Original | Odaily Planet Daily ( @OdailyChina )
Author | Ethan ( @ethanzhang_web3 )

On the evening of May 21, the Stablecoin Bill submitted by the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region Government at the end of 2024 was passed by the Legislative Council of Hong Kong after three readings . It will be officially effective after the Chief Executive signs it and the law is gazetted. So far, Hong Kong has become the first jurisdiction in the world to establish a comprehensive regulatory framework for fiat-pegged stablecoins, and compliant Hong Kong stablecoins are expected to be officially launched before the end of this year.
At the same time, the U.S. Senate passed the procedural vote of the United States Stablecoin Innovation Guidance and Establishment Act of 2025 (GENIUS Act) with a vote of 66:32 on May 19, attempting to provide federal supervision for dollar-pegged stablecoins (recommended reading: The GENIUS Act is expected to pass the Senate, and stablecoin supervision will usher in a historic breakthrough ).
In this article, the author will deconstruct the core content of the Hong Kong Stablecoin Act (Gazette No. C 3116-C 3684), compare it with the US Stablecoin Act GENIUS Act, and gather industry perspectives to explore the similarities, differences and impacts of the two major regulatory frameworks.
Hong Kong Stablecoin Bill Deconstructed

Original text of the Stablecoin Bill
The Stablecoin Bill consists of 11 parts, 175 articles and 8 schedules, covering the licensing system, licensee responsibilities, regulatory powers and sanctions. The following is a summary of some of the more important contents based on the original text:
Definition and Scope :
Definition of stablecoin: refers to fiat-pegged stablecoin, which is a token that uses legal tender (such as Hong Kong dollars and US dollars) as an anchor asset to maintain a stable value.
Regulated activities: including issuing stablecoins, managing reserve assets and providing stablecoin-related services .
Licensing System :
Issuers need to apply for a license from the Hong Kong Monetary Authority. Applicants are limited to companies or authorized institutions outside Hong Kong .
The minimum registered capital is HK$25 million to ensure financial strength .
Carrying out regulated activities without a licence or engaging in false advertising is a crime punishable by a fine and imprisonment.
Licensee Responsibilities :
Reserve management: Stablecoins must be anchored to fiat currencies at a 1:1 ratio, and reserve assets must be fully covered and audited regularly .
Consumer protection: Mandatory unconditional redemption right ensures that users can redeem at par value at any time.
Management requirements: The licensee must appoint a chief executive officer, directors and a stablecoin manager, which must be approved by the Hong Kong Monetary Authority.
Regulation and Sanctions :
The Hong Kong Monetary Authority may require licensees to provide information, conduct investigations or appoint statutory administrators.
Sanctions include fines, license revocation and criminal liability. Unlicensed activities, sales by non-approved providers, etc., may be subject to a maximum fine of HK$5 million and seven years imprisonment upon conviction through public prosecution procedures; fraudulent acts may be subject to a maximum fine of HK$10 million and 10 years imprisonment.
Transitional arrangements :
Existing stablecoin issuers must apply for a license or exit the market before the effective date (expected to take effect within 2025).
Comparison with the US GENIUS Act
Overview of the GENIUS Act
The GENIUS Act (S. 394) aims to provide a federal regulatory framework for dollar-pegged payment stablecoins, promote innovation, and maintain the global status of the dollar (as can be seen from Section 1 of the bill). The bill was submitted on February 4, 2025, passed a procedural vote on May 19, and has not yet been finally passed.
