so they are all in a race to run faster. Why can memecoins like Dogecoin continue to rise? The author believes that there are many reasons, and there will be opportunities to elaborate in depth later.
How can we inject long-term value? What are the ways to empower?
Looking back at previous Web3 project cases, such as how DeFi protocols capture value through liquidity mining, how NFT projects inject external value through royalty mechanisms, or how DAOs accumulate value through community contributions. As web3 technology matures, more application scenarios will be generated, and there will be more and more points of convergence that can generate value.
Value capture and external value injection are the two pillars of the Web3 economic model. The former focuses on retention, while the latter focuses on introduction. More popular terms such as value accumulation and flywheel effect can better reflect the dynamic combination of the two, while token empowerment and positive externalities are approached from the perspective of functional design.
The core challenge is to balance short-term incentives with long-term value and avoid falling into “paper models” and Ponzi cycles.
5. Analysis of the previous two bull markets of Crypto and the possibility of the next outbreak
The previous content analyzed the problems of VC coins and meme coins that the industry is currently paying more attention to. Will solving these problems drive the outbreak of the next bull market? Let’s first review the two bull markets in 2017 and 2021.
Note: On the one hand, the following content is based on information found on the Internet and drawing on exchanges with DeepSeek and Chatgpt. On the other hand, the author has personally experienced the bull markets in 2017 and 2021, and our team is currently also developing related products for the Bitcoin ecosystem, so some of my own feelings and judgments are added to the article.
5.1. The ICO craze in 2017
The bull market in the blockchain field in 2017 was the result of multiple factors, including technological breakthroughs and ecological development, as well as external macro-environmental factors. Based on professional analysis and classic literature in the industry, the reasons are summarized as follows:
(1) ICO (Initial Coin Offering) boom
Ethereums ERC-20 standard lowers the threshold for issuing coins, and a large number of projects have raised funds through ICOs (raising more than US$5 billion throughout the year).
(2) Bitcoin fork and expansion controversy
The disagreement in the Bitcoin community over the expansion plan (SegWit vs. large blocks) led to a fork. The Bitcoin Cash (BCH) fork in August 2017 drew market attention to the scarcity and technological evolution of Bitcoin. The price of BTC rose from $1,000 at the beginning of the year to a record high of $19,783 in December.
(3) The rise of Ethereum smart contract ecosystem
Smart contracts and DApp development tools matured, attracting developers. The concept of decentralized finance (DeFi) took root, and early DApps such as CryptoKitties sparked user participation.
(4) Global liquidity easing and regulatory gaps
The global low interest rate policy in 2017 led to funds seeking high-risk and high-yield assets. The regulation of ICOs and cryptocurrencies in various countries has not yet been perfected, and speculative activities lack constraints.
The bull market in 2017 laid the foundation for the industry’s infrastructure (such as wallets and exchanges), attracted technical talent and more new users to join, but it also exposed problems such as ICO fraud and lack of supervision, prompting the industry to turn to compliance and technological innovation (such as DeFi and NFT) after 2018.
5.2. DeFi Summer in 2021
The bull market in the blockchain field in 2021 is the result of the resonance of multiple factors such as industry ecology, macroeconomics, technological innovation and institutional participation. According to professional analysis and classic literature in the industry, the reasons are roughly summarized as follows:
(1) The explosion and maturity of DeFi (decentralized finance)
The maturity of Ethereum smart contracts and the testing and launch of Layer 2 expansion solutions (such as Optimism and Arbitrum) have reduced transaction costs and delays, leading to an explosion of applications: the total value locked (TVL) of DeFi protocols such as Uniswap V3, Aave, and Compound increased from 1.8 billion at the beginning of the year to 25 billion at the end of the year, attracting a large amount of funds and developers.
Yield Farming: High annualized returns (APY) attracted retail and institutional arbitrage funds to flow in. At that time, YF (yield finance, known as Uncle in the industry) was once higher than the price of BTC.
(2) NFT (non-fungible token) breaks through the circle and becomes mainstream
Beeples NFT work Everydays: The First 5000 Days was auctioned at Christies for $69 million. The market value of NFT projects such as CryptoPunks and Bored Ape Yacht Club (BAYC) exceeded $10 billion. NFT trading platforms such as Opensea emerged.
(3) Large-scale entry of institutional capital
Tesla announced the purchase of $1.5 billion in Bitcoin and will accept BTC payments.
MicroStrategy continues to increase its holdings of Bitcoin (holding 124,000 BTC as of the end of 2021).