Comparative Analysis
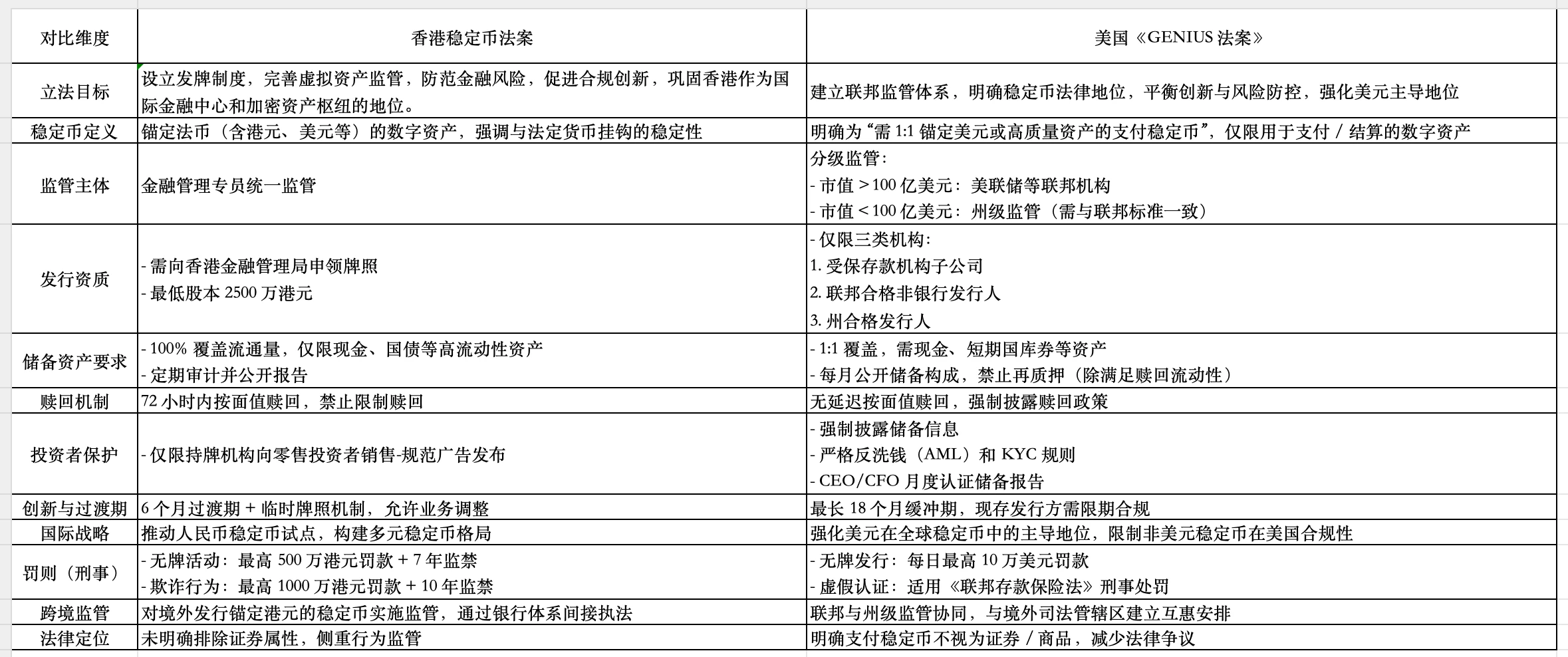
Summary of core differences and strategic positioning (differences):
Regulatory framework and market positioning
Hong Kong: It adopts a centralized and unified regulatory model, led by the Financial Services Commissioner, supports the issuance of stablecoins pegged to multiple currencies such as the Hong Kong dollar and the US dollar, and balances financial stability and innovation on a risk-based principle, aiming to create an international and diversified stablecoin ecosystem and enhance Hong Kongs compatibility as an international financial center.
United States: Implementing tiered supervision (federal and state coordination), focusing on the dominant position of US dollar stablecoins, requiring issuers with a market value of more than US$10 billion to be included in federal supervision, with protecting US dollar hegemony + preventing and controlling systemic risks as the core, restricting the compliance of non-US dollar stablecoins, and highlighting geopolitical considerations.
Regulatory stringency and market impact
Hong Kong: Strict requirements such as a minimum share capital of HK$25 million, 100% high-liquidity reserve assets, and 72-hour mandatory redemption will improve market stability, but may increase compliance costs for small and medium-sized institutions and may inhibit innovation in the short term, but will be beneficial to building investor trust in the long run.
United States: Reserve assets allow for a combination of short-term Treasury bonds, repurchase agreements, etc., with high investment flexibility, but strict restrictions on non-US dollar stablecoins; tiered supervision gives small issuers state-level regulatory options, but may lead to inconsistent regulatory standards and higher implementation complexity.
Consumer protection and international coordination
Hong Kong: Licensed institutions are required to sell to retail investors, advertising is regulated, and a temporary license transition period (6 months) is used to guide the market to orderly compliance. Consumer rights protection measures are more direct.
United States: Focuses on monthly disclosure of reserve assets and anti-money laundering requirements, but consumer redemption rights protection and information disclosure frequency (regular audits in Hong Kong and monthly disclosure in the United States) are relatively weakened, and rely on federal and state regulatory coordination. International mutual recognition mechanisms are still being explored (such as establishing reciprocal arrangements with overseas jurisdictions).
Core consensus and industry impact (similarities):
Regulatory consensus: Both require that stablecoin reserve assets cover 100% of the circulation volume, prohibit misappropriation or high-risk investment, and embody the international principle of same activities, same risks, same supervision.
Industry impact: The Hong Kong bill is more likely to promote the offshore RMB stablecoin pilot, thus becoming a digital bridge for cross-border RMB payments; the US bill consolidates the dollars dominant position in the stablecoin field. The two bills, starting from diversity and inclusion and dollar-centered respectively, shape different paradigms for global stablecoin regulation.
In general, the Hong Kong bill attracts global capital and diversified stablecoin projects with compliance-based foundation + open innovation, while the US bill maintains local financial hegemony with dollar dominance + risk prevention and control. The difference between the two essentially reflects the trade-offs between different economies in financial stability, monetary strategy and innovation inclusiveness.
Various views
Hong Kong community member GFF.eth ( @GF 41536085 ):
On May 19, the Senate passed the US stablecoin bill GENIUS Act procedurally , and then on May 21, Hong Kong passed the stablecoin bill. No matter whether it is just a pure performance or a process, at least all the preconditions for the internationalization of the RMB have been opened. Stablecoins are financial nuclear weapons. Now all kinds of pre-launch insurances have been opened, including fingerprints, passwords, and irises. Next, it depends on whether decision makers dare to press the button. Do they dare to issue RMB on Ethereum? If they issue the Hong Kong dollar stablecoin after all this time, it would be a joke. The Hong Kong dollar implements a linked exchange rate system, which is a US dollar stablecoin. It would be a waste of time to make the US dollar stablecoin into a stablecoin.
Gary Tiu: Executive Director and Head of Regulatory Affairs, OSL Group
OSL Group actively participates in the discussion of Hong Kongs stablecoin policy formulation, witnessing and promoting the formation of the stablecoin framework. The Hong Kong Stablecoin Act sets a unified standard for the development of the industry, which will help improve transparency and long-term stability.
Johnny Wu ( @Johnny_nkc ): Member of the Chinese Peoples Political Consultative Conference, Hong Kong Legislative Council Member, and Head of the Hong Kong Web3 Cryptocurrency Leadership Group
Hong Kong promotes crypto stablecoins to make Hong Kong an international Web3 financial center. Relying on the 1.4 billion population and dividends of mainland China, it will not only launch Hong Kong dollar stablecoins, but also offshore RMB stablecoins and other stablecoins, embracing cryptocurrencies, Web3, and stablecoins. Todays bill passage rate is only the first step in Web3 infrastructure. I hope to promote it with everyone: First, create application scenarios - the issuance of stablecoins is the first step, and the most important thing is to create more application scenarios for stablecoins. Whether it is physical retail, cross-border trade, or trading peers, I think there is great potential space and opportunities to promote the implementation of stablecoins. I call on friends from all walks of life in traditional and physical scenarios to understand and embrace stablecoins, which will be an important financial innovation; another is to improve the stable market attributes, including releasing stablecoin interest to holders. The release of interest will help enhance the market competitiveness of stablecoins, and can also release incentives for more people to participate, expand the market share of the entire stablecoin, and thus help the development of stablecoins.
Wall Street News:
On May 21, the Legislative Council of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region passed the Stablecoin Bill in the third reading, marking the formal inclusion of stablecoins, a virtual asset, into the legal regulatory system. At the same time, the US government is also stepping up its efforts to promote stablecoin legislation. As major financial centers are establishing their own digital currency systems to ensure that currencies have greater monetary control in the digital financial era, this battle for digital coinage rights may have just begun.