Canada approved the first Bitcoin ETF (Purpose Bitcoin ETF, February 2021).
Coinbase goes public directly on Nasdaq ($86 billion valuation).
(4) Global macroeconomics and monetary policy
Liquidity is flooding: The Federal Reserve maintains zero interest rates and quantitative easing policies, and funds are pouring into high-risk assets.
Inflation expectations: The year-on-year increase in the US CPI exceeded 7%, and Bitcoin is regarded by some investors as digital gold to hedge against inflation.
(5) Increased acceptance by mainstream society
Payment scenario expansion: PayPal supports users to buy and sell cryptocurrencies, and Visa allows the use of USDC for settlement.
El Salvador makes Bitcoin legal tender (September 2021).
Celebrity effect: Public figures such as Musk and Snoop Dogg frequently mention cryptocurrencies and NFTs.
(6) Multi-chain ecological competition and innovation
The rise of new public chains: High-performance chains such as Solana, Avalanche, and Polygon attract users and developers due to their low fees and high TPS.
Cross-chain technology breakthrough: Cosmos and Polkadot’s cross-chain protocols promote asset interoperability.
(7) Meme Coin and Community Culture
Phenomenal projects: Dogecoin (DOGE) and Shiba Inu Coin (SHIB) skyrocketed due to social media hype (DOGEs annual increase exceeded 12,000%).
Retail frenzy: Reddit forum WallStreetBets (WSB) and TikTok drive retail investors into the market.
Impact on subsequent markets
The bull market in 2021 promoted the institutionalization, compliance, and technological diversification of cryptocurrencies, but also exposed problems such as DeFi hacker attacks and NFT bubbles. Since then, the industry has shifted its focus to:
Regulatory compliance: The U.S. SEC has stepped up its scrutiny of stablecoins and security tokens.
Sustainable development: Ethereum turns to PoS (merged plan), Bitcoin mining explores clean energy.
Web3 narrative: concepts such as the metaverse and DAO (decentralized autonomous organization) have become new focuses.
5.3. When will the next bull market come? 2025? What will the theme be?
The following is a forecast analysis of the potential bull market drivers of the cryptocurrency market in 2025. Combining current industry trends, technological innovations, and macroeconomic backgrounds, the reasons are roughly summarized based on professional analysis and classic literature within the industry:
(1) Large-scale application of Web3 and the rise of user sovereignty
Scenario implementation: Decentralized social networking (such as Nostr, Lens Protocol), on-chain games (AAA-level GameFi), and decentralized identity (DID) have become mainstream, and user data ownership and revenue distribution models have subverted the traditional Internet.
Key events: Giants such as Meta and Google integrated blockchain technology and opened up cross-platform migration of user data.
Related technologies: Zero-knowledge proof (ZKP) and fully homomorphic encryption (FHE) are mature and ensure privacy and compliance.
(2) Deep integration of AI and blockchain
Decentralized AI network: Blockchain-based computing power markets (such as Render Network) and AI model training data rights confirmation (such as Ocean Protocol) solve the monopoly problem of centralized AI.
Autonomous Agent Economy: AI-driven DAOs (such as AutoGPT) automate on-chain transactions and governance, improving efficiency and creating new economic models.
(3) Global central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) and stablecoins interoperability
Policy push: CBDCs of major economies are launched (such as digital euro and digital dollar), forming a hybrid payment network with compliant stablecoins (such as USDC and EUROe).
Cross-chain settlement: The Bank for International Settlements (BIS) takes the lead in establishing a CBDC interoperability protocol, and cryptocurrency becomes a key component of cross-border payment channels.
(4) Bitcoin Ecosystem Revival and Layer 2 Innovation
Bitcoin Layer 2 exploded: Lightning Network capacity continued to hit new highs and the TaprootAssets protocol was created. The RGB protocol supported the issuance of assets on the Bitcoin chain, and the Stacks ecosystem introduced smart contract functions.
Institutional custody upgrade: BlackRock and Fidelity launched Bitcoin ETF options and mortgage lending services to release Bitcoins financial instrument attributes.
(5) Clarification of regulatory framework and full entry of institutions
Global compliance: The United States and Europe passed regulations such as the Markets in Crypto-Assets Act (MiCA) to clarify token classification and exchange licensing systems.
Traditional financial integration: JPMorgan Chase and Goldman Sachs launched crypto derivatives and structured products, and pension funds allocated more than 2% of their holdings in cryptocurrencies.
(6) Geopolitical Conflict and the De-Dollarization Narrative
Safe-haven demand: As geopolitical risks such as the Russia-Ukraine conflict and the situation in the Taiwan Strait escalate, cryptocurrencies have become neutral settlement tools.
Diversification of reserve assets: BRICS countries jointly issued blockchain-based trade settlement tokens, and some countries’ government bonds were denominated in Bitcoin.
(7) Meme Culture 3.0 and Community DAO
Next-generation Meme Coins: Meme projects that combine AI-generated content (AIGC) and dynamic NFTs (such as the AI-driven “immortal dog” character), with the community deciding the direction of IP development through DAO voting.
Fan Economy Chain Reform: Top stars such as Taylor Swift and BTS issue fan tokens to unlock exclusive content and participate in revenue sharing.
Note: In order not to leave out relevant possibilities, more analysis data is retained above.
By summarizing the bull markets in 2017 and 2021, and analyzing the possibilities for 2025, we can roughly make some judgments by referring to the figure below.
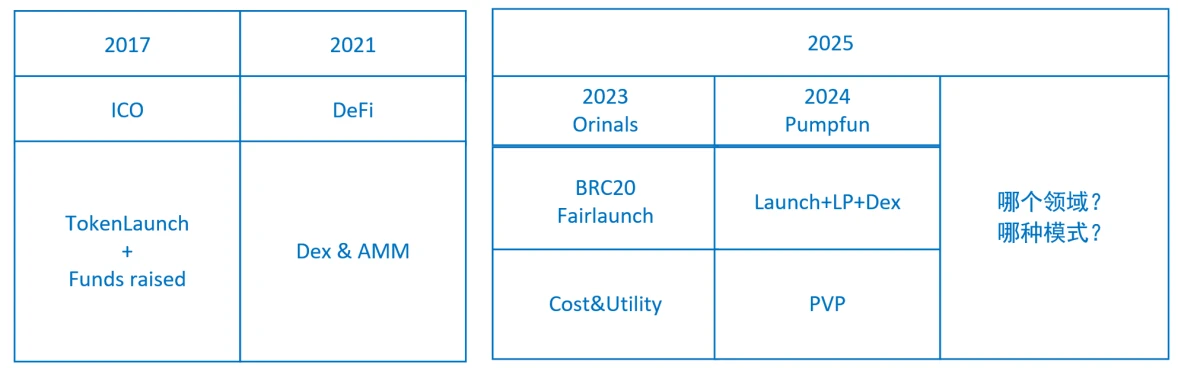
For the mode:
The inscriptions in 2023 and the pumpfun phenomenon in 2024 are some possible bull market outbreaks. If the problems of inscriptions and pumpfun themselves can be solved and a more complete model is produced, it may promote the outbreak of a bull market in some areas. The high probability is still related to issuing assets and trading assets.
For fields:
It is roughly generated in two areas: (1) pure Web3 field; (2) the combination of AI and web3.
Specific analysis:
Regarding (1) the large-scale application of Web3 and the rise of user sovereignty, I personally believe that the infrastructure is not yet perfect and the wealth effect is not that strong. It is difficult for it to become the main factor or field of the bull market alone, or it will not become the main factor of this bull market.
Regarding (2) the deep integration of AI and web3, almost everyone has experienced the power of AI. Will this field generate support factors for the bull market? It is indeed difficult to judge... I personally tend to think it is a bit early. But it is difficult to say in this field. The phenomena that can explode quickly, such as DeepSeek and Manus, are not new in the field of AI. What will happen to DeFi under the empowerment of AI?
Regarding (4) Bitcoin ecosystem revival and Layer 2 innovation, Bitcoin has had good price performance in the bull markets of 2017 and 2021. The current market value of Bitcoin accounts for 60% of the crypto market, and the wealth effect is strong enough. If there is a good model + good technology implementation in this field, the probability of a bull market will be very high.
Regarding (7) Meme culture 3.0 and community DAO, if meme culture solves the PVP problem and there is continuous external value injection, is it possible to become a driving factor for the bull market? Judging from the wealth effect, it is quite difficult.
Other factors (3), (5), and (6) should accelerate changes and add icing on the cake to the bull market. However, the direct factors that alone can generate a bull market are not strong enough.
If there is a bull market in 2025, the most likely scenario is:
Bitcoin Ecosystem and Layer 2 Innovation: New Models Based on New Asset Issuance and Trading
The integration of AI and Web3, AI-enabled trading models
In addition to judging the fields and models, as to when the bull market will break out, we also need to look at external macro-environmental factors.
The above judgment is purely personal thinking and does not constitute any investment advice.










